Abstract
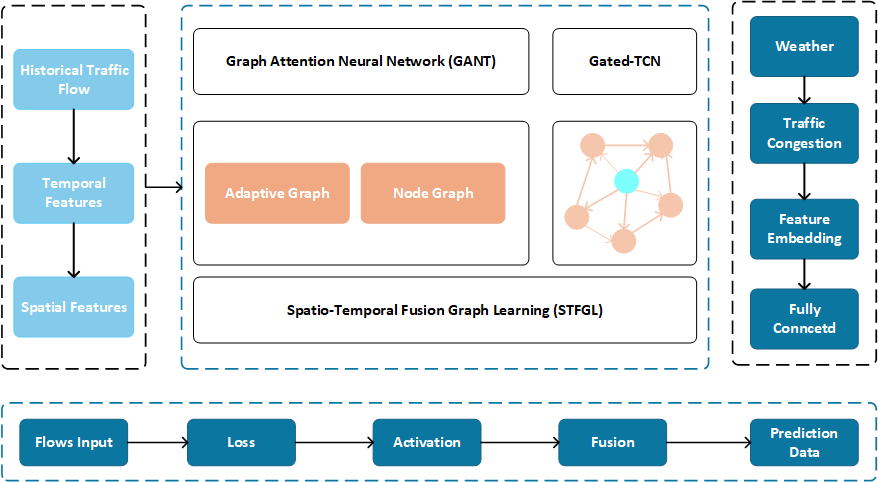
The rapid accumulation of large-scale, long-term meteorological data presents unprecedented opportunities for data-driven weather modeling and high-resolution numerical weather prediction. While various deep learning techniques—such as Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), and Graph Neural Networks (GNNs)—have been explored for weather forecasting, the complex spatial dependencies within historical meteorological data, particularly dynamic spatial correlations, remain insufficiently addressed. To tackle this challenge, we propose a Dynamic Spatio-Temporal Fusion Graph Network (DSTFGN), a novel module that integrates multivariate time-series analysis with graph-based causal inference to capture intricate and time-varying interdependencies among weather variables. The DSTFGN module fuses real-time inputs (e.g., sensor data, live weather feeds, external events) with historical records to model the propagation of disruptions—such as accidents or road closures—through the meteorological network. By effectively capturing dynamic spatial-temporal interactions, our approach significantly enhances forecasting accuracy and supports adaptive weather management strategies. Experimental evaluations on two real-world datasets demonstrate that DSTFGN consistently outperforms existing baseline models across short, medium, and long-term forecasting horizons.
Keywords
intelligent transportation systems
weather forecasting
causal graph learning
spatio-temporal attention
GCN
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62373255; in part by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province under Grant 2024A1515011204; in part by the Shenzhen Natural Science Fund through the Stable Support Plan Program under Grant 20220809175803001; in part by the Open Fund of National Engineering Laboratory for Big Data System Computing Technology under Grant SZU-BDSC-OF2024-15.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Ali, A., Naeem, H. M. Y., Ali, R., Asad, M., Heyat, M. B. B., & Alsarhan, T. (2025). An Efficient Algorithm for Weather Forecasting Using Causal Graph Neural Network. ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems, 1(4), 258–274. https://doi.org/10.62762/TACS.2025.619794
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions

Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
