ICCK Transactions on Advanced Functional Materials and Processing | Volume 1, Issue 2: 78-92, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/TAFMP.2025.952672
Abstract
Poor aqueous solubility is a critical challenge in drug development, often leading to low oral bioavailability and limited therapeutic efficacy. To address this issue, advanced manufacturing processes and 3D printing technologies have emerged as powerful strategies for improving drug solubility and dissolution behavior. Advanced techniques such as hot-melt extrusion, spray drying, nanocrystal technology, co-crystallization, lipid-based systems, and amorphous solid dispersions enable stable formulations with enhanced solubility and scalable production. In parallel, 3D printing offers unique advantages in fabricating personalized, complex, and controlled-release dosage forms, making it an attr... More >
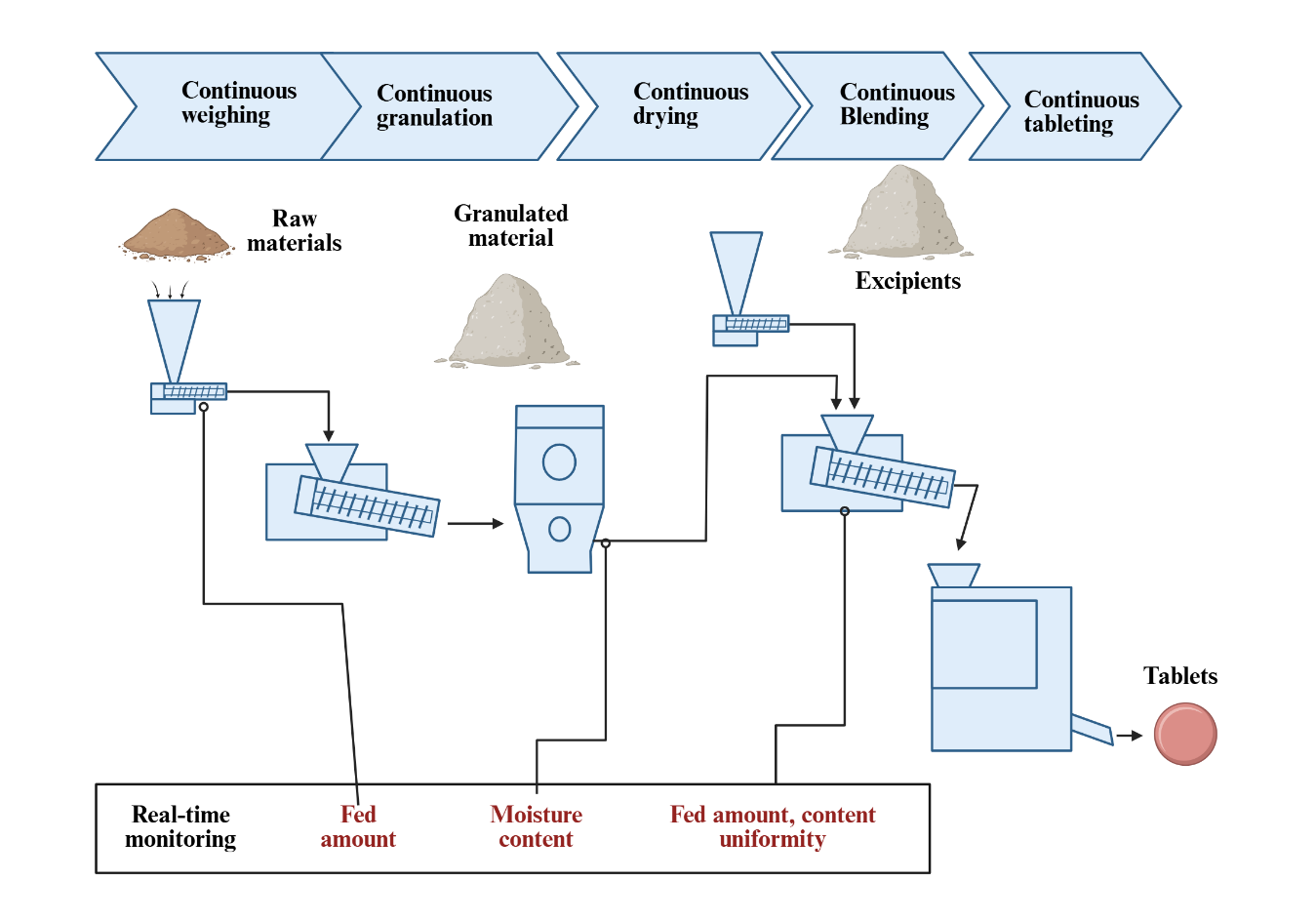
Graphical Abstract