ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems | Volume 1, Issue 3: 180-192, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/TACS.2025.952297
Abstract
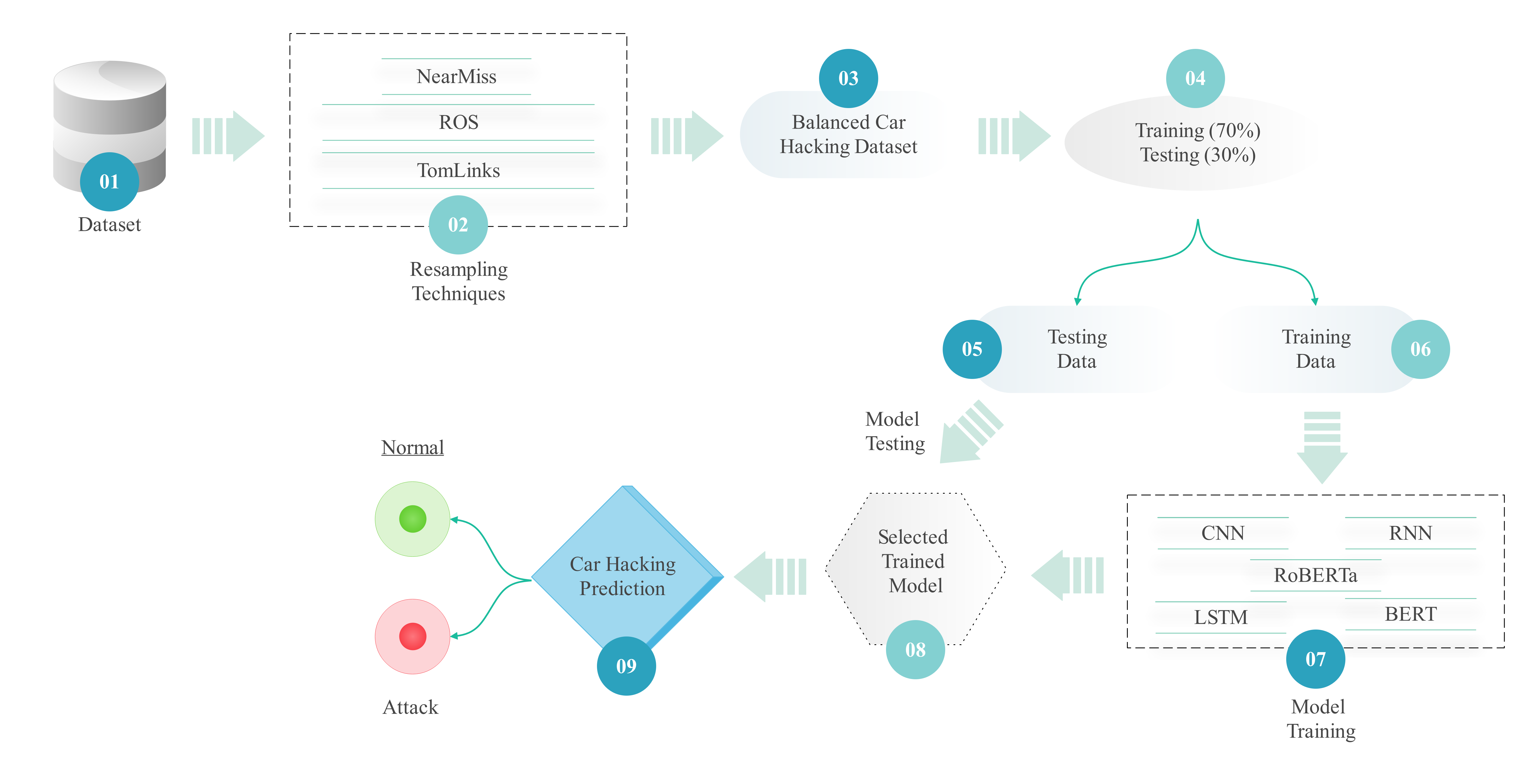
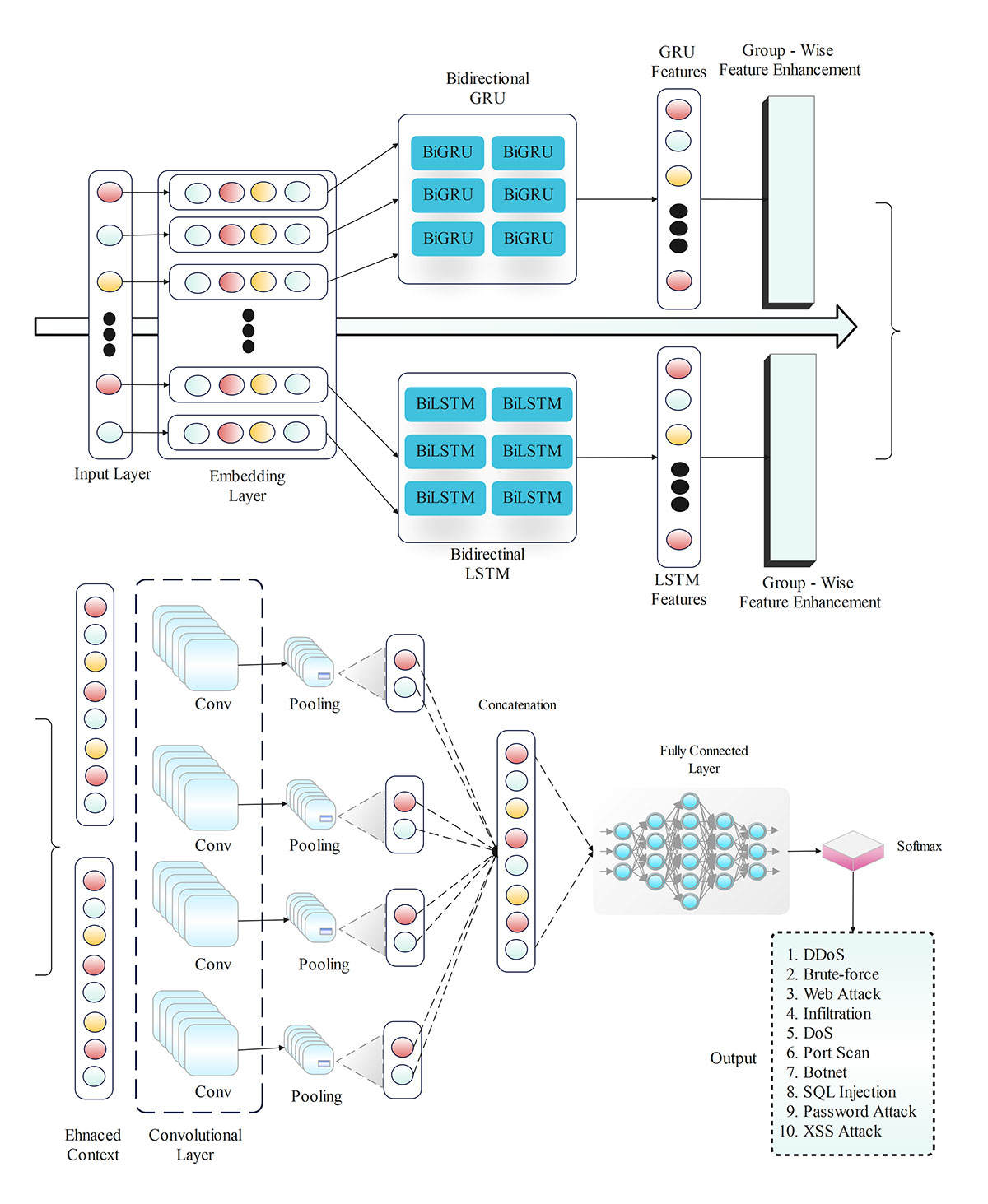
The Internet of Vehicles (IoV) has greatly influenced transportation by allowing autonomous vehicles to interact and communicate with other cars as well as with the surrounding traffic system. Even so, being interconnected comes with risks in terms of cyber attacks, for example, by injecting messages or fooling sensors through CAN systems. The study, consequently, suggests an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) that uses Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), and RoBERTa, to properly detect and handle these cyber threats. To solve the problem of unbalanced data, we use R... More >
Graphical Abstract