ICCK Journal of Applied Mathematics
ISSN: 3068-5656 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
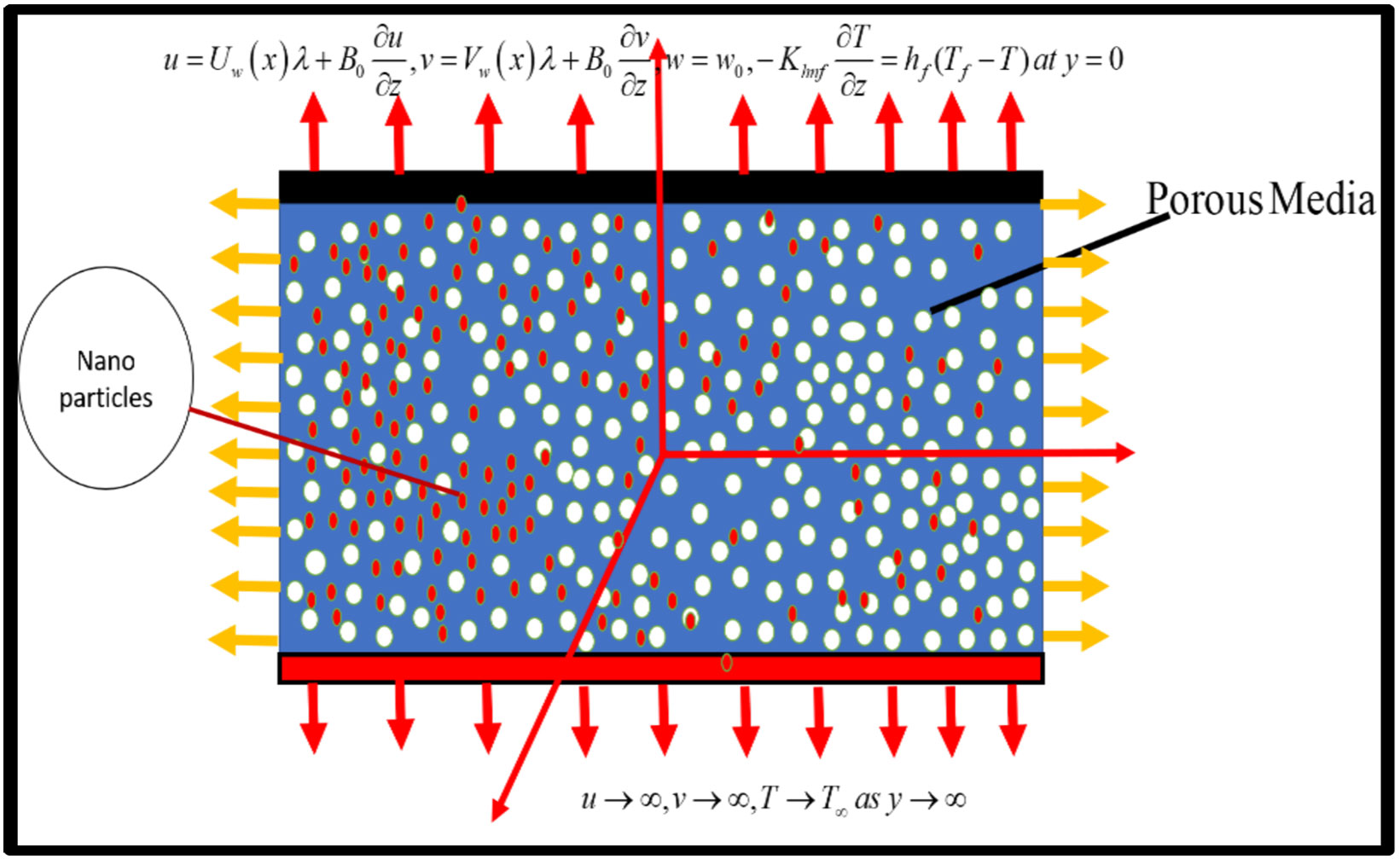
TY - JOUR AU - Ahmad, Waqas PY - 2026 DA - 2026/01/17 TI - Influence of Darcy-Forchheimer Effects on 3D MHD Rotating Flow of Casson Hybrid Nanofluid with Velocity Slip and Convective Boundary Conditions JO - ICCK Journal of Applied Mathematics T2 - ICCK Journal of Applied Mathematics JF - ICCK Journal of Applied Mathematics VL - 2 IS - 1 SP - 44 EP - 63 DO - 10.62762/JAM.2025.945696 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JAM.2025.945696 KW - hybrid nanofluids KW - casson fluid KW - MHD KW - velocity slip KW - Joule heating KW - darcy-forchheimer AB - In order to improve heat transfer efficiency, it is essential to examine that MHD hybrid nanofluid flows behave under convective and slip boundary conditions. Researchers have looked at a variety of factors when adding hybrid nanofluids to these flows, including Forchheimer number, radiation, magnetic fields, Biot number, and the Joule heating. The novelty of the current study lies in investigating the consequences of Casson fluid in the Darcy Forchheimer flow of a three-dimensional rotating hybrid nanofluid, which have not been thoroughly covered in the literature. This includes combinations of heat sources/sinks, magnetic parameters, and radiation absorption as well as convective conditions, slip boundary conditions, and Joule heating. By shedding light on these specific components, this endeavor seeks to bridge this knowledge gap. Hybrid nanofluids disperse two distinct nanoparticles in a fluid to increase heat conductivity for industrial purposes. The bvp5c approach may be used to, after converting non-linear PDEs into non-linear ODEs with similarity variables. The velocity pattern falls with increasing magnetic, suction, and slip parameters, however the sheet temperature profile rises with increasing Eckert and radiative values. The research discovered that a stretched sheet's temperature increases with a larger magnetic field, whereas a shrinking sheet has the reverse effect. Detailed explanations of the numerical data accompanying the skin friction coefficient and local Nusselt number graphs for various parameter values are provided. This work uses a new non-Newtonian three-dimensional model that offers more authentic and precise visualizations of heat transport and fluid movement than traditional two-dimensional simulations. This study, in contrast to other studies, considers the dispersion of Hybrid nanofluid, three-dimensional flow, and water as the regular fluid. SN - 3068-5656 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Ahmad2026Influence,
author = {Waqas Ahmad},
title = {Influence of Darcy-Forchheimer Effects on 3D MHD Rotating Flow of Casson Hybrid Nanofluid with Velocity Slip and Convective Boundary Conditions},
journal = {ICCK Journal of Applied Mathematics},
year = {2026},
volume = {2},
number = {1},
pages = {44-63},
doi = {10.62762/JAM.2025.945696},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JAM.2025.945696},
abstract = {In order to improve heat transfer efficiency, it is essential to examine that MHD hybrid nanofluid flows behave under convective and slip boundary conditions. Researchers have looked at a variety of factors when adding hybrid nanofluids to these flows, including Forchheimer number, radiation, magnetic fields, Biot number, and the Joule heating. The novelty of the current study lies in investigating the consequences of Casson fluid in the Darcy Forchheimer flow of a three-dimensional rotating hybrid nanofluid, which have not been thoroughly covered in the literature. This includes combinations of heat sources/sinks, magnetic parameters, and radiation absorption as well as convective conditions, slip boundary conditions, and Joule heating. By shedding light on these specific components, this endeavor seeks to bridge this knowledge gap. Hybrid nanofluids disperse two distinct nanoparticles in a fluid to increase heat conductivity for industrial purposes. The bvp5c approach may be used to, after converting non-linear PDEs into non-linear ODEs with similarity variables. The velocity pattern falls with increasing magnetic, suction, and slip parameters, however the sheet temperature profile rises with increasing Eckert and radiative values. The research discovered that a stretched sheet's temperature increases with a larger magnetic field, whereas a shrinking sheet has the reverse effect. Detailed explanations of the numerical data accompanying the skin friction coefficient and local Nusselt number graphs for various parameter values are provided. This work uses a new non-Newtonian three-dimensional model that offers more authentic and precise visualizations of heat transport and fluid movement than traditional two-dimensional simulations. This study, in contrast to other studies, considers the dispersion of Hybrid nanofluid, three-dimensional flow, and water as the regular fluid.},
keywords = {hybrid nanofluids, casson fluid, MHD, velocity slip, Joule heating, darcy-forchheimer},
issn = {3068-5656},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/