Abstract
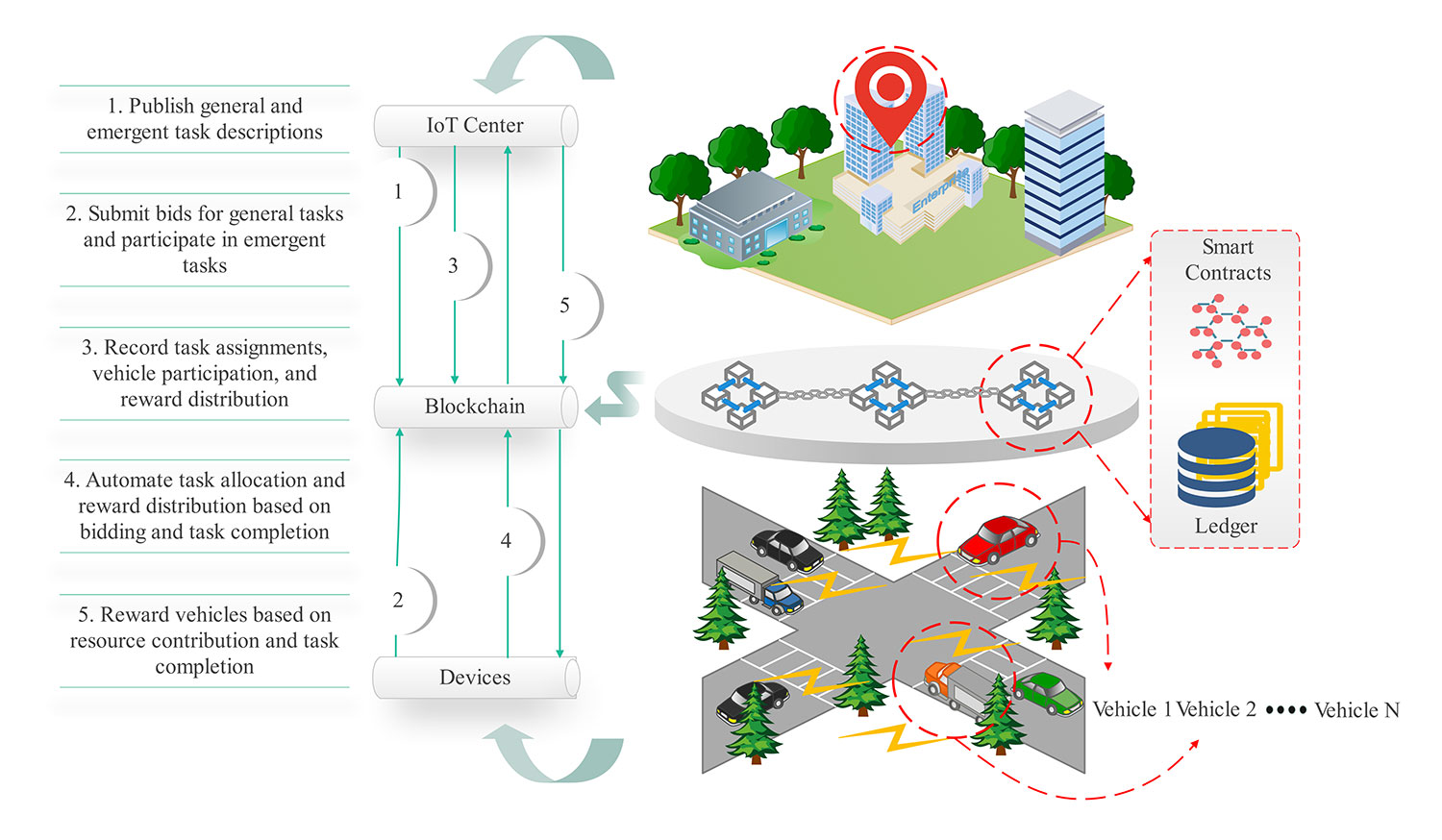
The Internet of Vehicles (IoV) is a core component of smart transportation systems, making it feasible to exchange information among vehicles, infrastructure, and central systems in real time. However, the effective use of resources and the efficient distribution of tasks in these dynamic environments is a challenging task. This paper presents a blockchain-based collaborative task allocation framework method that can solve these problems by using a greedy algorithm for general task allocation and adopting a dynamic collaboration scheduling algorithm for emergent tasks. Employing the blockchain-based reward mechanism, the transparency, fairness, and security in dynamic mobile crowdsensing (MCS) tasks encourage vehicle participation. Our experimental results show that our framework outperforms traditional task allocation methods in terms of resource optimization and task completion time, particularly for emergent tasks with real-time demand for multisite collaborative vehicles. Further results reveal that the blockchain mechanism can ensure fair rewards allocation and increase system scalability. Future work will focus on improving energy efficiency and scalability, as well as on how to apply privacy-preserving techniques to the IoV environment in the future.
Keywords
internet of vehicles (IoV)
blockchain
collaborative task allocation
incentive mechanism
general task
emergent tasks
task scheduling
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Haider, Z. A., Rahman, M. M., Khan, M. A., & Sohail, Q. (2025). Optimizing Collaborative Task Allocation in Internet of Vehicles (IoV) through Blockchain-Enabled Incentive Mechanisms. ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control, 2(3), 147–167. https://doi.org/10.62762/TSCC.2025.962030
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions
Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge (ICCK) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue