ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control
ISSN: 3068-9287 (Online) | ISSN: 3068-9279 (Print)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
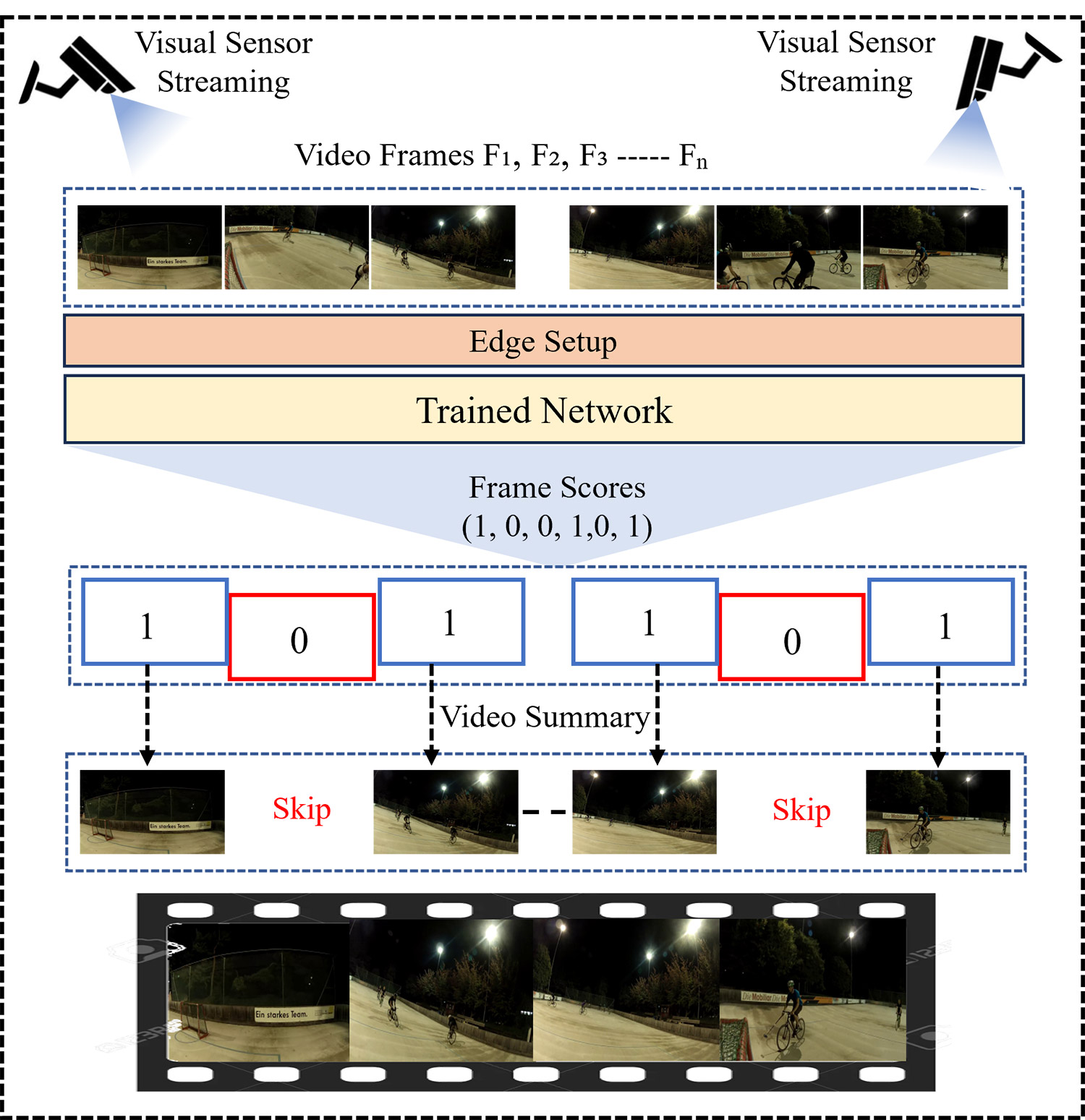
TY - JOUR AU - Khan, Taimur Ali AU - Ali, Danish AU - Ghazanfar, Zainab AU - Ahmad, Bilal PY - 2025 DA - 2025/12/30 TI - Dual-Pathway Sensing with Optimized Attention Network for Video Summarization in Surveillance Systems JO - ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control T2 - ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control JF - ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control VL - 2 IS - 4 SP - 276 EP - 289 DO - 10.62762/TSCC.2025.308540 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TSCC.2025.308540 KW - video summarization KW - visual intelligence KW - surveillance systems KW - dual-pathway KW - attention network AB - Video summarization (VS) aims to generate concise representations of long videos by extracting the most informative frames while maintaining essential content. Existing methods struggle to capture multi-scale dependencies and often rely on suboptimal feature representations, limiting their ability to model complex inter-frame relationships. To address these issues, we propose a multi-scale sensing network that incorporates three key innovations to improve VS. First, we introduce multi-scale dilated convolution blocks with progressively increasing dilation rates to capture temporal context at multiple levels, enabling the network to understand both local transitions and long-range dependencies. Second, we develop a Dual-Pathway Efficient Channel Attention (DECA) module that leverages statistics from Global Average Pooling and Global Max Pooling pathways. Third, we suggest an Optimized Spatial Attention (OSA) module that replaces standard $7\times7$ convolutions with more efficient operations while maintaining spatial dependency modeling. The proposed framework uses EfficientNetB7 as the backbone for robust spatial feature extraction, followed by multi-scale dilated blocks and dual attention mechanisms for detailed feature refinement. Extensive tests on the TVSum and SumMe benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of our method, achieving F1 Scores of 63.5% and 53.3%, respectively. SN - 3068-9287 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Khan2025DualPathwa,
author = {Taimur Ali Khan and Danish Ali and Zainab Ghazanfar and Bilal Ahmad},
title = {Dual-Pathway Sensing with Optimized Attention Network for Video Summarization in Surveillance Systems},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control},
year = {2025},
volume = {2},
number = {4},
pages = {276-289},
doi = {10.62762/TSCC.2025.308540},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TSCC.2025.308540},
abstract = {Video summarization (VS) aims to generate concise representations of long videos by extracting the most informative frames while maintaining essential content. Existing methods struggle to capture multi-scale dependencies and often rely on suboptimal feature representations, limiting their ability to model complex inter-frame relationships. To address these issues, we propose a multi-scale sensing network that incorporates three key innovations to improve VS. First, we introduce multi-scale dilated convolution blocks with progressively increasing dilation rates to capture temporal context at multiple levels, enabling the network to understand both local transitions and long-range dependencies. Second, we develop a Dual-Pathway Efficient Channel Attention (DECA) module that leverages statistics from Global Average Pooling and Global Max Pooling pathways. Third, we suggest an Optimized Spatial Attention (OSA) module that replaces standard \$7\times7\$ convolutions with more efficient operations while maintaining spatial dependency modeling. The proposed framework uses EfficientNetB7 as the backbone for robust spatial feature extraction, followed by multi-scale dilated blocks and dual attention mechanisms for detailed feature refinement. Extensive tests on the TVSum and SumMe benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of our method, achieving F1 Scores of 63.5\% and 53.3\%, respectively.},
keywords = {video summarization, visual intelligence, surveillance systems, dual-pathway, attention network},
issn = {3068-9287},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control
ISSN: 3068-9287 (Online) | ISSN: 3068-9279 (Print)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/