ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems | Volume 1, Issue 4: 275-290, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/TACS.2025.395911
Abstract
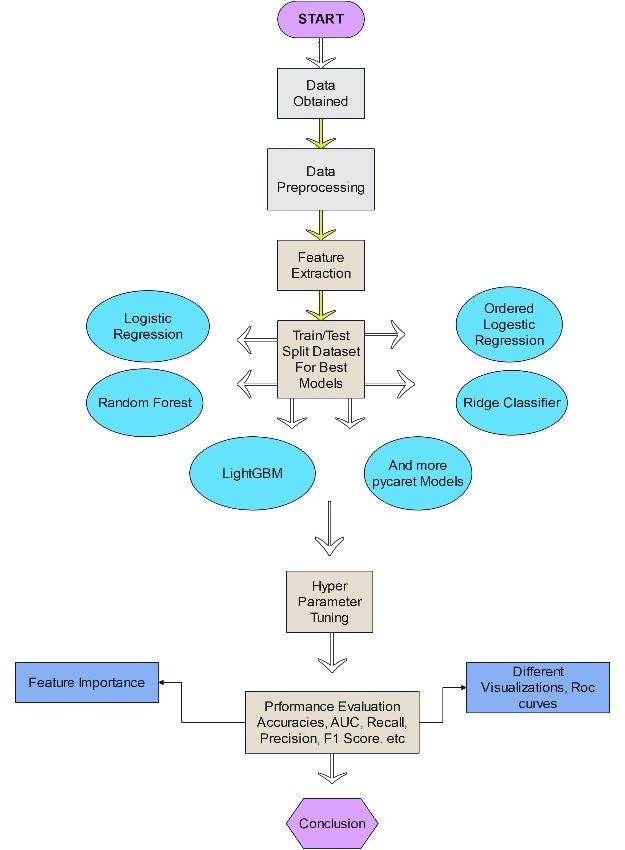
This paper examines the vulnerability of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) exposed to evolving climate changes in Pakistan, specifically the impacts of extreme weather events, including floods and drought. The earlier literature illustrates that SMEs are affected by climate-related risks, but the current study takes the discussion further by implementing machine learning algorithms to measure the vulnerabilities of SMEs more objectively. A mixed-methods design was used to combine surveys with machine-learning techniques. PyCaret was employed to tune instruments such as Logistic Regression (LR), Random Forest (RF), ordered logistic regression, LightGBM, ADA Boost, SVM, KNN, GBC, and N... More >
Graphical Abstract