ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems
ISSN: 3068-7969 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
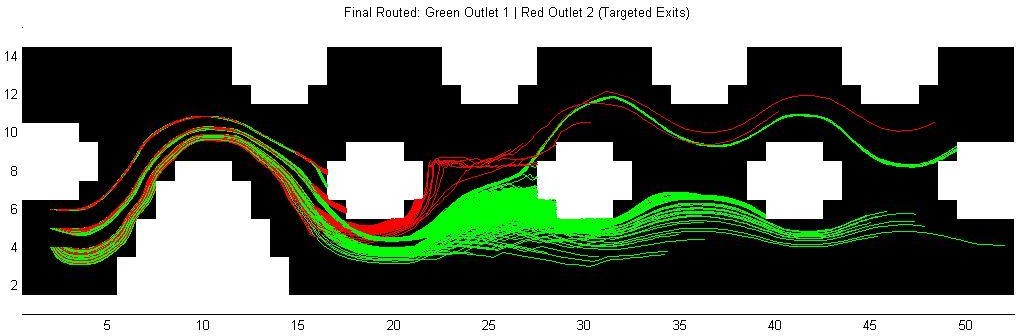
TY - JOUR AU - Raza, Kumail AU - Hussain, Sayed Akif AU - Ali, Saqib AU - Hussain, Syed Amer AU - Hussain, Syed Atif PY - 2026 DA - 2026/02/08 TI - Topological Optimization of a 2D Microfluidic Channel for Particle Separation JO - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems T2 - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems JF - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems VL - 2 IS - 2 SP - 74 EP - 84 DO - 10.62762/TACS.2025.192275 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TACS.2025.192275 KW - microfluidic particle separation KW - topology optimization KW - Navier-Stokes simulation KW - computational fluid dynamics (CFD) KW - passive sorting efficiency AB - The escalating demand for efficient particle separation in microfluidic systems necessitates innovative design solutions. This study presents a simulation-based topology optimization method to passively separate particles within a 2D microfluidic channel, eliminating the need for external forces. Leveraging a coupled Navier-Stokes solver and particle advection simulation, the framework iteratively refines the channel's geometry by minimizing an objective function quantifying particle mis-sorting. Our approach computationally generated optimal, manufacturable topologies, demonstrating a peak sorting efficiency of 0.6667 (66.67%) achieved by the second iteration, which then stabilized in subsequent iterations to 0.6111 (61.11%), significantly surpassing the adaptability and robustness of traditional, manually designed microfluidic channels. This work provides a robust, physics-based framework for exploring complex design spaces, representing a significant advancement in the development of high-performance, next-generation microfluidic devices. SN - 3068-7969 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Raza2026Topologica,
author = {Kumail Raza and Sayed Akif Hussain and Saqib Ali and Syed Amer Hussain and Syed Atif Hussain},
title = {Topological Optimization of a 2D Microfluidic Channel for Particle Separation},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems},
year = {2026},
volume = {2},
number = {2},
pages = {74-84},
doi = {10.62762/TACS.2025.192275},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TACS.2025.192275},
abstract = {The escalating demand for efficient particle separation in microfluidic systems necessitates innovative design solutions. This study presents a simulation-based topology optimization method to passively separate particles within a 2D microfluidic channel, eliminating the need for external forces. Leveraging a coupled Navier-Stokes solver and particle advection simulation, the framework iteratively refines the channel's geometry by minimizing an objective function quantifying particle mis-sorting. Our approach computationally generated optimal, manufacturable topologies, demonstrating a peak sorting efficiency of 0.6667 (66.67\%) achieved by the second iteration, which then stabilized in subsequent iterations to 0.6111 (61.11\%), significantly surpassing the adaptability and robustness of traditional, manually designed microfluidic channels. This work provides a robust, physics-based framework for exploring complex design spaces, representing a significant advancement in the development of high-performance, next-generation microfluidic devices.},
keywords = {microfluidic particle separation, topology optimization, Navier-Stokes simulation, computational fluid dynamics (CFD), passive sorting efficiency},
issn = {3068-7969},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems
ISSN: 3068-7969 (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/