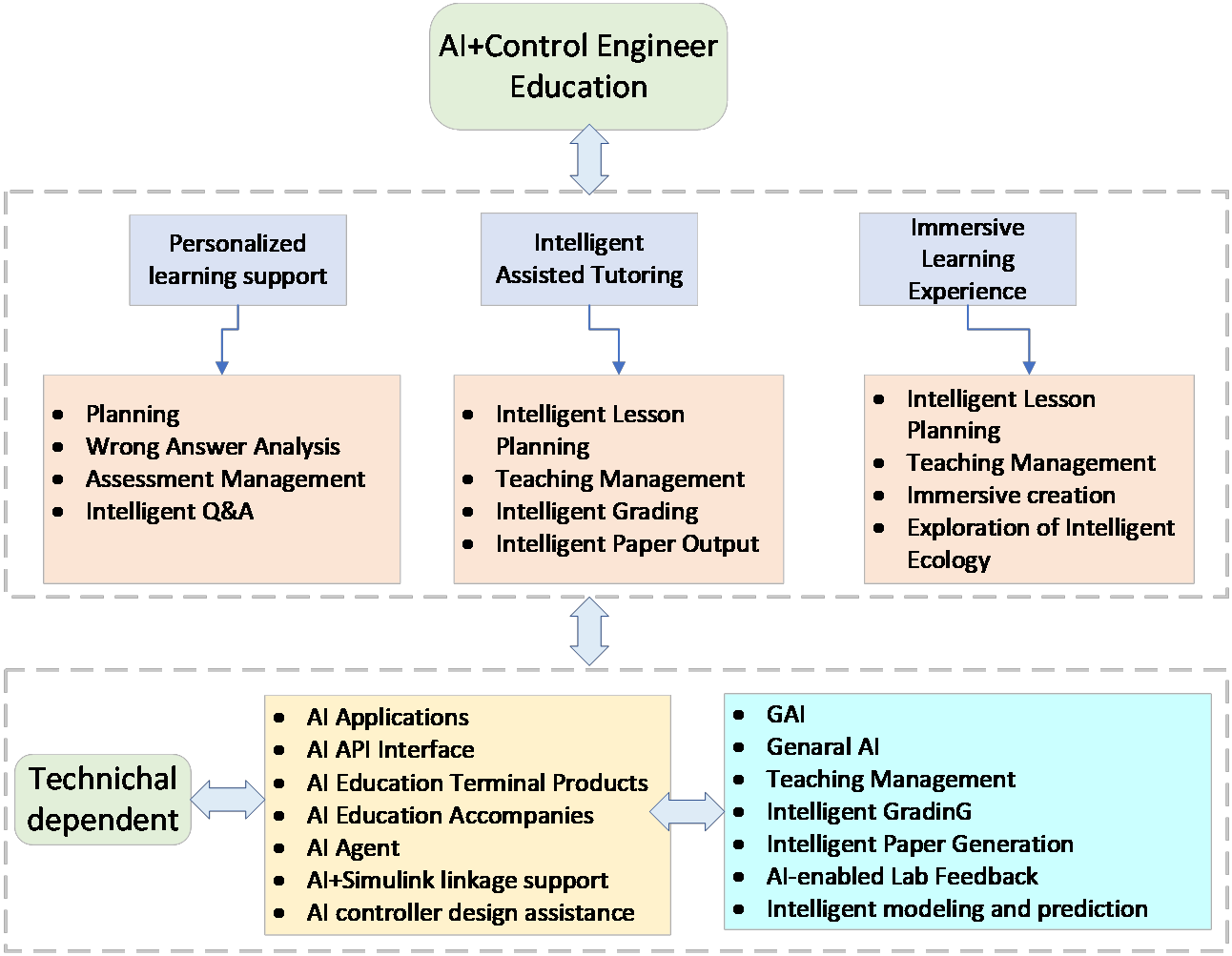
ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control | Volume 3, Issue 1: 27-38, 2026 | DOI: 10.62762/TSCC.2025.587957
Abstract
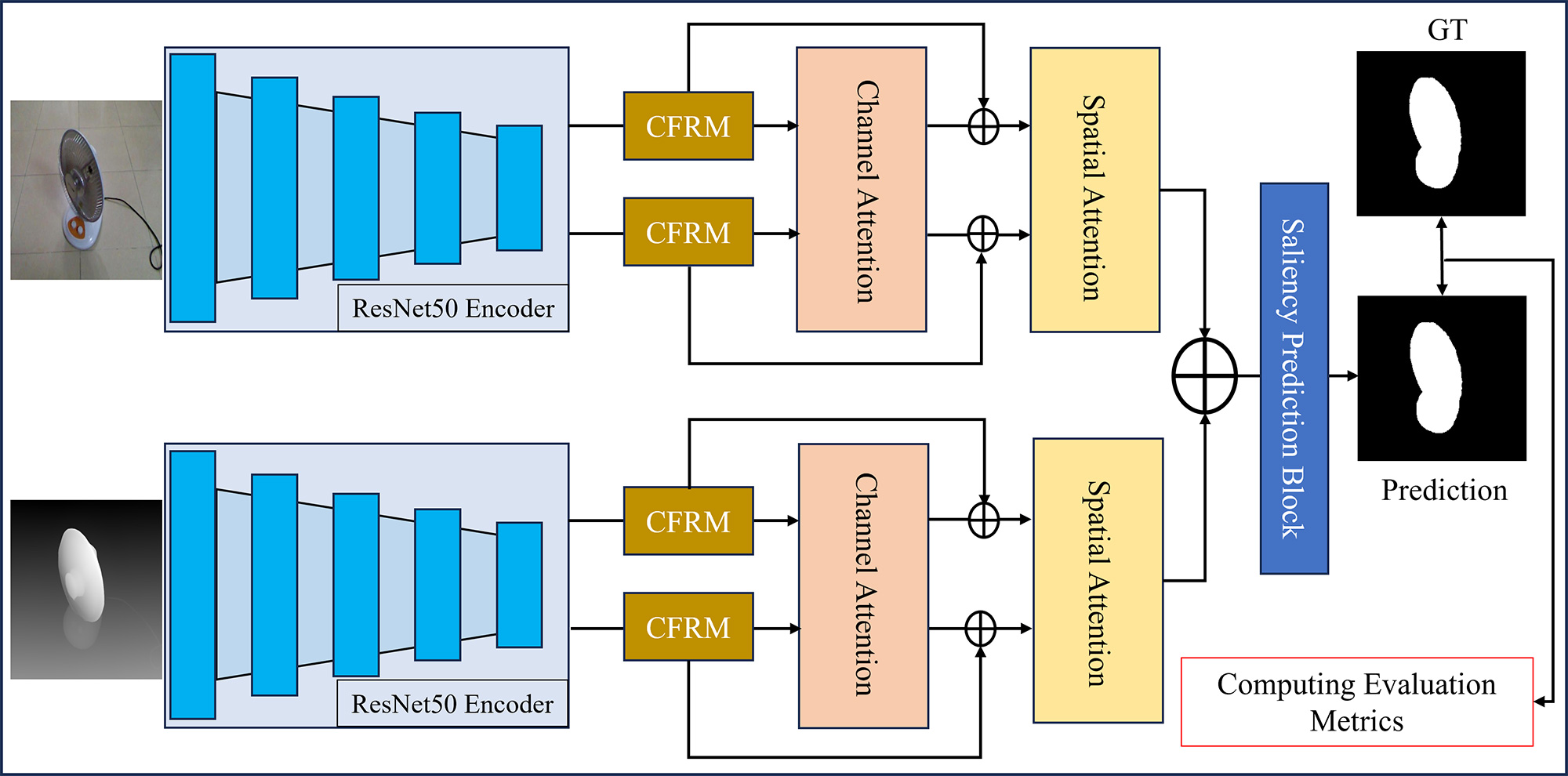
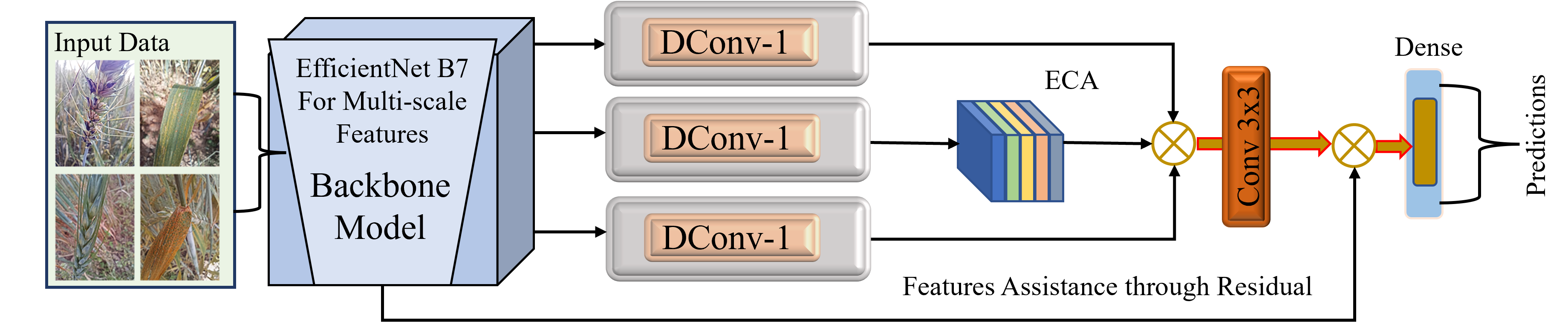
Salient object detection in RGB-D imagery remains challenging due to inconsistent depth quality and suboptimal cross-modal fusion strategies. This paper presents a novel dual-stream architecture that integrates contextual feature refinement with adaptive attention mechanisms for robust RGB-D saliency detection. We extract two features from the ResNet-50 backbone for both the RGB and depth streams, capturing low-level spatial details and high-level semantic representations. We introduce a Contextual Feature Refinement Module (CFRM) that captures multi-scale dependencies through parallel dilated convolutions, enabling hierarchical context aggregation without substantial computational overhead.... More >
Graphical Abstract