Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Bioinformatics | Volume 1, Issue 2: 79-84, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/JAIB.2025.677230
Abstract
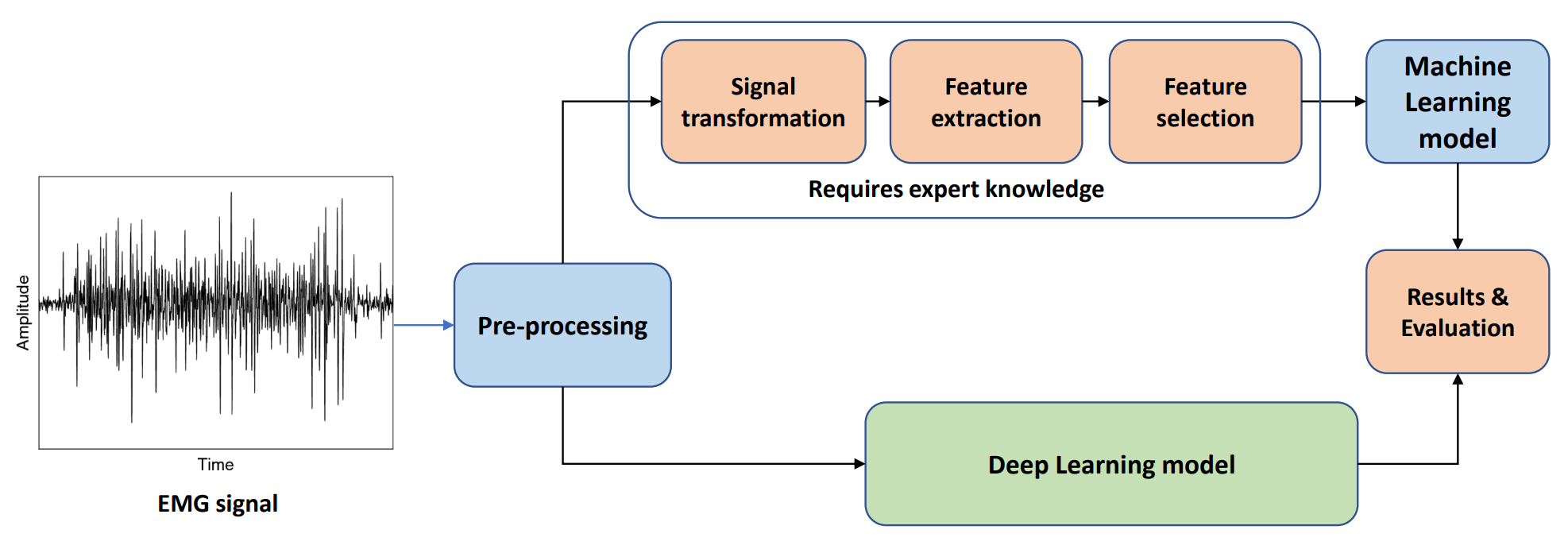
Electromyography (EMG) signals provide critical insights into neuromuscular function, yet their analysis remains challenging due to inherent noise, inter-subject variability, and non-stationary characteristics. Bio-inspired artificial intelligence (AI) models, drawing computational principles from biological neural systems, offer promising solutions to these challenges. This mini-review synthesizes recent advances in bio-inspired AI approaches for EMG signal processing, including spiking neural networks, hierarchical deep learning, attention mechanisms, and neuromorphic computing. We evaluate state-of-the-art methods, comparing their performance across key metrics including classification ac... More >
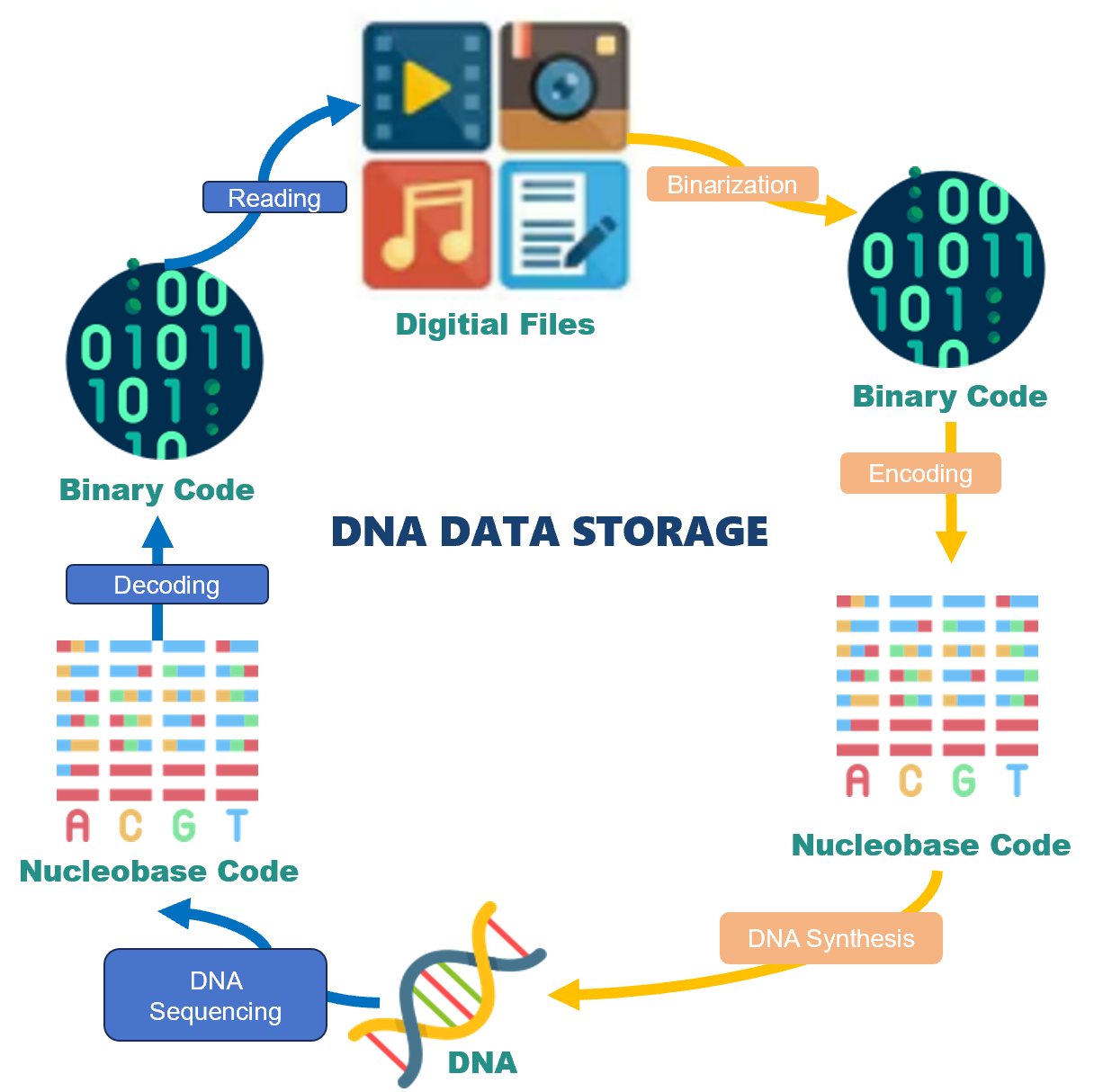
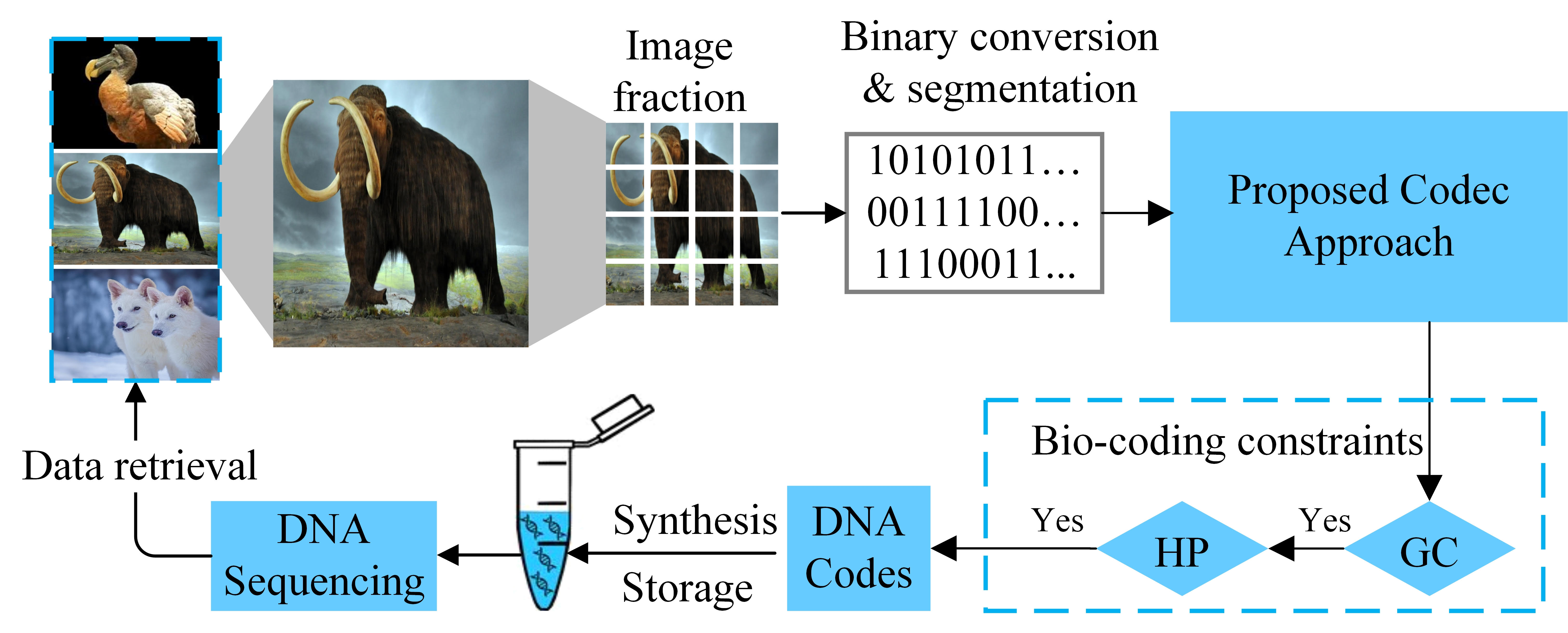
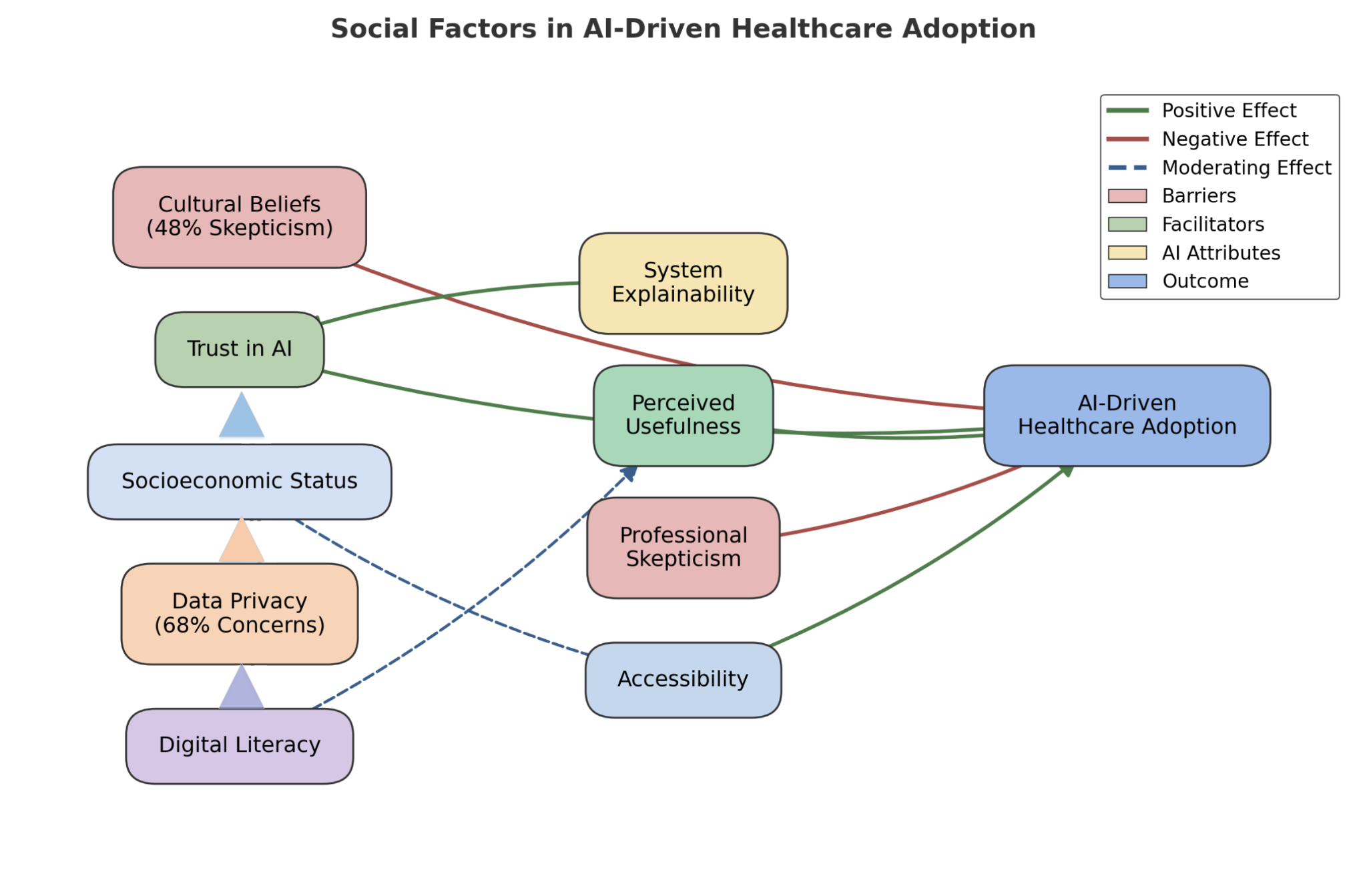
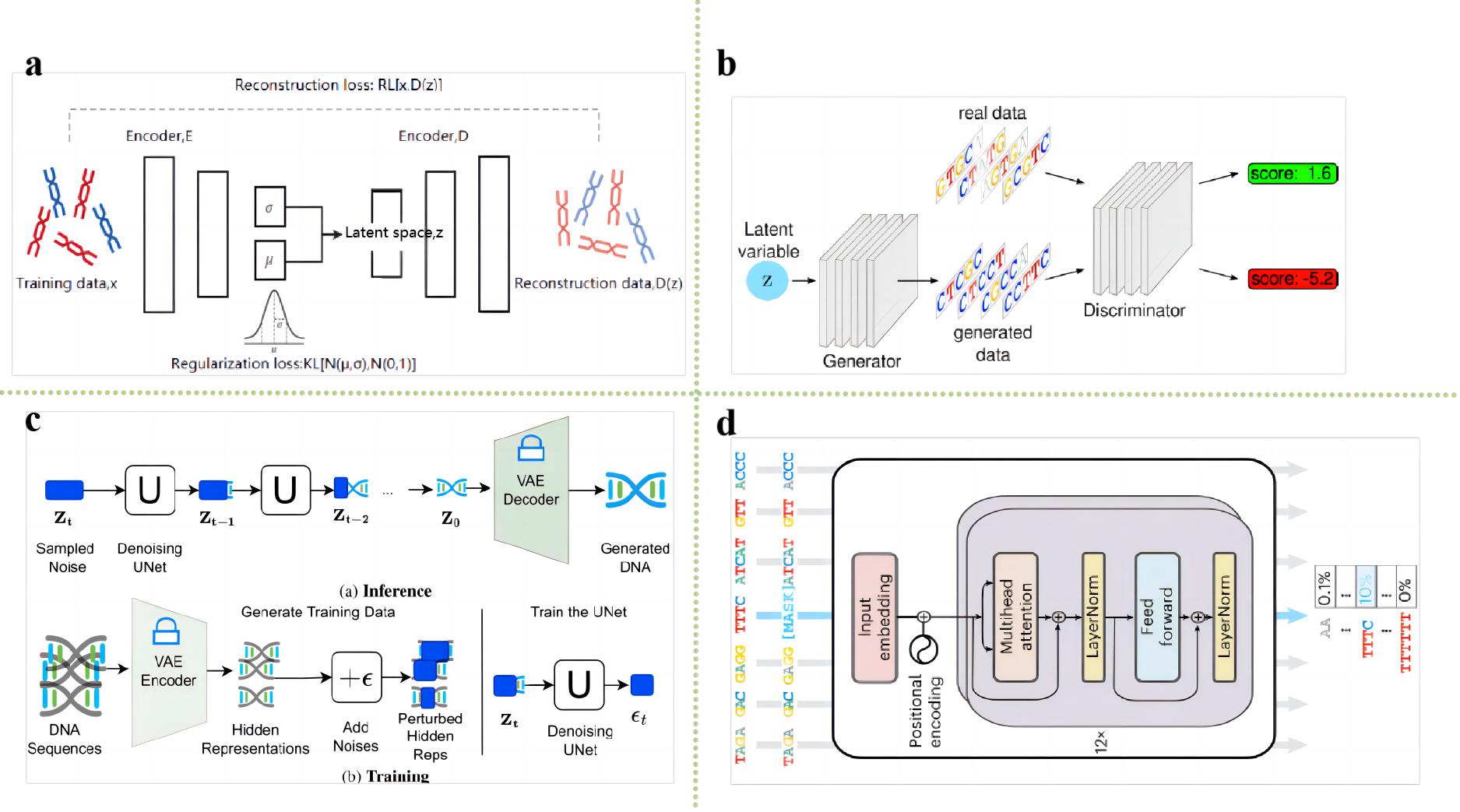
Graphical Abstract