Abstract
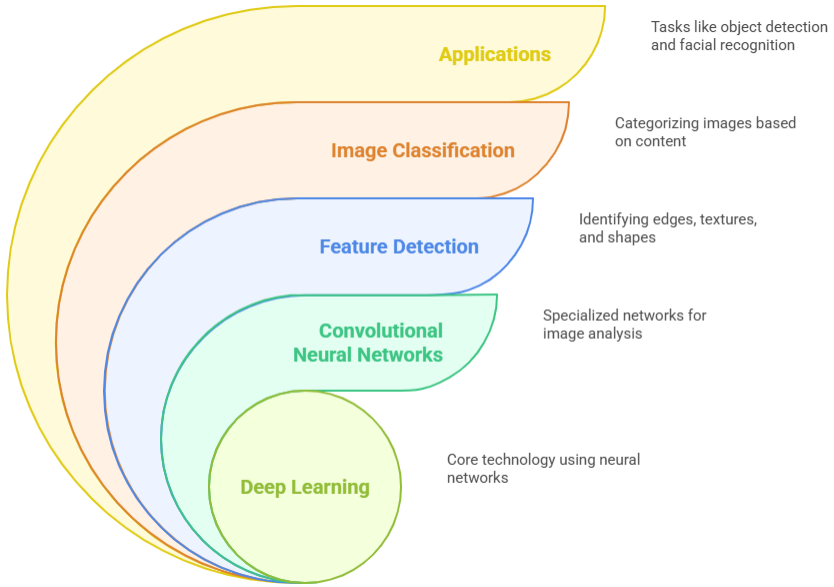
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become a critical tool for risk management across industries such as insurance, healthcare, business, and finance. It enables risk quantification, improves predictive accuracy, and supports decision-making in dynamic and uncertain environments. This paper examines models, methods, and frameworks for AI-based risk assessment, while addressing concerns of ethics, regulation, and explainability. Key technologies, including machine learning, deep learning, and reinforcement learning, are highlighted for their ability to transform traditional approaches by enhancing prediction, optimization, and decision processes. The second part focuses on AI-driven risk modeling techniques. Supervised learning methods such as support vector machines, random forests, and decision trees demonstrate strong predictive capacity from historical data. Unsupervised learning, including clustering methods, uncovers hidden patterns in risk datasets. Reinforcement learning is gaining prominence for adaptive risk optimization under changing conditions. Deep learning, particularly neural networks, offers significant improvements in handling large-scale data and achieving higher predictive accuracy. Finally, the paper outlines the future of AI in risk management, recognizing both its transformative potential and persistent challenges. With the rapid advancement of AI and increasing availability of big data, risk management practices are undergoing fundamental change. Yet, successful adoption requires careful attention to ethical, legal, and technological considerations. Organizations must continue to adapt to ensure that AI technologies are deployed transparently, responsibly, and to the benefit of enterprises and society as a whole.
Keywords
risk management
risk quantification
deep learning
artificial intelligence
NIST framework
proactive risk assessment
decision-making models
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Taj, S., Javed, M. D., Khan, R., Hassan, H., & Khan, Z. U. (2025). Quantifying Risk with AI: Models and Frameworks. ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems, 1(4), 222–237. https://doi.org/10.62762/TACS.2025.142506
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions

Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
