ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems
ISSN: 3068-7969 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
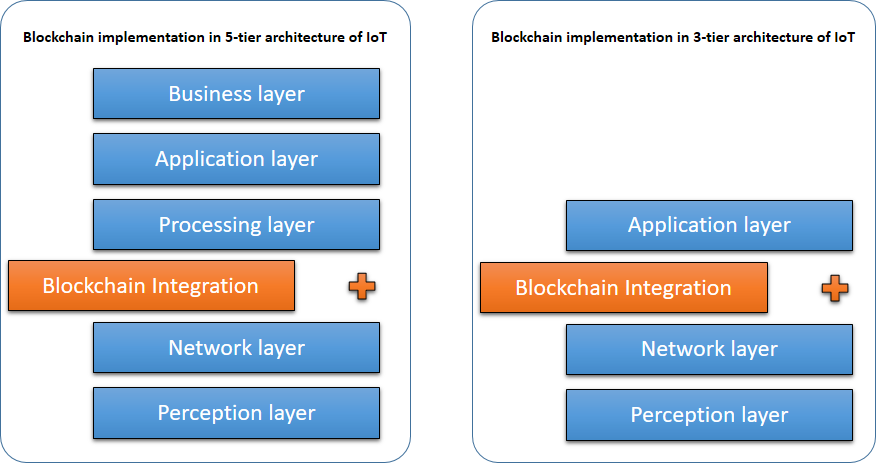
TY - JOUR AU - Umair, Muhammad Khurram AU - Khan, Muhammad Sohail AU - Abrar, Muhammad Faisal PY - 2026 DA - 2026/02/13 TI - Systematic Literature Review on Blockchain Based IoT Solutions JO - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems T2 - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems JF - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems VL - 2 IS - 2 SP - 116 EP - 136 DO - 10.62762/TACS.2025.327681 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TACS.2025.327681 KW - blockchain KW - IoT KW - literature review KW - secure IoT solutions KW - systematic review AB - The growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) has connected a massive number of devices, but its common centralized design creates major security, privacy, and scalability problems that old security methods cannot properly fix. This review explores how Blockchain Technology (BCT) offers a new approach to create trust and strong security for IoT systems without a central authority. Following the PRISMA guidelines, this study analyzes 68 research papers and uses a Chi-square test to statistically confirm the link between IoT problems and the use of blockchain solutions. The results show a strong, statistically proven connection, with a Chi-square value of 34.772 (p SN - 3068-7969 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Umair2026Systematic,
author = {Muhammad Khurram Umair and Muhammad Sohail Khan and Muhammad Faisal Abrar},
title = {Systematic Literature Review on Blockchain Based IoT Solutions},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems},
year = {2026},
volume = {2},
number = {2},
pages = {116-136},
doi = {10.62762/TACS.2025.327681},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TACS.2025.327681},
abstract = {The growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) has connected a massive number of devices, but its common centralized design creates major security, privacy, and scalability problems that old security methods cannot properly fix. This review explores how Blockchain Technology (BCT) offers a new approach to create trust and strong security for IoT systems without a central authority. Following the PRISMA guidelines, this study analyzes 68 research papers and uses a Chi-square test to statistically confirm the link between IoT problems and the use of blockchain solutions. The results show a strong, statistically proven connection, with a Chi-square value of 34.772 (p},
keywords = {blockchain, IoT, literature review, secure IoT solutions, systematic review},
issn = {3068-7969},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems
ISSN: 3068-7969 (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/