ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems
ISSN: 3068-7969 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
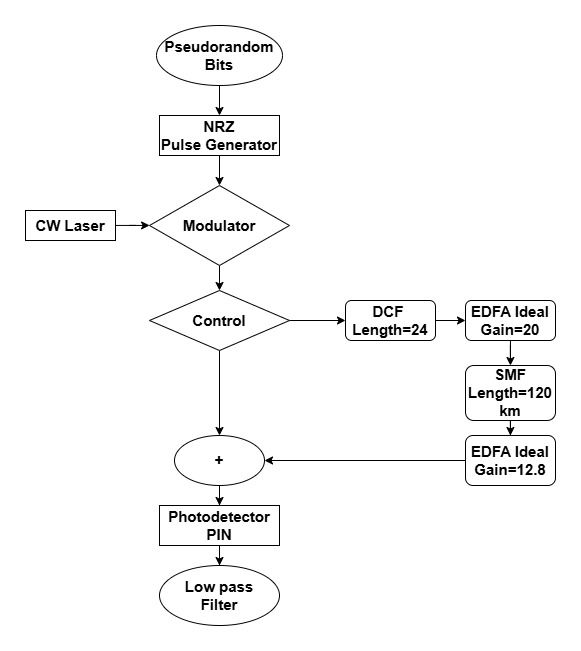
TY - JOUR AU - Rahman, Md. Moklesur AU - Alam, Md. Nazmul AU - Faisal, Tarek Mah AU - Hossain, Md. Najmul PY - 2026 DA - 2026/01/13 TI - Dispersion-Compensating Method for High-Capacity Fiber-Optic Communication System JO - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems T2 - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems JF - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems VL - 2 IS - 1 SP - 53 EP - 60 DO - 10.62762/TACS.2025.603512 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TACS.2025.603512 KW - fiber optic KW - high-capacity KW - SNR KW - optical dispersion KW - BER AB - Designing a reliable fiber optic communication network is crucial. High-speed optical networks are now a vital part of the communication system and the foundation of wireless and mobile networks, driven by their constant expansion and increasing demand. The high transmission rate improves spectral utilization, increases system capacity, and reduces overall system expenditure. To improve the communication channel and achieve high transmission performance and data rates, a spread-spectrum compensation scheme is required. The goal of fiber optic communication systems is to transmit as many bits per second as possible over the longest possible distance at an acceptable data rate. Two methods are presented, and the DCF diagram is shown in the first and second configurations. The simulation evaluates the communication performance at different speeds or bit rates, including (2.5, 10) Gbps. In the other system, the simulation is performed at various bit rates and cable lengths. SN - 3068-7969 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Rahman2026Dispersion,
author = {Md. Moklesur Rahman and Md. Nazmul Alam and Tarek Mah Faisal and Md. Najmul Hossain},
title = {Dispersion-Compensating Method for High-Capacity Fiber-Optic Communication System},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems},
year = {2026},
volume = {2},
number = {1},
pages = {53-60},
doi = {10.62762/TACS.2025.603512},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TACS.2025.603512},
abstract = {Designing a reliable fiber optic communication network is crucial. High-speed optical networks are now a vital part of the communication system and the foundation of wireless and mobile networks, driven by their constant expansion and increasing demand. The high transmission rate improves spectral utilization, increases system capacity, and reduces overall system expenditure. To improve the communication channel and achieve high transmission performance and data rates, a spread-spectrum compensation scheme is required. The goal of fiber optic communication systems is to transmit as many bits per second as possible over the longest possible distance at an acceptable data rate. Two methods are presented, and the DCF diagram is shown in the first and second configurations. The simulation evaluates the communication performance at different speeds or bit rates, including (2.5, 10) Gbps. In the other system, the simulation is performed at various bit rates and cable lengths.},
keywords = {fiber optic, high-capacity, SNR, optical dispersion, BER},
issn = {3068-7969},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems
ISSN: 3068-7969 (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/