ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control | Volume 2, Issue 3: 215-225, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/TSCC.2025.254228
Abstract
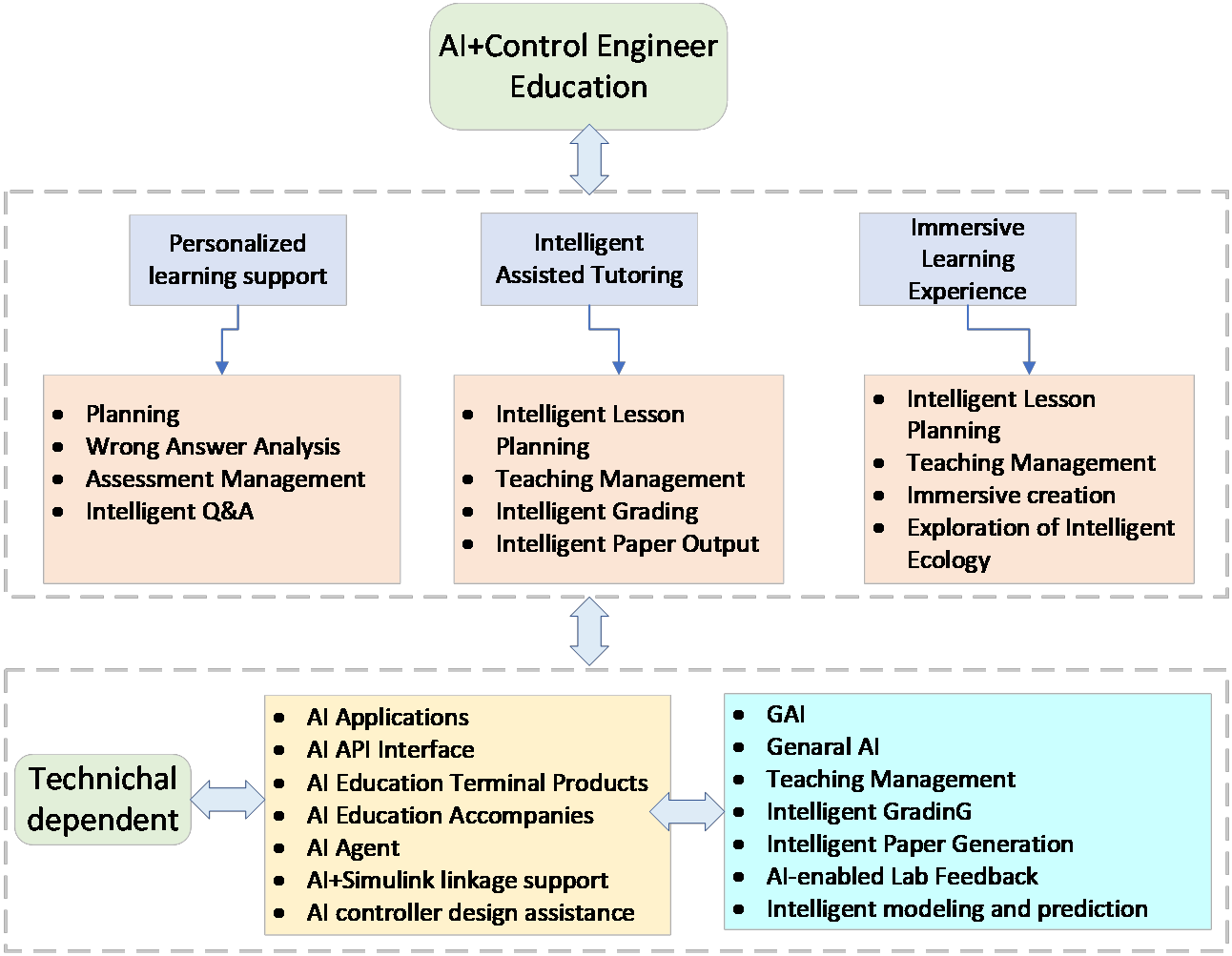
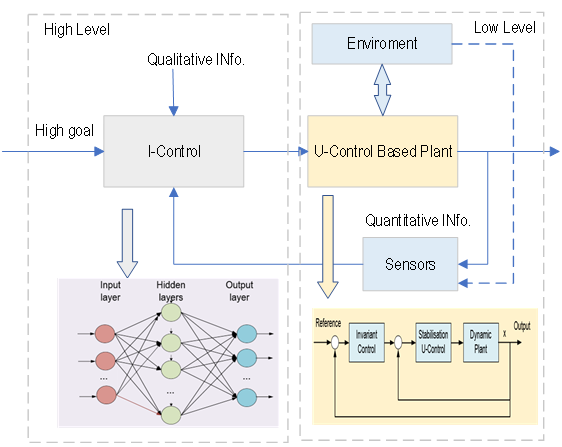
This study briefly discusses the primary AI’s roles in enhancing control engineering education (CEE), which has the potential to revolutionise the teaching-learning framework by making complex concepts and methodologies more intuitive, interactive, and application-driven. While understanding the potential benefits of these AI tools, such as assisting with problem-solving in education, some of the concerns about their use are summarised. An example is discussed how AI enhances CEE in MATLAB \& Simulink. The centre point in the brief paper is that AI should be a tool to enhance teaching-learning, rather than a shortcut to avoid it. More >
Graphical Abstract