Reservoir Science
ISSN: 3070-2356 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
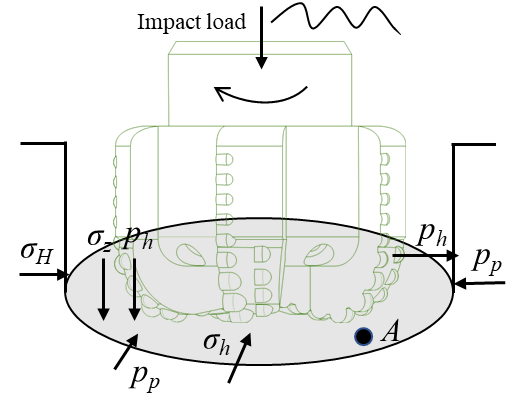
TY - JOUR AU - Yang, Yandong AU - Huang, Feifei AU - Kang, Shaofei PY - 2026 DA - 2026/01/26 TI - Mechanism of Penetration Rate Improvement in Hot Dry Rock Under the Coupling of Impact Load and Confining Pressure Release JO - Reservoir Science T2 - Reservoir Science JF - Reservoir Science VL - 2 IS - 1 SP - 52 EP - 64 DO - 10.62762/RS.2025.804345 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/RS.2025.804345 KW - percussion drilling KW - rock breaking efficiency KW - rate of penetration KW - confining pressure releasing KW - impact load AB - Deep geothermal resources are environmentally friendly and represent a highly competitive form of clean energy. However, low rock-breaking energy combined with high rock strength results in a low rate of penetration (ROP), which significantly restricts the efficient utilization of geothermal resources. Previous studies have shown that rock failure is primarily caused by shear stress. Therefore, this paper aims to enhance the shear stress level by increasing the impact load and releasing the confining pressure, thereby improving the ROP. Specifically, the rock-breaking efficiency under the coupling of impact load and confining pressure releasing is analyzed to reveal the influence of confining pressure releasing on shear stress. Furthermore, a rock-breaking model is established, and an impact load generator is employed to validate the proposed model, enabling the evaluation of rock-breaking efficiency under the coupled action of impact load and confining pressure releasing. The results indicate that the ratio of shear stress to $I_1$ dominates the rock-breaking process. When this ratio is low, the rock tends to remain in a compressed state, the hydrostatic pressure effect is enhanced, the shear stress effect is relatively weakened, and the rock-breaking efficiency decreases. The coupling of impact load with confining pressure releasing can achieve effective rock breaking under relatively low weight-on-bit conditions in deep wells, thereby providing theoretical support for improving rock-breaking efficiency in hot dry rock geothermal development. SN - 3070-2356 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Yang2026Mechanism,
author = {Yandong Yang and Feifei Huang and Shaofei Kang},
title = {Mechanism of Penetration Rate Improvement in Hot Dry Rock Under the Coupling of Impact Load and Confining Pressure Release},
journal = {Reservoir Science},
year = {2026},
volume = {2},
number = {1},
pages = {52-64},
doi = {10.62762/RS.2025.804345},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/RS.2025.804345},
abstract = {Deep geothermal resources are environmentally friendly and represent a highly competitive form of clean energy. However, low rock-breaking energy combined with high rock strength results in a low rate of penetration (ROP), which significantly restricts the efficient utilization of geothermal resources. Previous studies have shown that rock failure is primarily caused by shear stress. Therefore, this paper aims to enhance the shear stress level by increasing the impact load and releasing the confining pressure, thereby improving the ROP. Specifically, the rock-breaking efficiency under the coupling of impact load and confining pressure releasing is analyzed to reveal the influence of confining pressure releasing on shear stress. Furthermore, a rock-breaking model is established, and an impact load generator is employed to validate the proposed model, enabling the evaluation of rock-breaking efficiency under the coupled action of impact load and confining pressure releasing. The results indicate that the ratio of shear stress to \$I\_1\$ dominates the rock-breaking process. When this ratio is low, the rock tends to remain in a compressed state, the hydrostatic pressure effect is enhanced, the shear stress effect is relatively weakened, and the rock-breaking efficiency decreases. The coupling of impact load with confining pressure releasing can achieve effective rock breaking under relatively low weight-on-bit conditions in deep wells, thereby providing theoretical support for improving rock-breaking efficiency in hot dry rock geothermal development.},
keywords = {percussion drilling, rock breaking efficiency, rate of penetration, confining pressure releasing, impact load},
issn = {3070-2356},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/