Abstract
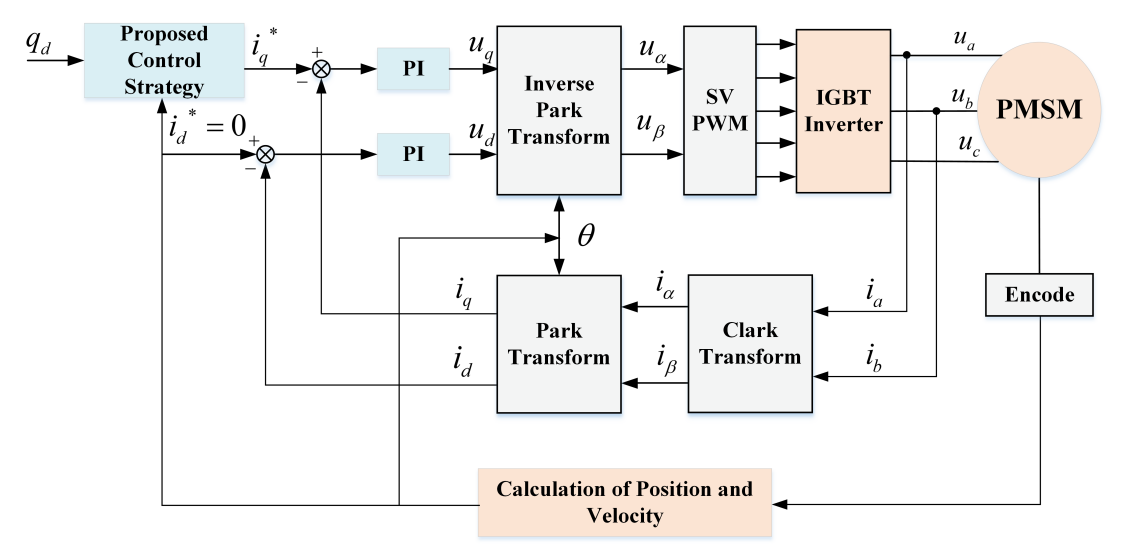
A fixed-time adaptive optimal parameter estimation (FxT-AOPE) scheme is proposed to address the difficulties in estimating dead zone parameters and slow convergence speed of tracking errors in permanent magnet synchronous motor systems. First, the continuous piecewise linear neural network is used to model the nonlinear dead zone dynamics. Second, an auxiliary filter is constructed to extract estimation errors, and this filter is used to drive an adaptive law with time-varying gain, minimizing the cost function of estimation errors and achieving adaptive optimal parameter estimation (AOPE). Then, the AOPE method is introduced into the fixed-time non-singular terminal sliding mode control (FxT-NTSMC) of the permanent magnet synchronous motor system, and the FxT-AOPE strategy is proposed to ensure the fixed time convergence of estimation error and tracking error. The stability of the closed-loop system is analyzed using Lyapunov stability theory. Finally, the feasibility of the proposed control strategy is verified through comparative simulations and experiments.
Keywords
servo system
adaptive optimal parameter estimation
fixed-time convergence
dead-zone
sliding mode control
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62173194.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Wang, S., & Wang, X. (2025). Fixed-Time Adaptive Optimal Parameter Estimation Subject to Dead-Zone and Control of Servo Systems. ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control, 2(3), 200–214. https://doi.org/10.62762/TSCC.2025.143677
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions
Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge (ICCK) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue