Journal of Numerical Simulations in Physics and Mathematics
ISSN: 3068-9082 (Online) | ISSN: 3068-9074 (Print)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
TY - JOUR
AU - Zhang, Xuelin
PY - 2025
DA - 2025/12/08
TI - On the Convergence of Nonconcave-Nonconvex Max-Min Optimization Problem
JO - Journal of Numerical Simulations in Physics and Mathematics
T2 - Journal of Numerical Simulations in Physics and Mathematics
JF - Journal of Numerical Simulations in Physics and Mathematics
VL - 1
IS - 2
SP - 76
EP - 83
DO - 10.62762/JNSPM.2025.112121
UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JNSPM.2025.112121
KW - max-min optimization
KW - convergence guarantee
KW - nonconvex-nonconcave problems
KW - two-sided polyak-lojasiewicz
KW - quadratic growth
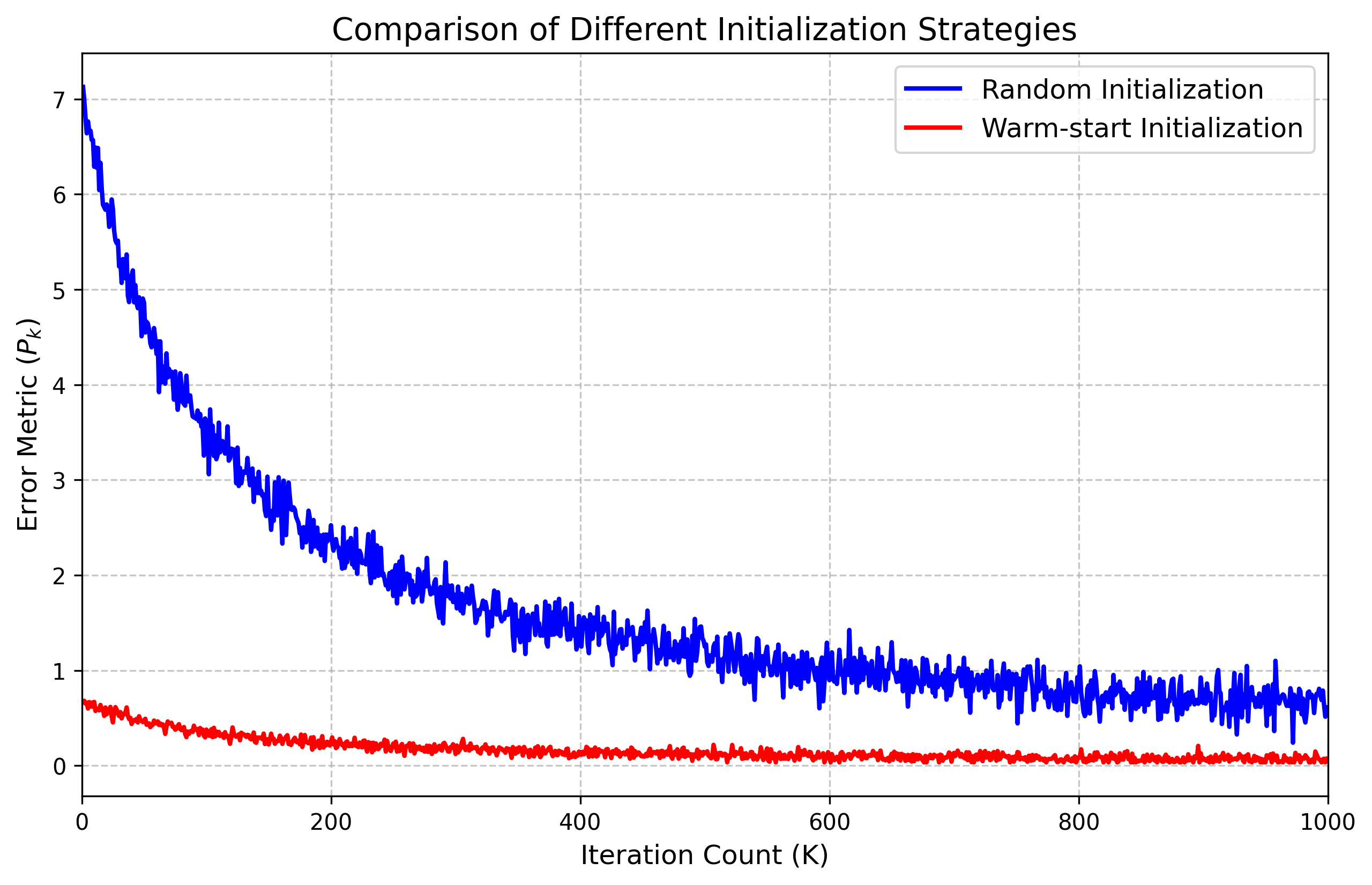
AB - Despite extensive study of max--min problems, convergence analysis for the challenging nonconvex--nonconcave setting remains limited. This paper addresses the convergence analysis of nonconvex--nonconcave max--min problems. A novel analytical framework is developed by employing carefully constructed auxiliary functions and leveraging two-sided Polyak--Łojasiewicz (PL) and Quadratic Growth (QG) conditions to characterize the convergence behavior. Under these conditions, it is shown that the Stochastic Alternating Gradient Descent Ascent (SAGDA) algorithm achieves a convergence rate of $\mathcal{O}\left(1/K\right)$, where $K$ denotes the number of iterations. Notably, this result matches convergence rates typically obtained in (weakly) convex--concave minimax settings while requiring significantly milder geometric assumptions. The theoretical results are further validated through empirical experiments on realistic examples.
SN - 3068-9082
PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge
LA - English
ER -
@article{Zhang2025On,
author = {Xuelin Zhang},
title = {On the Convergence of Nonconcave-Nonconvex Max-Min Optimization Problem},
journal = {Journal of Numerical Simulations in Physics and Mathematics},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {2},
pages = {76-83},
doi = {10.62762/JNSPM.2025.112121},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JNSPM.2025.112121},
abstract = {Despite extensive study of max--min problems, convergence analysis for the challenging nonconvex--nonconcave setting remains limited. This paper addresses the convergence analysis of nonconvex--nonconcave max--min problems. A novel analytical framework is developed by employing carefully constructed auxiliary functions and leveraging two-sided Polyak--Łojasiewicz (PL) and Quadratic Growth (QG) conditions to characterize the convergence behavior. Under these conditions, it is shown that the Stochastic Alternating Gradient Descent Ascent (SAGDA) algorithm achieves a convergence rate of \$\mathcal{O}\left(1/K\right)\$, where \$K\$ denotes the number of iterations. Notably, this result matches convergence rates typically obtained in (weakly) convex--concave minimax settings while requiring significantly milder geometric assumptions. The theoretical results are further validated through empirical experiments on realistic examples.},
keywords = {max-min optimization, convergence guarantee, nonconvex-nonconcave problems, two-sided polyak-lojasiewicz, quadratic growth},
issn = {3068-9082},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. Journal of Numerical Simulations in Physics and Mathematics
ISSN: 3068-9082 (Online) | ISSN: 3068-9074 (Print)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/