Journal of Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Applications
ISSN: pending (Online)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
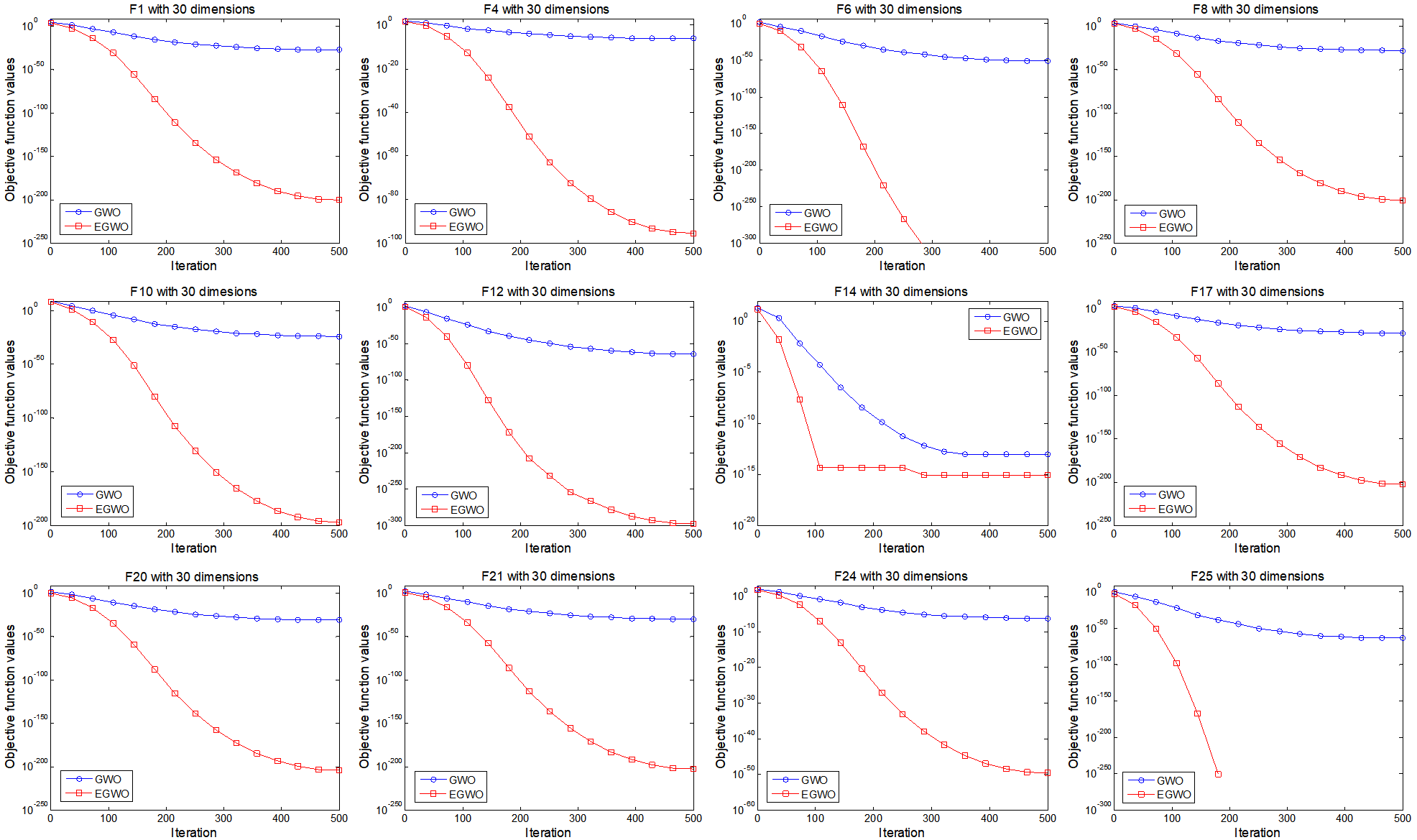
TY - JOUR AU - Xu, Wenmin AU - Long, Wen PY - 2025 DA - 2025/11/29 TI - Multi-strategy Enhanced Grey Wolf Optimizer for Numerical Optimization and Its Application to Feature Selection JO - Journal of Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Applications T2 - Journal of Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Applications JF - Journal of Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Applications VL - 1 IS - 1 SP - 51 EP - 71 DO - 10.62762/JMIA.2025.522565 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JMIA.2025.522565 KW - grey wolf optimizer KW - cuckoo search KW - numerical optimization KW - Engineering optimization KW - feature selection AB - Grey wolf optimizer (GWO) is an effective meta-heuristic technique which has been widely utilized to solve numerical optimization as well as real-world applications. However, GWO has some shortcomings, i.e., low solution accuracy, slow convergence, and easy stagnation at local optima in solving complex problems. To tackle these shortcomings, an enhanced GWO called EGWO is developed in this study. This enhancement is achieved by embedding three novel strategies into the basic GWO to improve its performance. Firstly, a new transition mechanism is designed instead of the original strategy to obtain a good transition from the exploration to exploitation. Secondly, the cuckoo search algorithm is introduced for the decision layer individuals ($\alpha$, $\beta$, and $\delta$) to further improve the local search capability. Thirdly, an adaptive position search equation is proposed by using a dynamical parameter to generate new potential candidate position. The effectiveness of EGWO is verified on 25 classical benchmarks, three engineering problems, and 16 feature selection problems. The results show that EGWO performs better than the original GWO and other meta-heuristic methods in terms of solution accuracy and convergence speed. SN - pending PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Xu2025Multistrat,
author = {Wenmin Xu and Wen Long},
title = {Multi-strategy Enhanced Grey Wolf Optimizer for Numerical Optimization and Its Application to Feature Selection},
journal = {Journal of Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Applications},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {1},
pages = {51-71},
doi = {10.62762/JMIA.2025.522565},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JMIA.2025.522565},
abstract = {Grey wolf optimizer (GWO) is an effective meta-heuristic technique which has been widely utilized to solve numerical optimization as well as real-world applications. However, GWO has some shortcomings, i.e., low solution accuracy, slow convergence, and easy stagnation at local optima in solving complex problems. To tackle these shortcomings, an enhanced GWO called EGWO is developed in this study. This enhancement is achieved by embedding three novel strategies into the basic GWO to improve its performance. Firstly, a new transition mechanism is designed instead of the original strategy to obtain a good transition from the exploration to exploitation. Secondly, the cuckoo search algorithm is introduced for the decision layer individuals (\$\alpha\$, \$\beta\$, and \$\delta\$) to further improve the local search capability. Thirdly, an adaptive position search equation is proposed by using a dynamical parameter to generate new potential candidate position. The effectiveness of EGWO is verified on 25 classical benchmarks, three engineering problems, and 16 feature selection problems. The results show that EGWO performs better than the original GWO and other meta-heuristic methods in terms of solution accuracy and convergence speed.},
keywords = {grey wolf optimizer, cuckoo search, numerical optimization, Engineering optimization, feature selection},
issn = {pending},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. Journal of Mathematics and Interdisciplinary Applications
ISSN: pending (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/