Reservoir Science
ISSN: 3070-2356 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
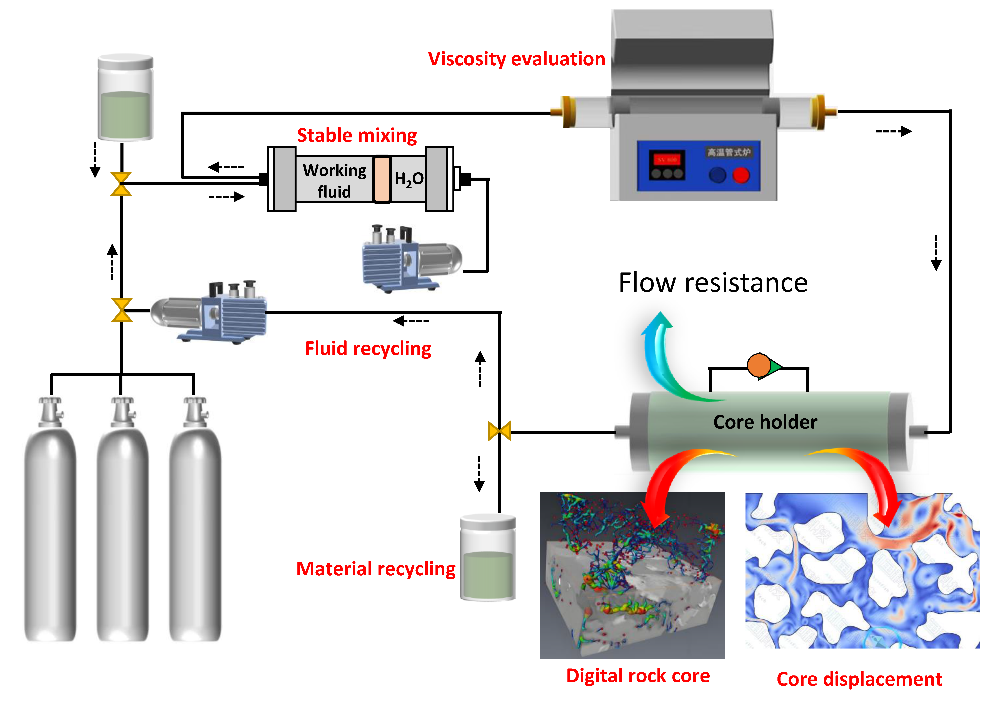
TY - JOUR AU - Li, Wusheng AU - Liao, Junying PY - 2026 DA - 2026/01/15 TI - Microscopic Analysis of Flow Resistance of Oil Displacement Fluid in Reservoir Fractures JO - Reservoir Science T2 - Reservoir Science JF - Reservoir Science VL - 2 IS - 1 SP - 16 EP - 33 DO - 10.62762/RS.2025.837826 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/RS.2025.837826 KW - geological exploration KW - reservoir flooding KW - reservoir transformation KW - energy extraction KW - petroleum geology AB - The flow resistance of displacement fluids within reservoir fractures directly influences oil recovery efficiency and sweep efficiency, thereby exerting a substantial impact on reservoir recovery and overall oilfield production. To address the significant flow resistance of contemporary displacement fluids, this study developed a multi-performance evaluation apparatus capable of simultaneously measuring fluid viscosity, flow resistance, and displacement efficiency. The effects of various reservoir parameters and fluid compositions on flow resistance and sweep area were systematically analyzed. Elevated reservoir temperatures clearly reduce fluid flow resistance within fractures, allowing displacement fluids to penetrate more deeply into the reservoir. In contrast, an inverse relationship between reservoir pressure and flow resistance was observed, which poses a significant barrier to reducing flow resistance and achieving rapid fluid penetration. Moreover, through a micromolecular perspective and adsorption theory, this study identifies strategies to modify flow resistance, thereby substantially enhancing displacement efficiency and sweep area by lowering flow resistance. This study provides foundational data and a theoretical framework for mitigating fluid flow resistance within reservoir fractures during oil recovery, thereby facilitating enhanced oil recovery over a larger reservoir area. SN - 3070-2356 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Li2026Microscopi,
author = {Wusheng Li and Junying Liao},
title = {Microscopic Analysis of Flow Resistance of Oil Displacement Fluid in Reservoir Fractures},
journal = {Reservoir Science},
year = {2026},
volume = {2},
number = {1},
pages = {16-33},
doi = {10.62762/RS.2025.837826},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/RS.2025.837826},
abstract = {The flow resistance of displacement fluids within reservoir fractures directly influences oil recovery efficiency and sweep efficiency, thereby exerting a substantial impact on reservoir recovery and overall oilfield production. To address the significant flow resistance of contemporary displacement fluids, this study developed a multi-performance evaluation apparatus capable of simultaneously measuring fluid viscosity, flow resistance, and displacement efficiency. The effects of various reservoir parameters and fluid compositions on flow resistance and sweep area were systematically analyzed. Elevated reservoir temperatures clearly reduce fluid flow resistance within fractures, allowing displacement fluids to penetrate more deeply into the reservoir. In contrast, an inverse relationship between reservoir pressure and flow resistance was observed, which poses a significant barrier to reducing flow resistance and achieving rapid fluid penetration. Moreover, through a micromolecular perspective and adsorption theory, this study identifies strategies to modify flow resistance, thereby substantially enhancing displacement efficiency and sweep area by lowering flow resistance. This study provides foundational data and a theoretical framework for mitigating fluid flow resistance within reservoir fractures during oil recovery, thereby facilitating enhanced oil recovery over a larger reservoir area.},
keywords = {geological exploration, reservoir flooding, reservoir transformation, energy extraction, petroleum geology},
issn = {3070-2356},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/