Journal of Numerical Simulations in Physics and Mathematics | Volume 1, Issue 2: 84-97, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/JNSPM.2025.826101
Abstract
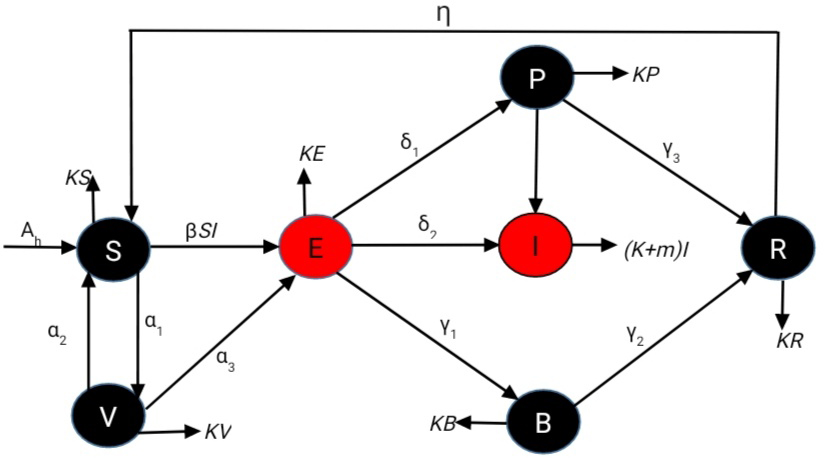
Rabies remains a serious public health concern, as dog bites account for the majority of human cases. In this study, we develop a comprehensive mathematical model to investigate the dynamics of rabies transmission by incorporating two key intervention strategies: an asymptotic class (\(P\)) and a booster vaccination class (\(B\)). The basic reproduction number (\(R_0\)) is derived as a threshold parameter that governs whether the disease spreads or dies out, based on a system of nonlinear differential equations. A sensitivity analysis of \(R_0\) is conducted to identify the most influential parameters affecting disease transmission. The results indicate that the transmission rate (\(\beta\))... More >
Graphical Abstract