ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems
ISSN: 3068-7969 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
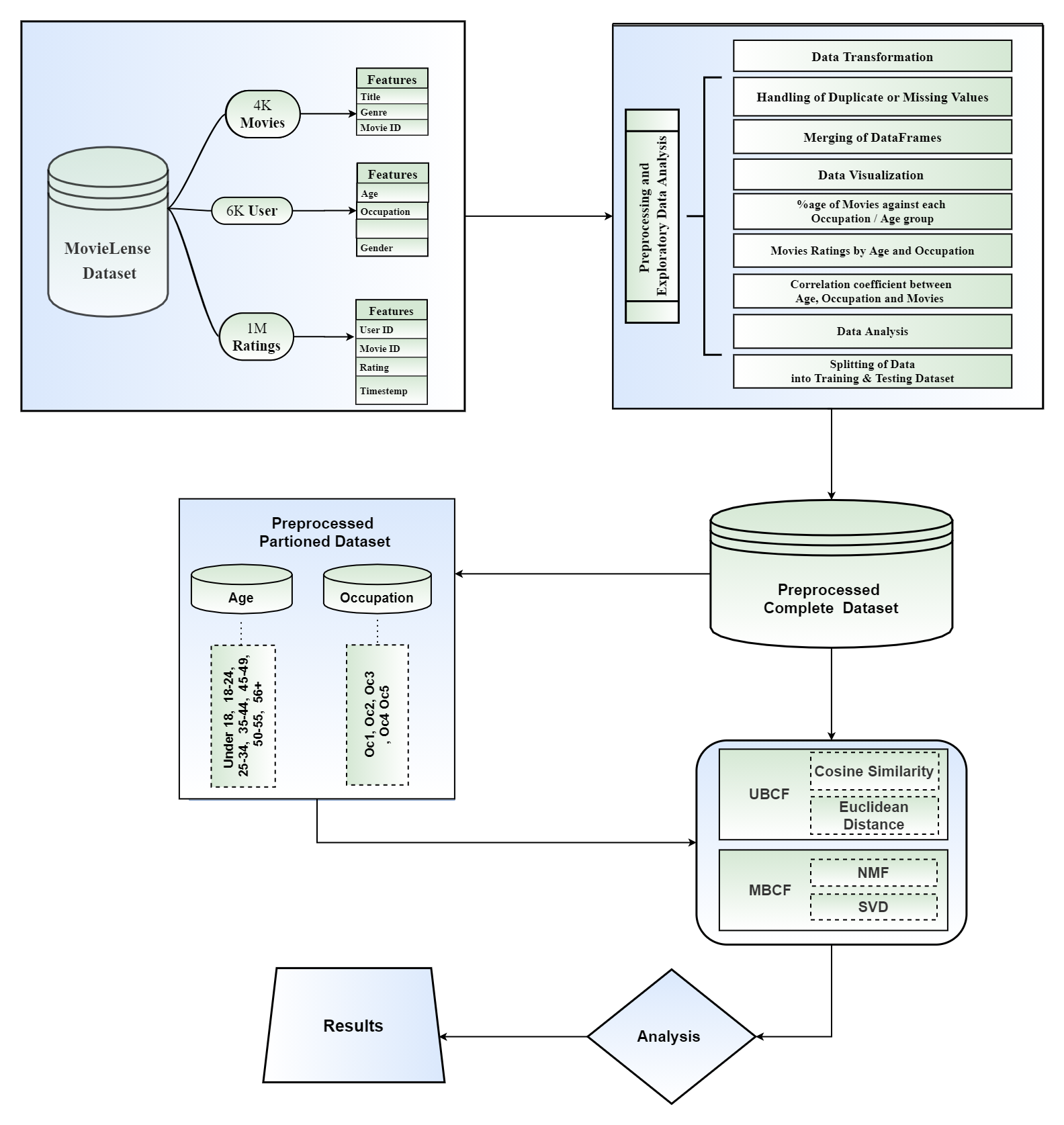
TY - JOUR AU - Hafeez, Muhammad Ahmad AU - Sher, Tahir AU - Rehman, Abdul AU - Ihsan, Imran PY - 2026 DA - 2026/02/14 TI - Performance Evaluation of Collaborative Filtering Recommender System on MovieLens Dataset JO - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems T2 - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems JF - ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems VL - 2 IS - 2 SP - 137 EP - 157 DO - 10.62762/TACS.2025.714333 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TACS.2025.714333 KW - recommender system KW - user-based & model-based collaborative filtering KW - cosine similarity KW - euclidean similarity KW - non-negative matrix factorization KW - singular value decomposition KW - mean absolute error KW - root mean squared error AB - In today's technological landscape, recommender systems provide essential personalized suggestions by leveraging user preferences. This study evaluates User-Based (UBCF) and Model-Based Collaborative Filtering (MBCF) on the MovieLens 1M dataset, comparing performance on complete data versus partitions based on age and occupation. Using MAE and RMSE metrics, we assessed UBCF with Euclidean/Cosine similarity and MBCF with NMF/SVD. Results show MBCF with SVD achieved the best performance (MAE: 0.6909, RMSE: 0.8761), outperforming UBCF by approximately 5.2% in MAE and 5.4% in RMSE. This confirms model-based approaches, particularly SVD, excel with complete datasets, while demographic partitioning reduces accuracy due to data sparsity. Future work will explore hybrid models combining global and partition-based analysis with deep learning for enhanced personalization. SN - 3068-7969 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Hafeez2026Performanc,
author = {Muhammad Ahmad Hafeez and Tahir Sher and Abdul Rehman and Imran Ihsan},
title = {Performance Evaluation of Collaborative Filtering Recommender System on MovieLens Dataset},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems},
year = {2026},
volume = {2},
number = {2},
pages = {137-157},
doi = {10.62762/TACS.2025.714333},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TACS.2025.714333},
abstract = {In today's technological landscape, recommender systems provide essential personalized suggestions by leveraging user preferences. This study evaluates User-Based (UBCF) and Model-Based Collaborative Filtering (MBCF) on the MovieLens 1M dataset, comparing performance on complete data versus partitions based on age and occupation. Using MAE and RMSE metrics, we assessed UBCF with Euclidean/Cosine similarity and MBCF with NMF/SVD. Results show MBCF with SVD achieved the best performance (MAE: 0.6909, RMSE: 0.8761), outperforming UBCF by approximately 5.2\% in MAE and 5.4\% in RMSE. This confirms model-based approaches, particularly SVD, excel with complete datasets, while demographic partitioning reduces accuracy due to data sparsity. Future work will explore hybrid models combining global and partition-based analysis with deep learning for enhanced personalization.},
keywords = {recommender system, user-based \& model-based collaborative filtering, cosine similarity, euclidean similarity, non-negative matrix factorization, singular value decomposition, mean absolute error, root mean squared error},
issn = {3068-7969},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems
ISSN: 3068-7969 (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/