ICCK Transactions on Advanced Functional Materials and Processing
ISSN: 3068-8973 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
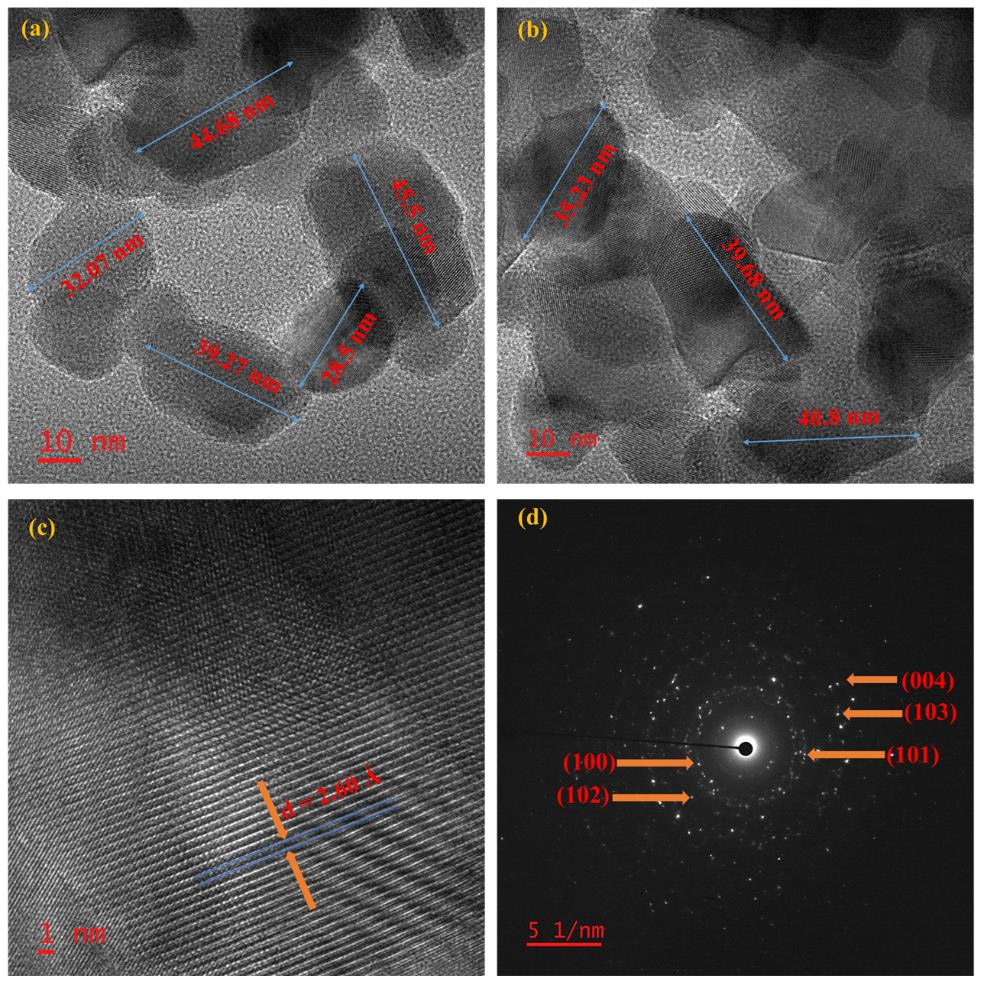
TY - JOUR AU - Singh, Gurjinder AU - Kumar, Vijay AU - Gaur, Jyoti AU - Kumar, Sanjeev PY - 2025 DA - 2025/12/30 TI - Sustainable Hydrothermal Route for ZnO Nanoparticles using Berseem extract: A Structure–Property Correlation Study JO - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Functional Materials and Processing T2 - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Functional Materials and Processing JF - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Functional Materials and Processing VL - 1 IS - 2 SP - 68 EP - 77 DO - 10.62762/TAFMP.2025.399354 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TAFMP.2025.399354 KW - green synthesis KW - optical properties KW - structural characterization KW - zinc oxide nanoparticles AB - This article explores the successful green synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles with a sustainable approach without using toxic chemicals or external stabilizers. The synthesized ZnO nanoparticles were characterized, and the investigation bridged the gap among physical, morphological, and optical properties. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis indicated the successful formation of a hexagonal wurtzite ZnO structure with an average crystallite size of 39.89 nm, representing high crystallinity and phase purity. The band gap energy was approximately 3.79 eV. UV-Visible results represented a strong optical absorption peak at 327 nm, proving the optical quality of the particles and exhibiting strong electronic transitions. Field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) results indicated the progression of rough agglomerated clusters into quasi-spherical well-dispersed particles through the growth process, while high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) images revealed uniformly sized particles of around 37 nm with a d-spacing of 2.60 Å between lattice fringes for further characterization. Meanwhile, the selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern obtained showed rings for polycrystalline ZnO representing the (100), (101), (102), (104), and (004) planes of the structure. Overall, the green-mediated synthesis approach resulted in high-purity and nanocrystalline ZnO particles with excellent structural and optical properties. The fabricated nanoparticles exhibit high potential for photocatalytic application, optoelectronic use, and UV-protective coatings; thus, efficiency suggests that a sustainable approach to fabrication allows for functionally efficient nanomaterials. SN - 3068-8973 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Singh2025Sustainabl,
author = {Gurjinder Singh and Vijay Kumar and Jyoti Gaur and Sanjeev Kumar},
title = {Sustainable Hydrothermal Route for ZnO Nanoparticles using Berseem extract: A Structure–Property Correlation Study},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Advanced Functional Materials and Processing},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {2},
pages = {68-77},
doi = {10.62762/TAFMP.2025.399354},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TAFMP.2025.399354},
abstract = {This article explores the successful green synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles with a sustainable approach without using toxic chemicals or external stabilizers. The synthesized ZnO nanoparticles were characterized, and the investigation bridged the gap among physical, morphological, and optical properties. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis indicated the successful formation of a hexagonal wurtzite ZnO structure with an average crystallite size of 39.89 nm, representing high crystallinity and phase purity. The band gap energy was approximately 3.79 eV. UV-Visible results represented a strong optical absorption peak at 327 nm, proving the optical quality of the particles and exhibiting strong electronic transitions. Field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) results indicated the progression of rough agglomerated clusters into quasi-spherical well-dispersed particles through the growth process, while high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) images revealed uniformly sized particles of around 37 nm with a d-spacing of 2.60 Å between lattice fringes for further characterization. Meanwhile, the selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern obtained showed rings for polycrystalline ZnO representing the (100), (101), (102), (104), and (004) planes of the structure. Overall, the green-mediated synthesis approach resulted in high-purity and nanocrystalline ZnO particles with excellent structural and optical properties. The fabricated nanoparticles exhibit high potential for photocatalytic application, optoelectronic use, and UV-protective coatings; thus, efficiency suggests that a sustainable approach to fabrication allows for functionally efficient nanomaterials.},
keywords = {green synthesis, optical properties, structural characterization, zinc oxide nanoparticles},
issn = {3068-8973},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. ICCK Transactions on Advanced Functional Materials and Processing
ISSN: 3068-8973 (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/