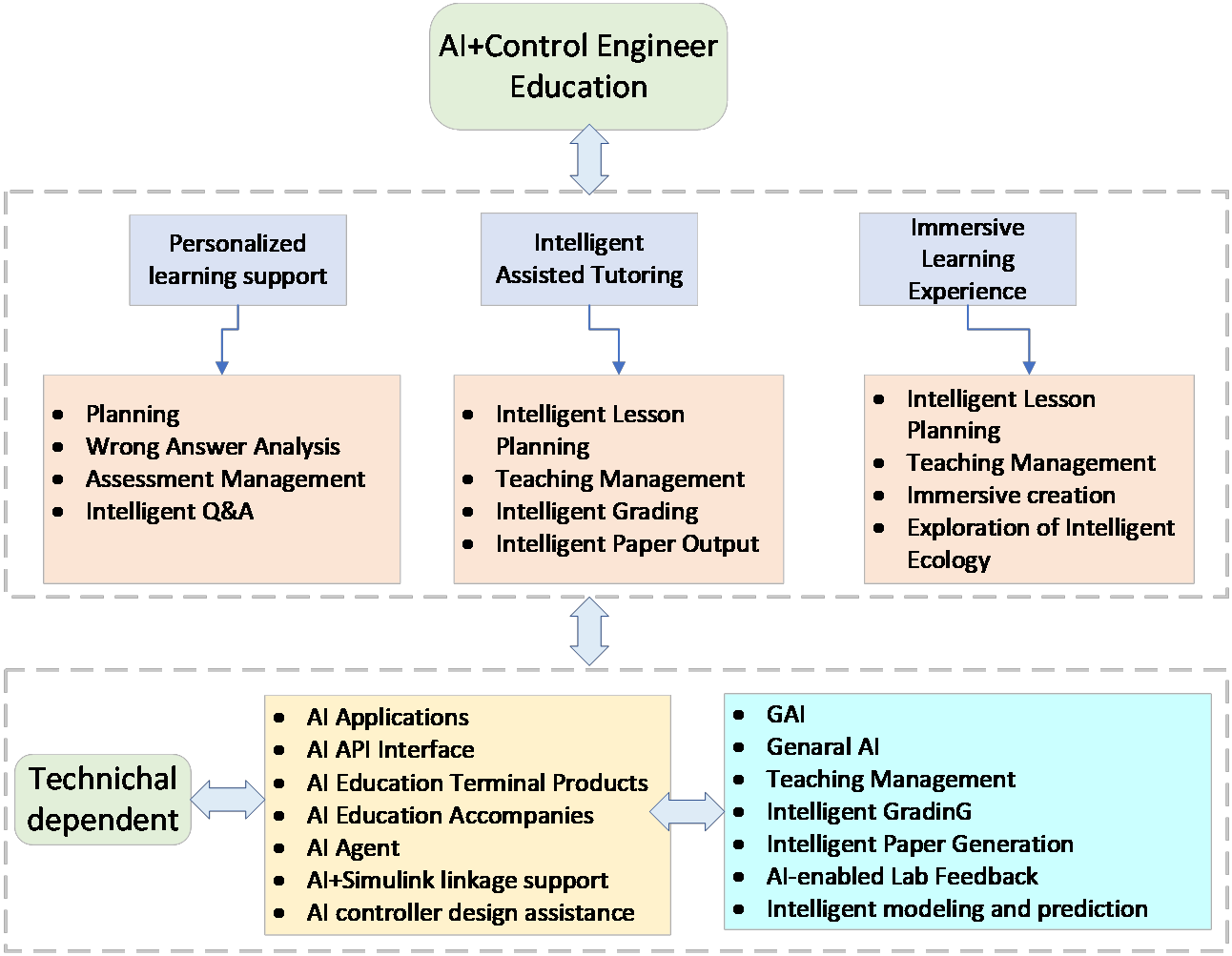
Abstract
This study briefly discusses the primary AI’s roles in enhancing control engineering education (CEE), which has the potential to revolutionise the teaching-learning framework by making complex concepts and methodologies more intuitive, interactive, and application-driven. While understanding the potential benefits of these AI tools, such as assisting with problem-solving in education, some of the concerns about their use are summarised. An example is discussed how AI enhances CEE in MATLAB \& Simulink. The centre point in the brief paper is that AI should be a tool to enhance teaching-learning, rather than a shortcut to avoid it.
Keywords
generative AI
computational framework
virtual demonstration platform
MATLAB/Simulink
new assessment
AI in education community of practice
ethical issues
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Zhu, Q., & Wang, H. (2025). Primary Thought on Artificial Intelligence (AI) Enhanced Control Engineering Education. ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control, 2(3), 215–225. https://doi.org/10.62762/TSCC.2025.254228
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions
Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge (ICCK) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue