Abstract
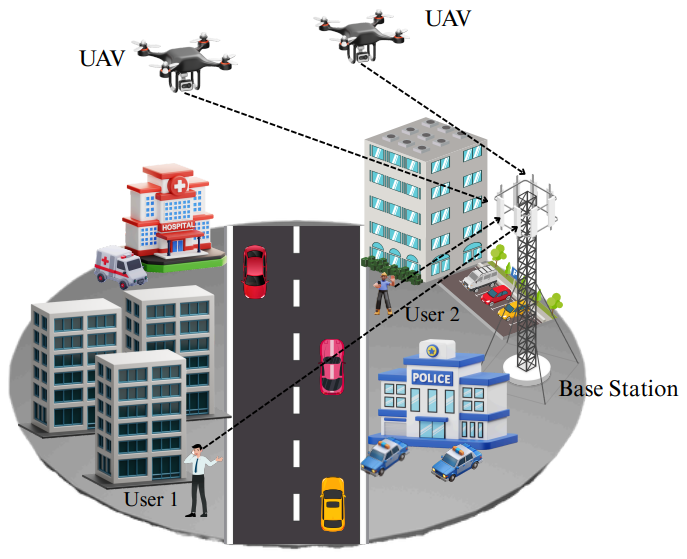
The work presents a joint design framework that combines an energy-efficient MIMO receiver architecture with an optimized power allocation strategy for spatial NOMA in miniature UAV-assisted IoT networks. Specifically, we design a low-power receiver using spatial modulation and intelligent transmit antenna selection to minimize energy usage. Simultaneously, a dynamic power allocation scheme is developed to ensure fairness by allowing all users to act as active data users in different time slots. The air-to-ground channel is modeled by considering UAV altitude, mobility, and probabilistic line-of-sight characteristics. Simulation results demonstrate that at a UAV altitude of 50 meters, the proposed method achieves a peak energy efficiency of approximately 7.8 bits/Joule, compared to 6.0 bits/Joule for traditional NOMA schemes. The system also maintains a target user data rate of 2 bits/s/Hz and performs optimally at a transmit power of 20 dBm and UAV velocity of 5 m/s. These results highlight the effectiveness of jointly optimizing receiver design, power control, and UAV parameters to achieve sustainable and high-performance communication in future 6G-enabled IoT networks.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Soni, L., & Taneja, A. (2025). Joint Design of Energy-Efficient MIMO Receiver and Power Allocation for Spatial NOMA in Miniature UAV-Assisted IoT Networks. ICCK Transactions on Wireless Networks, 1(1), 42–50. https://doi.org/10.62762/TWN.2025.484759
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions

Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 