ICCK Transactions on Educational Data Mining
ISSN: pending (Online)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
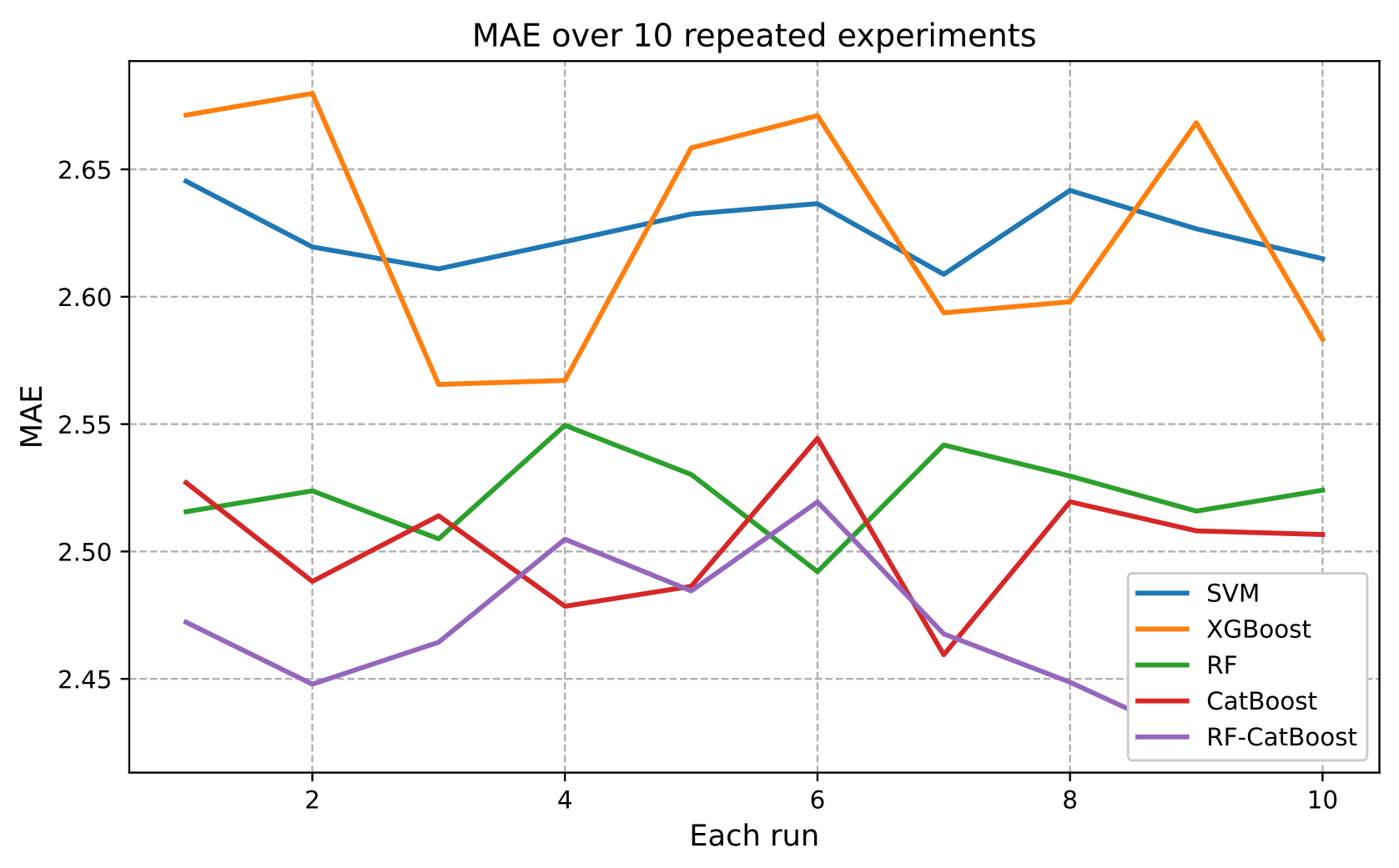
TY - JOUR AU - Zhao, Jing PY - 2025 DA - 2025/11/25 TI - A Stacking-Based RF-CatBoost Model for Student Performance Prediction JO - ICCK Transactions on Educational Data Mining T2 - ICCK Transactions on Educational Data Mining JF - ICCK Transactions on Educational Data Mining VL - 1 IS - 1 SP - 16 EP - 24 DO - 10.62762/TEDM.2025.397583 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TEDM.2025.397583 KW - stacking KW - random forest KW - CatBoost KW - student performance prediction AB - To address the student performance problem in educational data mining, this study proposes a stacking-based RF-CatBoost model that integrates the complementary strengths of ensemble learning methods to enhance prediction accuracy and robustness. In the proposed framework, Random Forest (RF) and CatBoost are employed as the base learners to capture both global feature interactions and complex non-linear relationships within multi-source educational data. Their outputs are then stacked and fused using a combination strategy to generate the final prediction. Experimental results based on two educational datasets demonstrate that the stacking-based RF-CatBoost model consistently achieves superior predictive performance, reflected in prediction accuracy and robustness. The results confirm that the proposed hybrid stacking RF-CatBoost can effectively leverage the diversity of ensemble learners, offering a robust solution for early student performance prediction, enabling timely interventions and personalized learning support in educational setting. SN - pending PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Zhao2025A,
author = {Jing Zhao},
title = {A Stacking-Based RF-CatBoost Model for Student Performance Prediction},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Educational Data Mining},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {1},
pages = {16-24},
doi = {10.62762/TEDM.2025.397583},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TEDM.2025.397583},
abstract = {To address the student performance problem in educational data mining, this study proposes a stacking-based RF-CatBoost model that integrates the complementary strengths of ensemble learning methods to enhance prediction accuracy and robustness. In the proposed framework, Random Forest (RF) and CatBoost are employed as the base learners to capture both global feature interactions and complex non-linear relationships within multi-source educational data. Their outputs are then stacked and fused using a combination strategy to generate the final prediction. Experimental results based on two educational datasets demonstrate that the stacking-based RF-CatBoost model consistently achieves superior predictive performance, reflected in prediction accuracy and robustness. The results confirm that the proposed hybrid stacking RF-CatBoost can effectively leverage the diversity of ensemble learners, offering a robust solution for early student performance prediction, enabling timely interventions and personalized learning support in educational setting.},
keywords = {stacking, random forest, CatBoost, student performance prediction},
issn = {pending},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/