ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control
ISSN: 3068-9287 (Online) | ISSN: 3068-9279 (Print)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
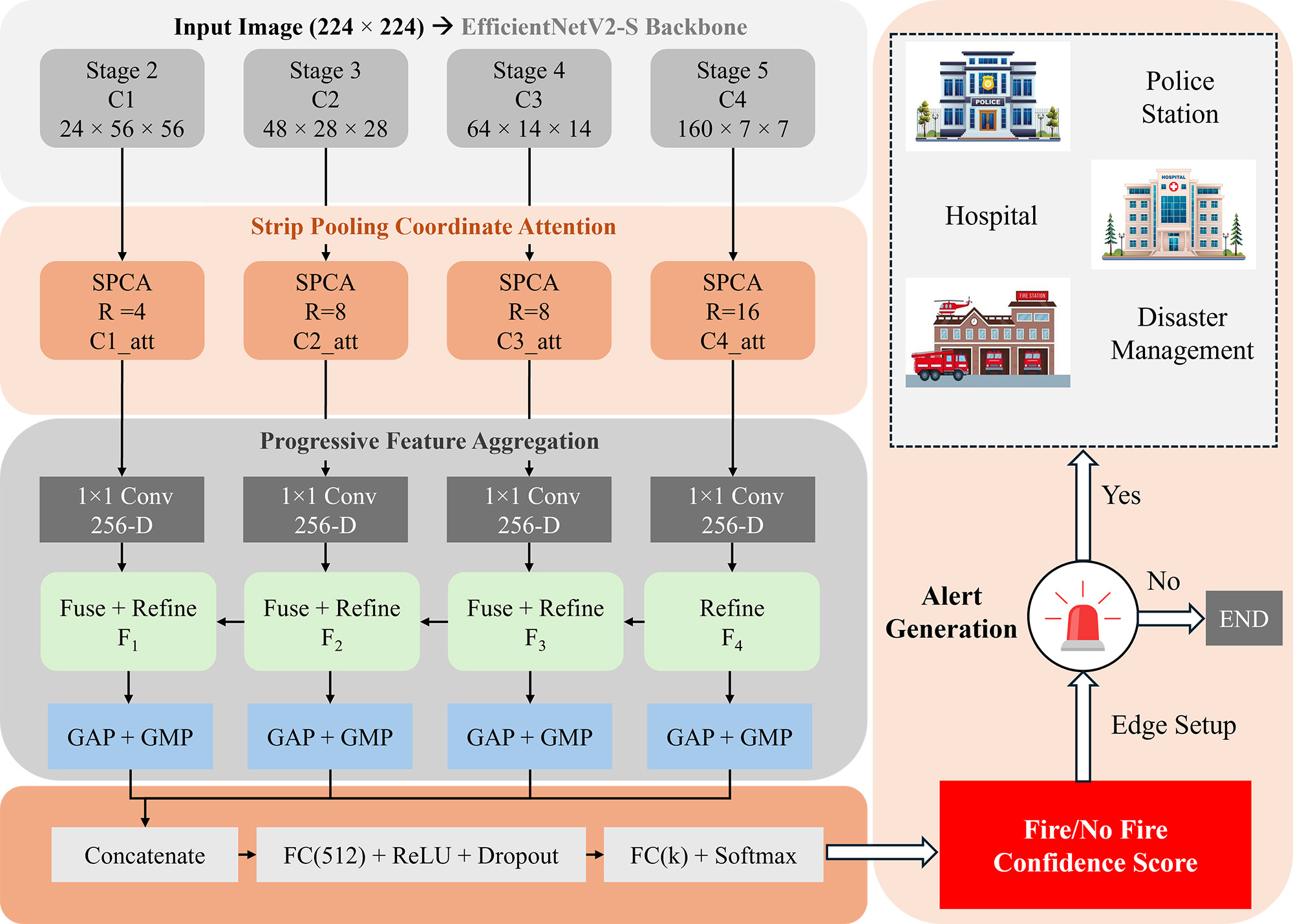
TY - JOUR AU - Haider, Asad Ullah AU - Khan, Shadab AU - Ahmed, Muhammad Jamal AU - Khan, Taimur Ali PY - 2025 DA - 2025/12/20 TI - Strip Pooling Coordinate Attention with Directional Learning for Intelligent Fire Recognition in Smart Cities JO - ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control T2 - ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control JF - ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control VL - 2 IS - 4 SP - 263 EP - 275 DO - 10.62762/TSCC.2025.675097 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TSCC.2025.675097 KW - fire detection KW - directional attention KW - strip pooling KW - smart cities KW - anisotropic feature learning KW - multi-scale fusion AB - Fire detection in smart cities requires intelligent visual recognition systems capable of distinguishing fire from visually similar phenomena while maintaining real-time performance under diverse environmental conditions. Existing deep learning approaches employ attention mechanisms that aggregate spatial information isotropically, failing to capture the inherently directional characteristics of fire and smoke patterns. This paper presents DirFireNet, a novel fire detection framework that exploits directional fire dynamics through Strip Pooling Coordinate Attention (SPCA). Unlike conventional attention mechanisms, DirFireNet explicitly models vertical flame propagation and horizontal smoke dispersion via directional strip pooling operations that decompose features along horizontal and vertical axes. The framework integrates a progressive top-down fusion pathway with attention-guided weighting that synthesizes multi-scale representations from coarse to fine resolutions. Furthermore, dual global pooling captures complementary scene statistics holistic fire intensity and salient flame regions. Built upon the lightweight EfficientNetV2-S backbone, DirFireNet achieves superior accuracy while maintaining computational efficiency. Extensive experiments on the FD and BoWFire benchmark demonstrate state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance. Comprehensive ablation studies validate that directional attention contributes to accuracy gain, validating that attention mechanism provides strong inductive biases for intelligent fire recognition in smart city applications. SN - 3068-9287 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Haider2025Strip,
author = {Asad Ullah Haider and Shadab Khan and Muhammad Jamal Ahmed and Taimur Ali Khan},
title = {Strip Pooling Coordinate Attention with Directional Learning for Intelligent Fire Recognition in Smart Cities},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control},
year = {2025},
volume = {2},
number = {4},
pages = {263-275},
doi = {10.62762/TSCC.2025.675097},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TSCC.2025.675097},
abstract = {Fire detection in smart cities requires intelligent visual recognition systems capable of distinguishing fire from visually similar phenomena while maintaining real-time performance under diverse environmental conditions. Existing deep learning approaches employ attention mechanisms that aggregate spatial information isotropically, failing to capture the inherently directional characteristics of fire and smoke patterns. This paper presents DirFireNet, a novel fire detection framework that exploits directional fire dynamics through Strip Pooling Coordinate Attention (SPCA). Unlike conventional attention mechanisms, DirFireNet explicitly models vertical flame propagation and horizontal smoke dispersion via directional strip pooling operations that decompose features along horizontal and vertical axes. The framework integrates a progressive top-down fusion pathway with attention-guided weighting that synthesizes multi-scale representations from coarse to fine resolutions. Furthermore, dual global pooling captures complementary scene statistics holistic fire intensity and salient flame regions. Built upon the lightweight EfficientNetV2-S backbone, DirFireNet achieves superior accuracy while maintaining computational efficiency. Extensive experiments on the FD and BoWFire benchmark demonstrate state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance. Comprehensive ablation studies validate that directional attention contributes to accuracy gain, validating that attention mechanism provides strong inductive biases for intelligent fire recognition in smart city applications.},
keywords = {fire detection, directional attention, strip pooling, smart cities, anisotropic feature learning, multi-scale fusion},
issn = {3068-9287},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control
ISSN: 3068-9287 (Online) | ISSN: 3068-9279 (Print)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/