ICCK Transactions on Advanced Functional Materials and Processing
ISSN: 3068-8973 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
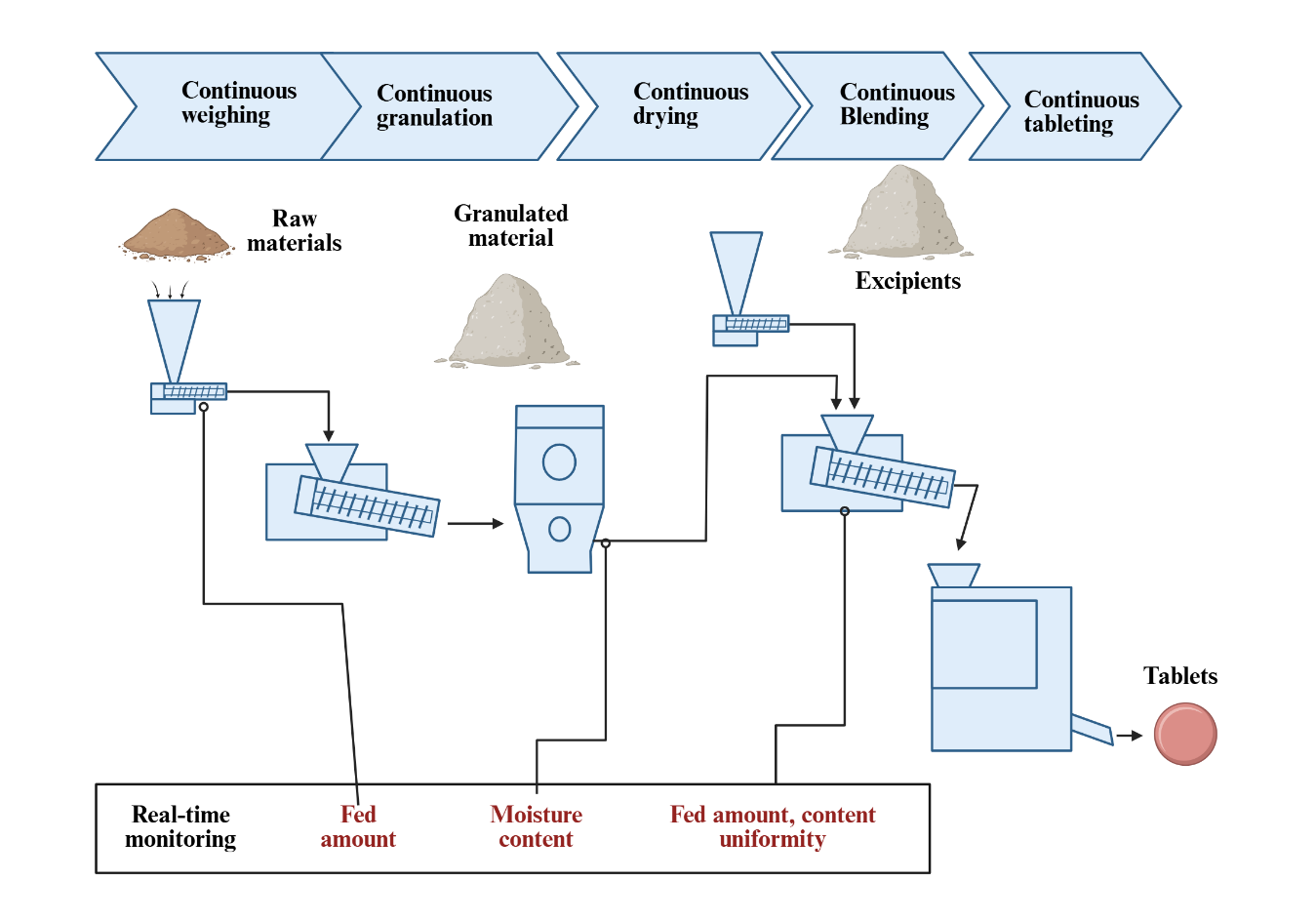
TY - JOUR AU - Sihmar, Amit AU - Dudhe, Rupesh AU - Porwal, Omji AU - Shivani, Km AU - Dudhe, Anshu R. PY - 2025 DA - 2025/12/31 TI - Advanced Manufacturing Processes and 3D Printing Approaches for Enhancing Solubility and Bioavailability of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs JO - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Functional Materials and Processing T2 - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Functional Materials and Processing JF - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Functional Materials and Processing VL - 1 IS - 2 SP - 78 EP - 92 DO - 10.62762/TAFMP.2025.952672 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TAFMP.2025.952672 KW - 3D Printing KW - bioavailability KW - water-soluble drugs KW - aqueous solubility KW - permeability AB - Poor aqueous solubility is a critical challenge in drug development, often leading to low oral bioavailability and limited therapeutic efficacy. To address this issue, advanced manufacturing processes and 3D printing technologies have emerged as powerful strategies for improving drug solubility and dissolution behavior. Advanced techniques such as hot-melt extrusion, spray drying, nanocrystal technology, co-crystallization, lipid-based systems, and amorphous solid dispersions enable stable formulations with enhanced solubility and scalable production. In parallel, 3D printing offers unique advantages in fabricating personalized, complex, and controlled-release dosage forms, making it an attractive approach for precision medicine. This review highlights the principles, advantages, and applications of these technologies in enhancing the solubility and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. Comparative insights into their effectiveness, case studies of successful formulations, and emerging trends are discussed. While challenges remain in terms of stability, regulatory acceptance, and large-scale translation, the integration of advanced manufacturing with 3D printing and computational tools holds immense potential to revolutionize future pharmaceutical development and patient-centered therapies. SN - 3068-8973 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Sihmar2025Advanced,
author = {Amit Sihmar and Rupesh Dudhe and Omji Porwal and Km Shivani and Anshu R. Dudhe},
title = {Advanced Manufacturing Processes and 3D Printing Approaches for Enhancing Solubility and Bioavailability of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Advanced Functional Materials and Processing},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {2},
pages = {78-92},
doi = {10.62762/TAFMP.2025.952672},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TAFMP.2025.952672},
abstract = {Poor aqueous solubility is a critical challenge in drug development, often leading to low oral bioavailability and limited therapeutic efficacy. To address this issue, advanced manufacturing processes and 3D printing technologies have emerged as powerful strategies for improving drug solubility and dissolution behavior. Advanced techniques such as hot-melt extrusion, spray drying, nanocrystal technology, co-crystallization, lipid-based systems, and amorphous solid dispersions enable stable formulations with enhanced solubility and scalable production. In parallel, 3D printing offers unique advantages in fabricating personalized, complex, and controlled-release dosage forms, making it an attractive approach for precision medicine. This review highlights the principles, advantages, and applications of these technologies in enhancing the solubility and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. Comparative insights into their effectiveness, case studies of successful formulations, and emerging trends are discussed. While challenges remain in terms of stability, regulatory acceptance, and large-scale translation, the integration of advanced manufacturing with 3D printing and computational tools holds immense potential to revolutionize future pharmaceutical development and patient-centered therapies.},
keywords = {3D Printing, bioavailability, water-soluble drugs, aqueous solubility, permeability},
issn = {3068-8973},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. ICCK Transactions on Advanced Functional Materials and Processing
ISSN: 3068-8973 (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/