ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control
ISSN: 3068-9287 (Online) | ISSN: 3068-9279 (Print)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
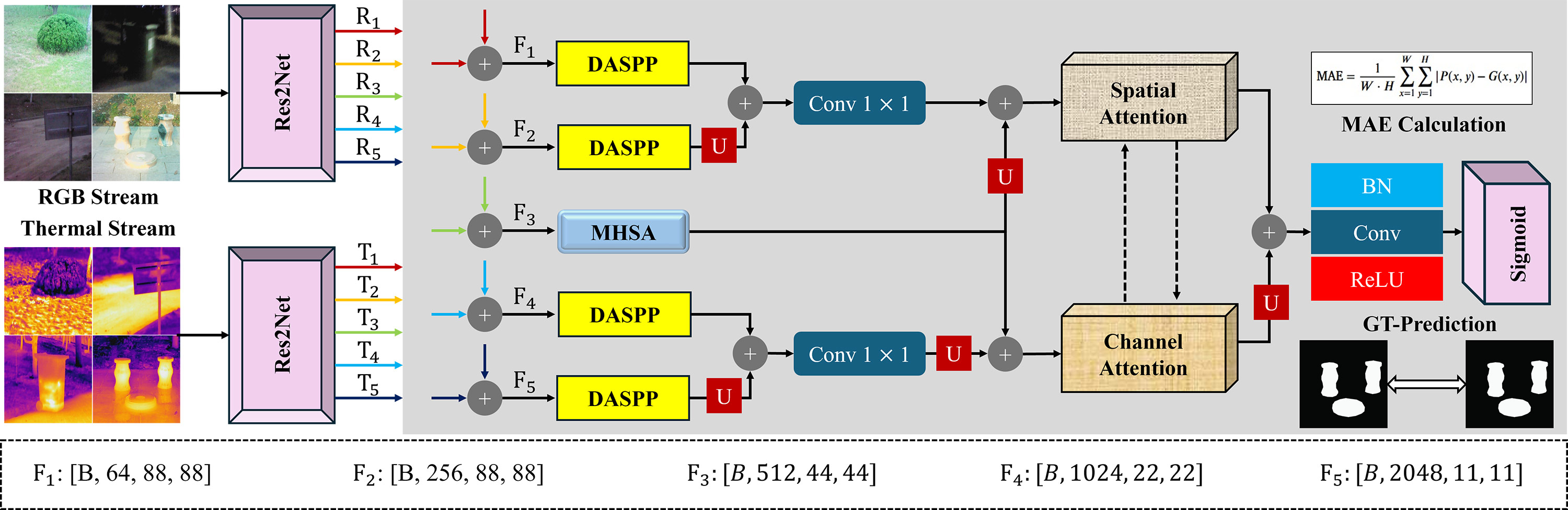
TY - JOUR AU - Hassan, Muhammad Zain AU - Gazis, Alexandros AU - Khan, Abdurrahman AU - Ghazanfar, Zainab PY - 2026 DA - 2026/01/29 TI - Learning Cross-Modal Collaboration via Pyramid Attention for RGB Thermal Sensing in Saliency Detection JO - ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control T2 - ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control JF - ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control VL - 3 IS - 1 SP - 1 EP - 14 DO - 10.62762/TSCC.2025.210523 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TSCC.2025.210523 KW - salient object detection KW - RGB-thermal fusion KW - cross-interactive dual attention KW - multi-modal learning AB - RGB–thermal (RGB-T) salient object detection exploits complementary cues from visible and thermal sensors to maintain reliable performance in adverse environments. However, many existing methods (i) fuse modalities before sufficiently enhancing intra-modal semantics and (ii) are sensitive to modality discrepancies caused by heterogeneous sensor characteristics. To address these issues, we propose PACNet (Pyramid Attention Collaboration Network), a hierarchical RGB-T framework that jointly models multi-scale and global context and performs refinement-before-fusion with cross-modal collaboration. Specifically, Dense Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (DASPP) captures multi-scale contextual cues across semantic stages, while Multi-Head Self-Attention (MHSA) establishes long-range dependencies for global context modeling. We further design a hierarchical feature integration scheme that constructs two complementary feature streams, preserving fine-grained spatial details and strengthening high-level semantics. These streams are refined using a cross-interactive dual-attention module that enables bidirectional interaction between spatial and channel attention, improving localization and semantic discrimination while mitigating modality imbalance. Experiments on three public benchmarks (VT821, VT1000, and VT5000) demonstrate that PACNet achieves state-of-the-art performance and delivers consistent gains in challenging conditions such as low illumination, thermal clutter, and multi-scale targets. SN - 3068-9287 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Hassan2026Learning,
author = {Muhammad Zain Hassan and Alexandros Gazis and Abdurrahman Khan and Zainab Ghazanfar},
title = {Learning Cross-Modal Collaboration via Pyramid Attention for RGB Thermal Sensing in Saliency Detection},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control},
year = {2026},
volume = {3},
number = {1},
pages = {1-14},
doi = {10.62762/TSCC.2025.210523},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TSCC.2025.210523},
abstract = {RGB–thermal (RGB-T) salient object detection exploits complementary cues from visible and thermal sensors to maintain reliable performance in adverse environments. However, many existing methods (i) fuse modalities before sufficiently enhancing intra-modal semantics and (ii) are sensitive to modality discrepancies caused by heterogeneous sensor characteristics. To address these issues, we propose PACNet (Pyramid Attention Collaboration Network), a hierarchical RGB-T framework that jointly models multi-scale and global context and performs refinement-before-fusion with cross-modal collaboration. Specifically, Dense Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (DASPP) captures multi-scale contextual cues across semantic stages, while Multi-Head Self-Attention (MHSA) establishes long-range dependencies for global context modeling. We further design a hierarchical feature integration scheme that constructs two complementary feature streams, preserving fine-grained spatial details and strengthening high-level semantics. These streams are refined using a cross-interactive dual-attention module that enables bidirectional interaction between spatial and channel attention, improving localization and semantic discrimination while mitigating modality imbalance. Experiments on three public benchmarks (VT821, VT1000, and VT5000) demonstrate that PACNet achieves state-of-the-art performance and delivers consistent gains in challenging conditions such as low illumination, thermal clutter, and multi-scale targets.},
keywords = {salient object detection, RGB-thermal fusion, cross-interactive dual attention, multi-modal learning},
issn = {3068-9287},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control
ISSN: 3068-9287 (Online) | ISSN: 3068-9279 (Print)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/