Journal of Geo-Energy and Environment
ISSN: 3069-3268 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
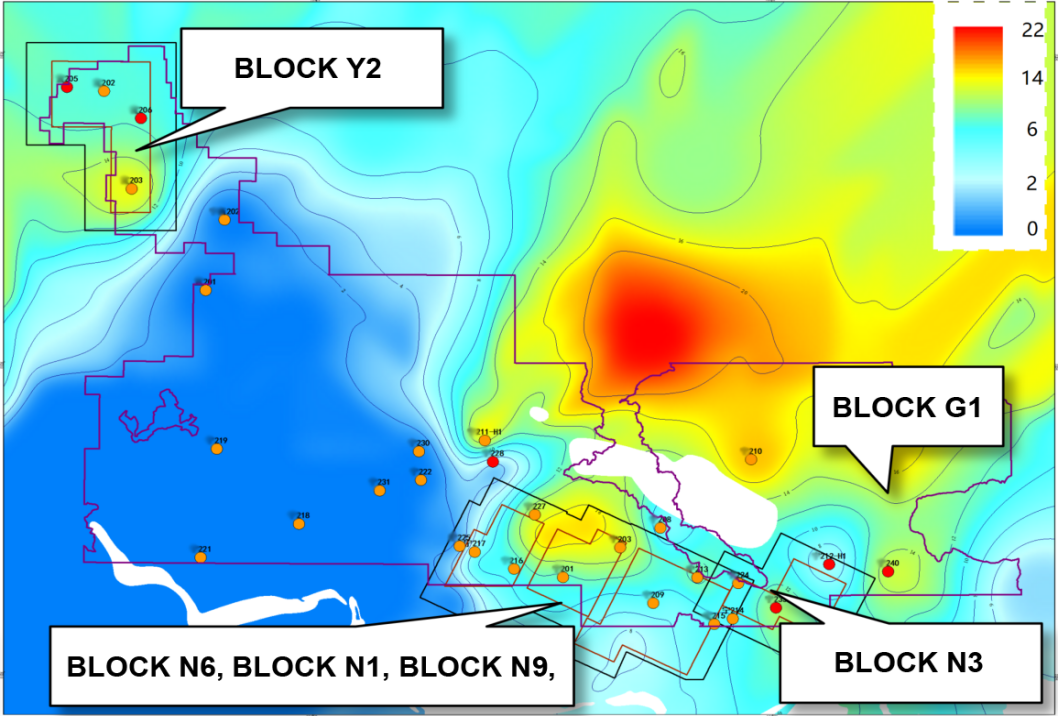
TY - JOUR AU - Ma, Geli AU - Huang, Rong AU - Dong, Yichen AU - Lv, Chao AU - Lin, Wenjing PY - 2026 DA - 2026/02/04 TI - A High-Accuracy Cost Prediction Model for Shale Gas Drilling in Southern Sichuan Using PCA and BP Neural Network JO - Journal of Geo-Energy and Environment T2 - Journal of Geo-Energy and Environment JF - Journal of Geo-Energy and Environment VL - 2 IS - 1 SP - 46 EP - 55 DO - 10.62762/JGEE.2026.416866 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JGEE.2026.416866 KW - shale gas KW - principal component analysis KW - drilling cost prediction KW - BP neural network KW - software system AB - Shale gas, as a typical low-quality marginal hydrocarbon resource, faces persistently high drilling costs, which have become one of the main bottlenecks restricting its large-scale development. The Southern Sichuan region of China holds enormous shale gas reserves and is a strategically important area for achieving cost-effective large-scale development. However, as production capacity construction intensifies and the volume of investment and cost data increases, traditional data processing methods can no longer meet the timeliness and accuracy requirements for handling massive data. Accurate prediction of oil and gas drilling costs will help in making scientific decisions and evaluations. In this study, based on the costs and engineering parameters of settled wells in the Southern Sichuan Block N shale gas field, we established a Back-Propagation (BP) neural network model incorporating principal component analysis (PCA) to achieve accurate prediction of single-well drilling costs. Results show that: (1) PCA can effectively extract useful information from the shale gas drilling cost influence factors. Specifically, the number of fracturing stages, drilling duration, well depth, total proppant volume, horizontal section length, etc., are identified as key parameters affecting single-well drilling cost. (2) Using Matlab programming and a graphical user interface (GUI), we developed an integrated shale gas single-well cost prediction software system that combines data import, model training, cost prediction, and results export. The BP neural network model’s predictions achieved an average relative error of only -0.57\%, demonstrating convenience, practicality, and high accuracy. This system can provide a basis for investment decision-making in the Southern Sichuan shale gas block and has value for commercial application. SN - 3069-3268 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Ma2026A,
author = {Geli Ma and Rong Huang and Yichen Dong and Chao Lv and Wenjing Lin},
title = {A High-Accuracy Cost Prediction Model for Shale Gas Drilling in Southern Sichuan Using PCA and BP Neural Network},
journal = {Journal of Geo-Energy and Environment},
year = {2026},
volume = {2},
number = {1},
pages = {46-55},
doi = {10.62762/JGEE.2026.416866},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JGEE.2026.416866},
abstract = {Shale gas, as a typical low-quality marginal hydrocarbon resource, faces persistently high drilling costs, which have become one of the main bottlenecks restricting its large-scale development. The Southern Sichuan region of China holds enormous shale gas reserves and is a strategically important area for achieving cost-effective large-scale development. However, as production capacity construction intensifies and the volume of investment and cost data increases, traditional data processing methods can no longer meet the timeliness and accuracy requirements for handling massive data. Accurate prediction of oil and gas drilling costs will help in making scientific decisions and evaluations. In this study, based on the costs and engineering parameters of settled wells in the Southern Sichuan Block N shale gas field, we established a Back-Propagation (BP) neural network model incorporating principal component analysis (PCA) to achieve accurate prediction of single-well drilling costs. Results show that: (1) PCA can effectively extract useful information from the shale gas drilling cost influence factors. Specifically, the number of fracturing stages, drilling duration, well depth, total proppant volume, horizontal section length, etc., are identified as key parameters affecting single-well drilling cost. (2) Using Matlab programming and a graphical user interface (GUI), we developed an integrated shale gas single-well cost prediction software system that combines data import, model training, cost prediction, and results export. The BP neural network model’s predictions achieved an average relative error of only -0.57\\%, demonstrating convenience, practicality, and high accuracy. This system can provide a basis for investment decision-making in the Southern Sichuan shale gas block and has value for commercial application.},
keywords = {shale gas, principal component analysis, drilling cost prediction, BP neural network, software system},
issn = {3069-3268},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/