Abstract
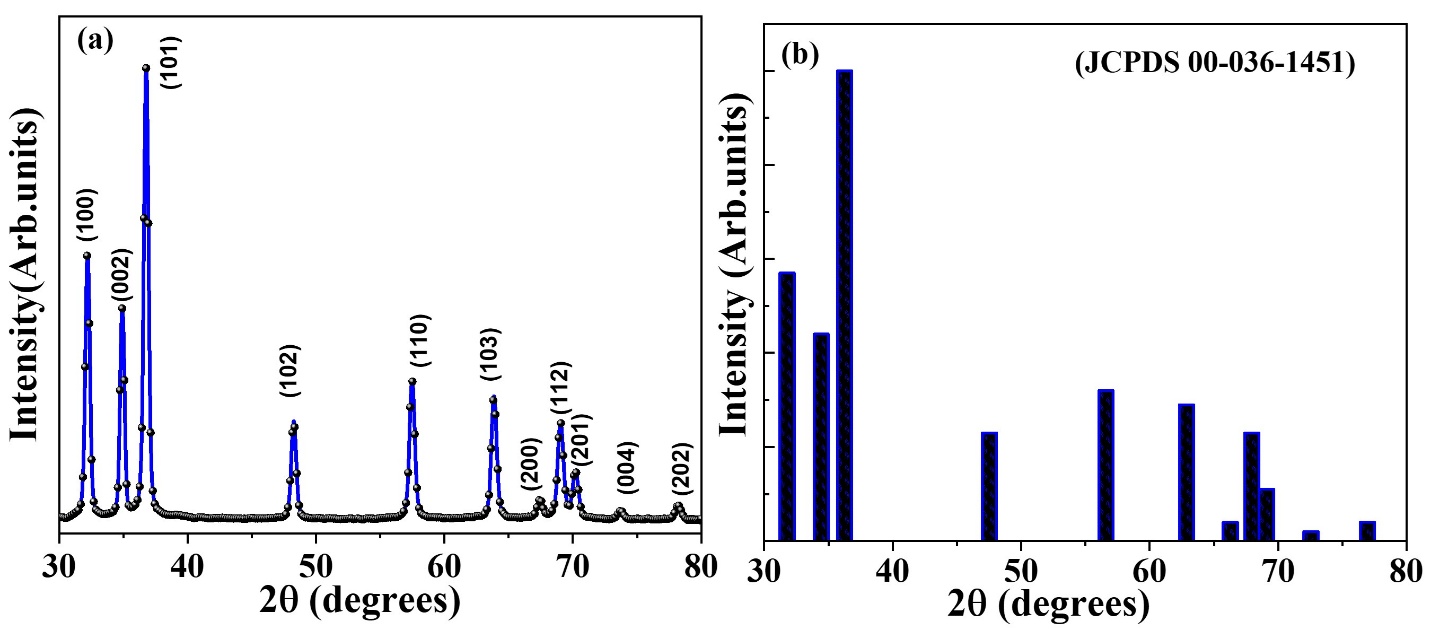
The present study delves into an eco-friendly and scalable method for creating zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles using extract from Piper betle leaves. By harnessing the natural bio-reductive and capping abilities of the phytochemicals found in P. betle, the ZnO nanoparticles formed a hexagonal wurtzite structure, with an average crystallite size of about 20.3 nm, as confirmed by XRD analysis. The UV–Visible spectroscopy results showed a notable blue shift in absorption, leading to an estimated band gap of 4.10 eV, which is linked to quantum confinement effects. FTIR spectra confirmed the presence of biomolecules on the surface, while SEM imaging displayed quasi-spherical polycrystalline particles with some aggregation. To assess the photocatalytic potential, we evaluated the degradation of methylene blue (MB) dye under UV light, where the Piper betle–ZnO catalyst achieved over 90% degradation efficiency in just ~80 minutes, with a pseudo-first-order rate constant of 0.0342 min^-1. These results highlight the collaborative role of P. betle's phytoconstituents in shaping the nucleation, growth, and surface chemistry of ZnO nanoparticles, which enhances their ability to absorb light and separate charge carriers. This green approach presents a promising strategy for developing effective photocatalysts aimed at cleaning up wastewater.
Keywords
ZnO nanoparticles
piper betle extract
precipitation
methylene blue dye degradation
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Gaur, J., & Kaushal, S. (2025). Role of Piper betle extract in the Precipitation of ZnO Nanoparticles for improved Photocatalytic Efficiency. ICCK Transactions on Advanced Functional Materials and Processing, 1(1), 11–17. https://doi.org/10.62762/TAFMP.2025.164661
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions

Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 