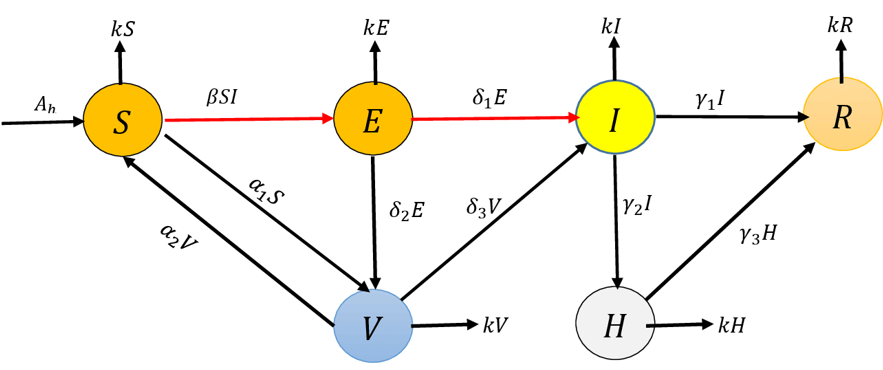
ICCK Journal of Applied Mathematics | Volume 2, Issue 1: 87-110, 2026 | DOI: 10.62762/JAM.2026.213905
Abstract
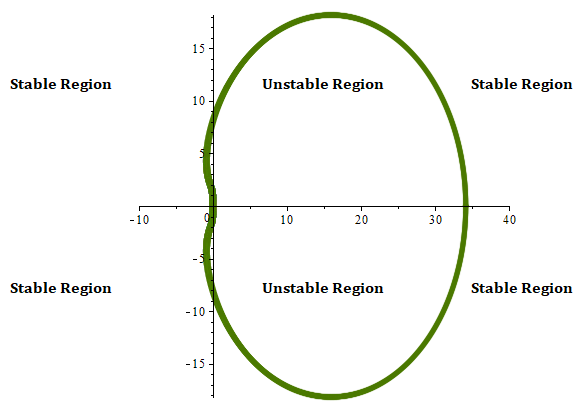
In this paper, we present a modified three-point superclass of Block Backward Differentiation Formula (BBDF) for the efficient numerical solution of stiff systems of ordinary differential equations (ODEs). The principal enhancement of this work is a structural modification of the classical BBDF that forms a new parameterized superclass of methods, leading to improved stability and reduced error constants compared with the standard three-point BBDFs. The proposed scheme is formulated as a fully implicit block method capable of simultaneously producing three solution approximations within each integration step. A detailed theoretical analysis is conducted to establish the order of accuracy, co... More >
Graphical Abstract