Journal of Geo-Energy and Environment
ISSN: 3069-3268 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
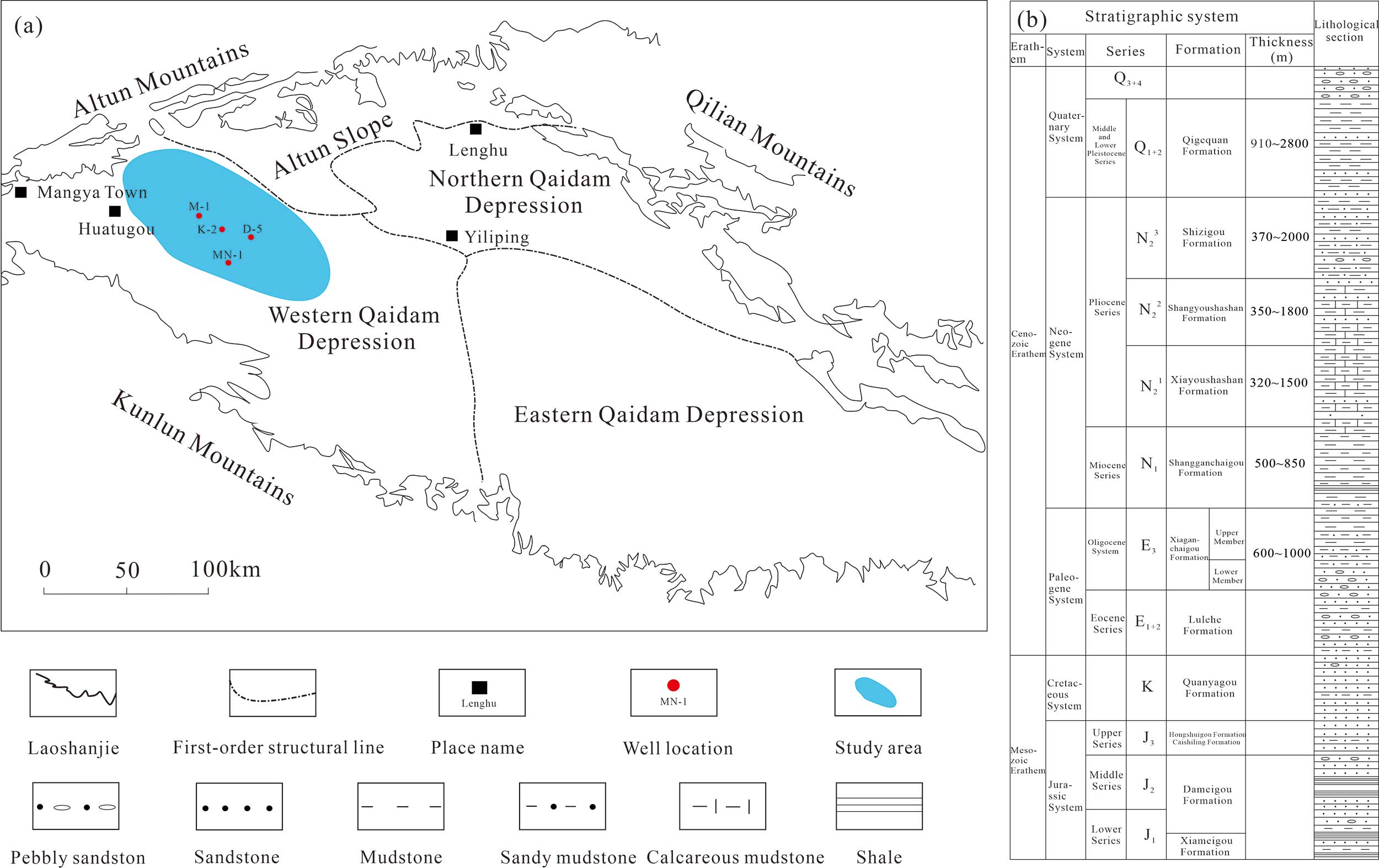
TY - JOUR AU - Shi, Shiling AU - Shan, Changan AU - Zhao, Ze AU - Fei, Yue AU - Zhang, Jiaqi PY - 2026 DA - 2026/02/08 TI - Organic Geochemical Characteristics and Thermal Evolution Characteristics of Paleogene to Neogene Source Rocks in Mangai Area, Qaidam Basin JO - Journal of Geo-Energy and Environment T2 - Journal of Geo-Energy and Environment JF - Journal of Geo-Energy and Environment VL - 2 IS - 1 SP - 56 EP - 72 DO - 10.62762/JGEE.2025.781750 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JGEE.2025.781750 KW - qaidam basin KW - mangai area KW - thermal evolution KW - paleogene to neogene KW - hydrocarbon source rocks AB - The Paleogene-Neogene lacustrine source rocks in the Mangai area of the Qaidam Basin are significant exploration targets. A comprehensive evaluation of four major intervals (E$_3^2$, N$_1$, N$_2^1$, N$_2^2$) was conducted through systematic organic geochemistry, maceral identification, thermal maturity analysis, and burial-thermal history modeling. Results show TOC contents of 0.203~1.28% (avg. 0.74%), chloroform bitumen "A" of 0.0164~0.2495% (avg. 0.132%), and total hydrocarbon contents of 69.29~1637.48 $\mu$g/g (avg. 853.39 $\mu$g/g), indicating fair to good quality. Kerogen elemental analysis (H/C=0.97~1.21), maceral composition (sapropelinite+exinite=70~98%), and saturated hydrocarbon chromatography (dominant peaks at C17, C19, C21, C23) collectively indicate predominantly Type II$_1$ organic matter, with locally developed Type I. Thermal evolution exhibits distinct vertical zonation controlled by Neogene tectonic-thermal events: an immature-low maturity zone (R$_0$1.0%) characterized by gas generation via cracking. The saline to semi-saline reducing environment favored organic matter preservation, while mixed algal-terrestrial inputs (Type II$_1$) determined mainly oil-prone characteristics. The thick succession in the central depression, especially the Kaitemilike-Fenghuangtai region, shows the highest hydrocarbon potential. The mature zone (R$_0$=0.7~1.0%) is optimal for conventional oil exploration, while the high maturity zone (R$_0$>1.0%) holds promise for natural gas. This multi-parameter study deepens the understanding of hydrocarbon generation mechanisms and provides an important case for evaluating Paleogene-Neogene lacustrine source rocks in the northern Tibetan Plateau. SN - 3069-3268 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Shi2026Organic,
author = {Shiling Shi and Changan Shan and Ze Zhao and Yue Fei and Jiaqi Zhang},
title = {Organic Geochemical Characteristics and Thermal Evolution Characteristics of Paleogene to Neogene Source Rocks in Mangai Area, Qaidam Basin},
journal = {Journal of Geo-Energy and Environment},
year = {2026},
volume = {2},
number = {1},
pages = {56-72},
doi = {10.62762/JGEE.2025.781750},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JGEE.2025.781750},
abstract = {The Paleogene-Neogene lacustrine source rocks in the Mangai area of the Qaidam Basin are significant exploration targets. A comprehensive evaluation of four major intervals (E\$\_3^2\$, N\$\_1\$, N\$\_2^1\$, N\$\_2^2\$) was conducted through systematic organic geochemistry, maceral identification, thermal maturity analysis, and burial-thermal history modeling. Results show TOC contents of 0.203~1.28\% (avg. 0.74\%), chloroform bitumen "A" of 0.0164~0.2495\% (avg. 0.132\%), and total hydrocarbon contents of 69.29~1637.48 \$\mu\$g/g (avg. 853.39 \$\mu\$g/g), indicating fair to good quality. Kerogen elemental analysis (H/C=0.97~1.21), maceral composition (sapropelinite+exinite=70~98\%), and saturated hydrocarbon chromatography (dominant peaks at C17, C19, C21, C23) collectively indicate predominantly Type II\$\_1\$ organic matter, with locally developed Type I. Thermal evolution exhibits distinct vertical zonation controlled by Neogene tectonic-thermal events: an immature-low maturity zone (R\$\_0\$1.0\%) characterized by gas generation via cracking. The saline to semi-saline reducing environment favored organic matter preservation, while mixed algal-terrestrial inputs (Type II\$\_1\$) determined mainly oil-prone characteristics. The thick succession in the central depression, especially the Kaitemilike-Fenghuangtai region, shows the highest hydrocarbon potential. The mature zone (R\$\_0\$=0.7~1.0\%) is optimal for conventional oil exploration, while the high maturity zone (R\$\_0\$>1.0\%) holds promise for natural gas. This multi-parameter study deepens the understanding of hydrocarbon generation mechanisms and provides an important case for evaluating Paleogene-Neogene lacustrine source rocks in the northern Tibetan Plateau.},
keywords = {qaidam basin, mangai area, thermal evolution, paleogene to neogene, hydrocarbon source rocks},
issn = {3069-3268},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/