Aerospace Engineering Communications
ISSN: pending (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
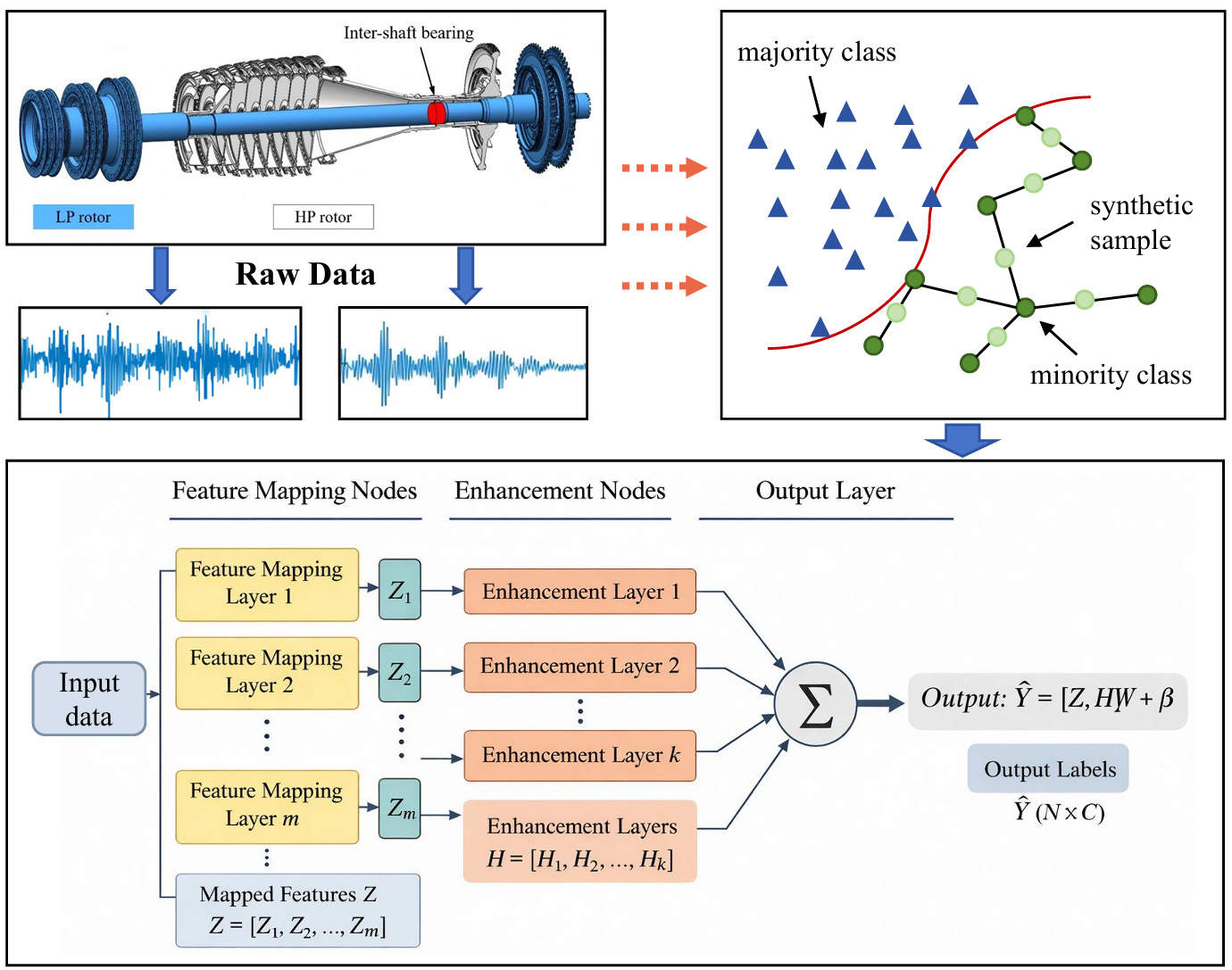
TY - JOUR AU - Gao, Yang AU - Dong, Jingjing PY - 2026 DA - 2026/02/19 TI - Robust Imbalanced Learning for Aero-Engine Bearing Anomaly Detection via a Hybrid SMOTE-BLS Framework JO - Aerospace Engineering Communications T2 - Aerospace Engineering Communications JF - Aerospace Engineering Communications VL - 1 IS - 1 SP - 47 EP - 56 DO - 10.62762/AEC.2026.599020 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/AEC.2026.599020 KW - aircraft engine KW - fault diagnosis KW - imbalance learning KW - broad learning system AB - The operational reliability of aeroengines is vital to civil aviation safety; however, bearings and other key components are prone to failure under harsh operating conditions. In real-world monitoring data, severe class imbalance often leads conventional fault diagnosis methods to be biased toward majority classes, limiting their ability to identify critical faults. To address this issue, this paper proposes a robust anomaly detection framework that integrates the Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE) with a Broad Learning System (BLS). SMOTE is first applied to generate synthetic fault samples in the feature space, thereby balancing the data distribution and reducing bias. The balanced data are then fed into a BLS classifier, which exploits its flat architecture to achieve high-dimensional feature representation and fast non-iterative training. Experimental results on multiple aeroengine bearing datasets demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms comparative approaches in terms of fault detection accuracy and robustness. SN - pending PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Gao2026Robust,
author = {Yang Gao and Jingjing Dong},
title = {Robust Imbalanced Learning for Aero-Engine Bearing Anomaly Detection via a Hybrid SMOTE-BLS Framework},
journal = {Aerospace Engineering Communications},
year = {2026},
volume = {1},
number = {1},
pages = {47-56},
doi = {10.62762/AEC.2026.599020},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/AEC.2026.599020},
abstract = {The operational reliability of aeroengines is vital to civil aviation safety; however, bearings and other key components are prone to failure under harsh operating conditions. In real-world monitoring data, severe class imbalance often leads conventional fault diagnosis methods to be biased toward majority classes, limiting their ability to identify critical faults. To address this issue, this paper proposes a robust anomaly detection framework that integrates the Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE) with a Broad Learning System (BLS). SMOTE is first applied to generate synthetic fault samples in the feature space, thereby balancing the data distribution and reducing bias. The balanced data are then fed into a BLS classifier, which exploits its flat architecture to achieve high-dimensional feature representation and fast non-iterative training. Experimental results on multiple aeroengine bearing datasets demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms comparative approaches in terms of fault detection accuracy and robustness.},
keywords = {aircraft engine, fault diagnosis, imbalance learning, broad learning system},
issn = {pending},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/