ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control
ISSN: 3068-9287 (Online) | ISSN: 3068-9279 (Print)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
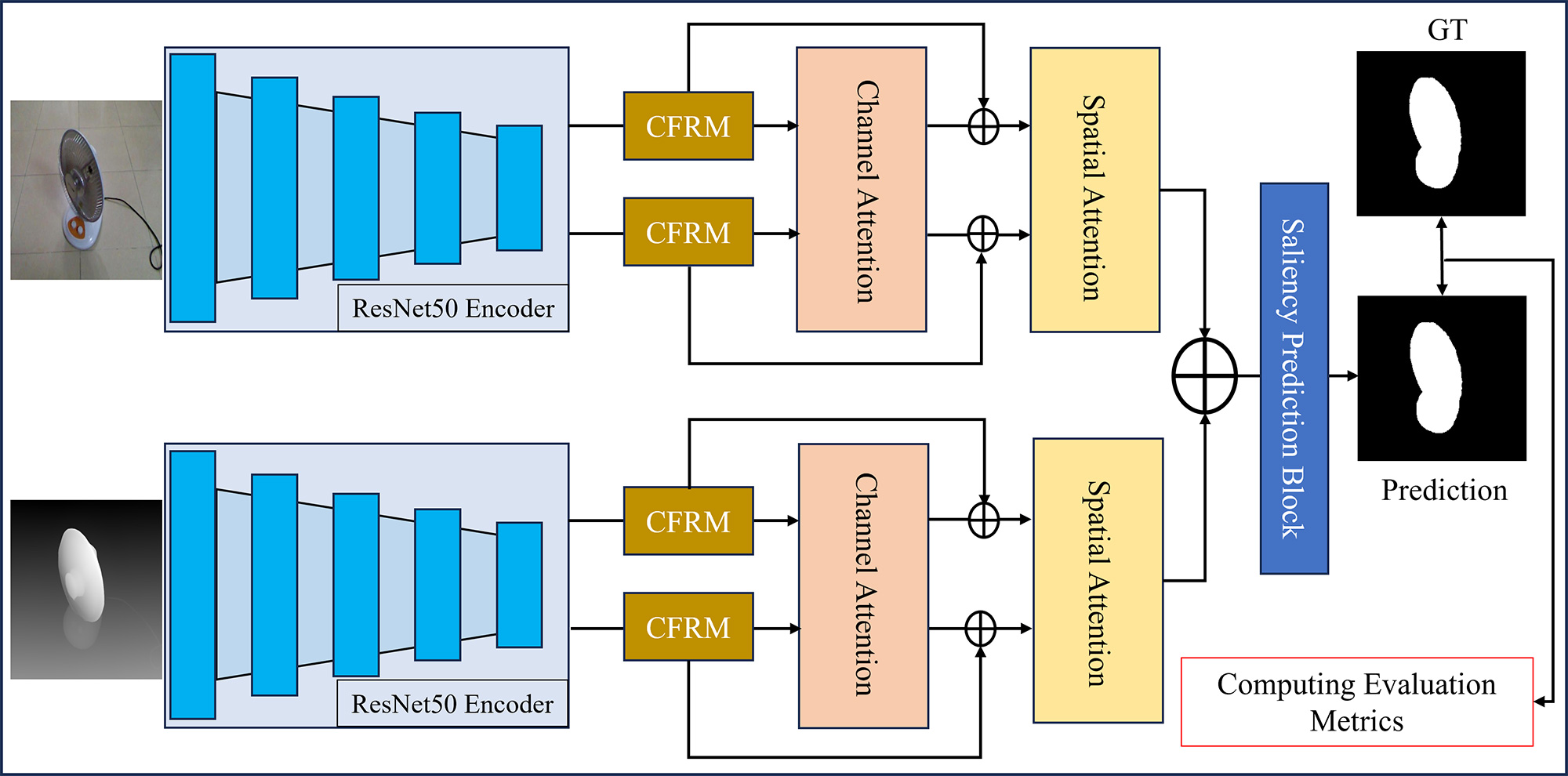
TY - JOUR AU - Khan, Abdurrahman AU - Shah, Hasnain Ali PY - 2026 DA - 2026/02/14 TI - Context Refinement with Multi-Attention Fusion for Saliency Segmentation Using Depth-Aware RGBD Sensing JO - ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control T2 - ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control JF - ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control VL - 3 IS - 1 SP - 27 EP - 38 DO - 10.62762/TSCC.2025.587957 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TSCC.2025.587957 KW - RGB-D saliency KW - attention mechanisms KW - multi-modal fusion KW - depth refinement KW - contextual features AB - Salient object detection in RGB-D imagery remains challenging due to inconsistent depth quality and suboptimal cross-modal fusion strategies. This paper presents a novel dual-stream architecture that integrates contextual feature refinement with adaptive attention mechanisms for robust RGB-D saliency detection. We extract two features from the ResNet-50 backbone for both the RGB and depth streams, capturing low-level spatial details and high-level semantic representations. We introduce a Contextual Feature Refinement Module (CFRM) that captures multi-scale dependencies through parallel dilated convolutions, enabling hierarchical context aggregation without substantial computational overhead. To enhance discriminative feature learning, we employ channel attention for inter-channel recalibration and a modified spatial attention mechanism utilizing quadruple feature statistics for precise localization. Recognizing that existing depth maps in benchmark datasets are outdated and degraded in quality, we introduce refined depth maps generated with Depth AnythingV2, which significantly improve cross-modal alignment and detection performance. The progressive fusion strategy integrates complementary RGB and depth information across semantic hierarchies, while the saliency prediction block generates high-resolution predictions via gradual spatial expansion. Extensive experiments across six benchmark datasets validate our approach, achieving competitive performance with recent state-of-the-art methods. SN - 3068-9287 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Khan2026Context,
author = {Abdurrahman Khan and Hasnain Ali Shah},
title = {Context Refinement with Multi-Attention Fusion for Saliency Segmentation Using Depth-Aware RGBD Sensing},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control},
year = {2026},
volume = {3},
number = {1},
pages = {27-38},
doi = {10.62762/TSCC.2025.587957},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TSCC.2025.587957},
abstract = {Salient object detection in RGB-D imagery remains challenging due to inconsistent depth quality and suboptimal cross-modal fusion strategies. This paper presents a novel dual-stream architecture that integrates contextual feature refinement with adaptive attention mechanisms for robust RGB-D saliency detection. We extract two features from the ResNet-50 backbone for both the RGB and depth streams, capturing low-level spatial details and high-level semantic representations. We introduce a Contextual Feature Refinement Module (CFRM) that captures multi-scale dependencies through parallel dilated convolutions, enabling hierarchical context aggregation without substantial computational overhead. To enhance discriminative feature learning, we employ channel attention for inter-channel recalibration and a modified spatial attention mechanism utilizing quadruple feature statistics for precise localization. Recognizing that existing depth maps in benchmark datasets are outdated and degraded in quality, we introduce refined depth maps generated with Depth AnythingV2, which significantly improve cross-modal alignment and detection performance. The progressive fusion strategy integrates complementary RGB and depth information across semantic hierarchies, while the saliency prediction block generates high-resolution predictions via gradual spatial expansion. Extensive experiments across six benchmark datasets validate our approach, achieving competitive performance with recent state-of-the-art methods.},
keywords = {RGB-D saliency, attention mechanisms, multi-modal fusion, depth refinement, contextual features},
issn = {3068-9287},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control
ISSN: 3068-9287 (Online) | ISSN: 3068-9279 (Print)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/