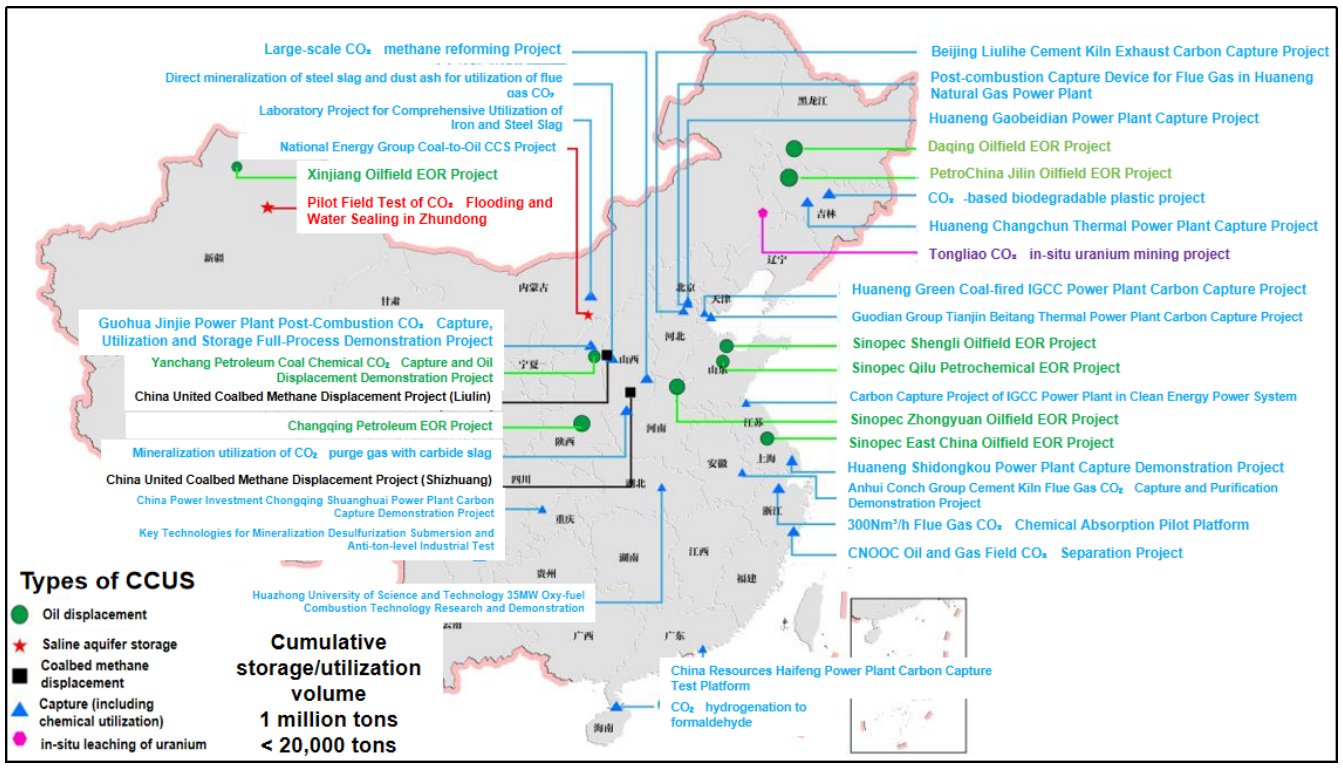
Journal of Geo-Energy and Environment | Volume 2, Issue 1: 1-33, 2026 | DOI: 10.62762/JGEE.2025.372522
Abstract
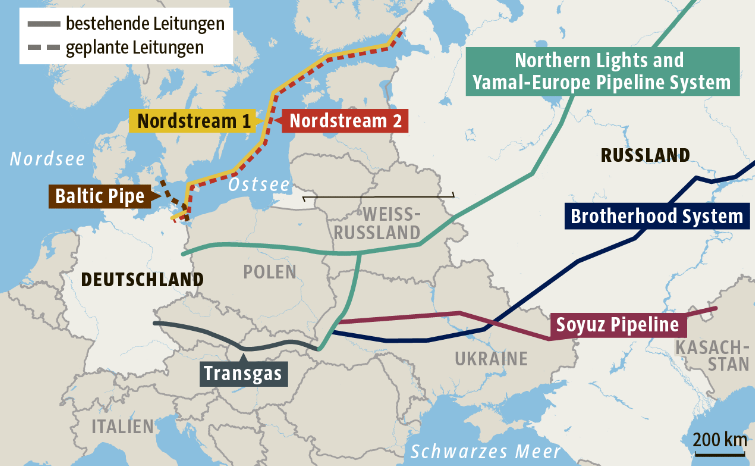
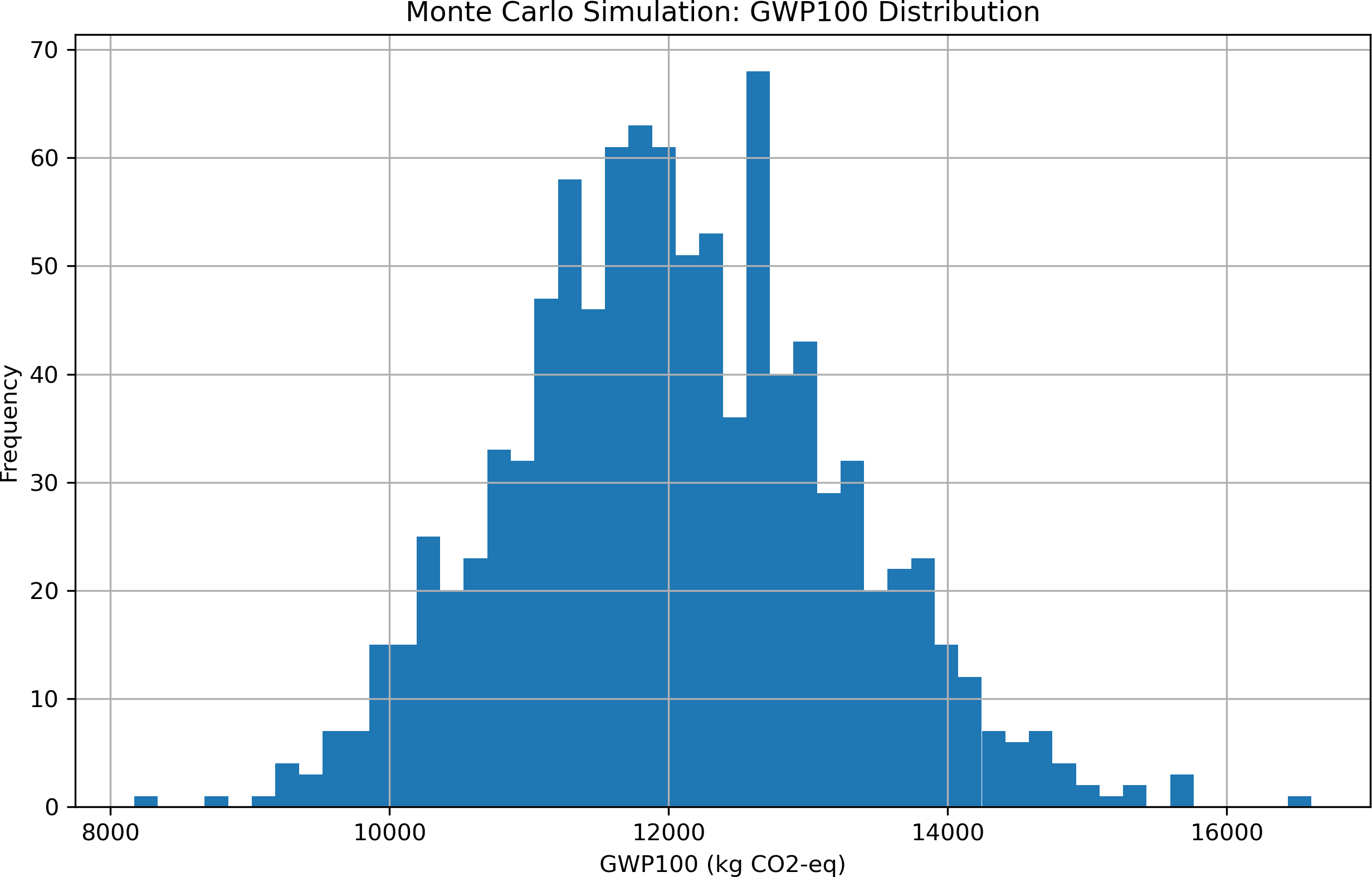
The Africa-Atlantic Gas Pipeline (AAGP), also known as the Nigeria-Morocco Gas Pipeline, is a major transcontinental infrastructure project poised to connect West African gas reserves with North African networks and European markets, potentially reshaping regional energy dynamics, boosting economic development, and enhancing energy security. Its strategic importance has grown amid Europe’s urgent need to diversify away from Russian gas imports and Africa’s dual challenge of resource-based development and sustainable local energy access. Despite increasing interest, there is a lack of integrated, quantitative evaluation of competing gas transit strategies considering technical, economic,... More >
Graphical Abstract