ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems
ISSN: 3068-7969 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
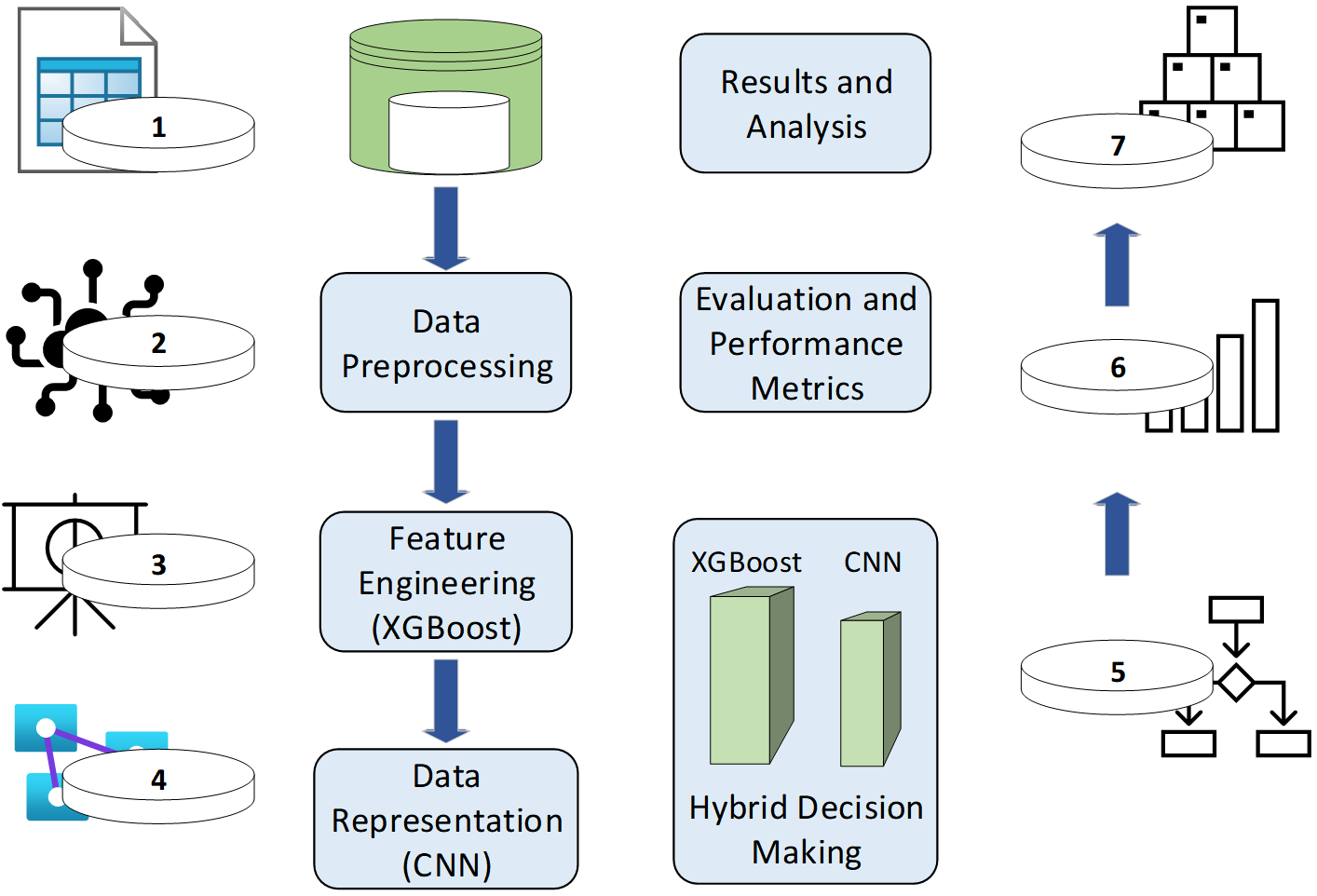
TY - JOUR AU - Dashdondov, Khongorzul AU - Chamazkoti, Mahjoobe Nazari AU - Abdusalomov, Akmalbek AU - Ullah, Habib AU - Khan, Muhammad Zubair AU - Ali, Bakht Sher PY - 2026 DA - 2026/01/12 TI - Hybrid XGBoost-CNN Model for Anomaly Detection: A New Approach for IoT Wireless Sensor Networks JO - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems T2 - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems JF - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems VL - 2 IS - 1 SP - 42 EP - 52 DO - 10.62762/TACS.2025.354651 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TACS.2025.354651 KW - IoT wireless sensor networks KW - anomaly detection KW - XGBoost KW - convolutional neural networks KW - feature selection KW - hybrid model KW - real-time detection AB - The Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand rapidly, resulting in increasingly heterogeneous and complex wireless sensor networks (WSNs). Traditional anomaly detection approaches cannot cope with dynamic traffic patterns, high data volumes, and strict resource constraints. This study presents a hybrid XGBoost–CNN model that integrates XGBoost-based feature selection with a lightweight Convolutional Neural Network optimized for IoT environments. The proposed model was evaluated using real-world IoT traffic data and benchmarked against XGBoost, KNN, and SVM. Experimental results show that the hybrid approach improves detection accuracy by over 1%, increases throughput by 22–40%, and reduces computational cost by 4–8% compared with the baseline models. The model also demonstrated 1% higher energy efficiency under varying attack scenarios. These results indicate that combining the feature selection capabilities of XGBoost with CNN’s pattern extraction of CNN yields a scalable, accurate, and resource-efficient anomaly detection solution suitable for IoT-WSN devices. SN - 3068-7969 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Dashdondov2026Hybrid,
author = {Khongorzul Dashdondov and Mahjoobe Nazari Chamazkoti and Akmalbek Abdusalomov and Habib Ullah and Muhammad Zubair Khan and Bakht Sher Ali},
title = {Hybrid XGBoost-CNN Model for Anomaly Detection: A New Approach for IoT Wireless Sensor Networks},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems},
year = {2026},
volume = {2},
number = {1},
pages = {42-52},
doi = {10.62762/TACS.2025.354651},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TACS.2025.354651},
abstract = {The Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand rapidly, resulting in increasingly heterogeneous and complex wireless sensor networks (WSNs). Traditional anomaly detection approaches cannot cope with dynamic traffic patterns, high data volumes, and strict resource constraints. This study presents a hybrid XGBoost–CNN model that integrates XGBoost-based feature selection with a lightweight Convolutional Neural Network optimized for IoT environments. The proposed model was evaluated using real-world IoT traffic data and benchmarked against XGBoost, KNN, and SVM. Experimental results show that the hybrid approach improves detection accuracy by over 1\%, increases throughput by 22–40\%, and reduces computational cost by 4–8\% compared with the baseline models. The model also demonstrated 1\% higher energy efficiency under varying attack scenarios. These results indicate that combining the feature selection capabilities of XGBoost with CNN’s pattern extraction of CNN yields a scalable, accurate, and resource-efficient anomaly detection solution suitable for IoT-WSN devices.},
keywords = {IoT wireless sensor networks, anomaly detection, XGBoost, convolutional neural networks, feature selection, hybrid model, real-time detection},
issn = {3068-7969},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems
ISSN: 3068-7969 (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/