ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Cyber-Physical Systems
ISSN: pending (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
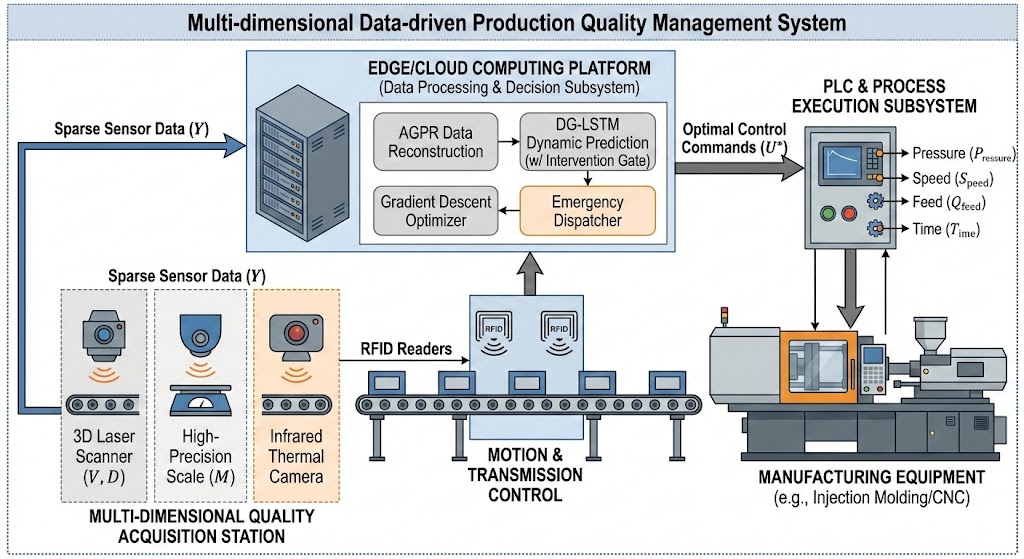
TY - JOUR AU - Ding, Yuxing AU - Yin, Leilei PY - 2026 DA - 2026/02/17 TI - A Multi-Dimensional Data Learning-Based Production Quality Management Method for Intelligent Manufacturing JO - ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Cyber-Physical Systems T2 - ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Cyber-Physical Systems JF - ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Cyber-Physical Systems VL - 1 IS - 1 SP - 38 EP - 50 DO - 10.62762/TICPS.2026.380630 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TICPS.2026.380630 KW - production quality management KW - multi-dimensional data learning KW - adaptive gaussian process regression KW - dynamic gated LSTM KW - error elimination KW - smart manufacturing AB - In the field of high-end precision manufacturing, quality control in production processes has long been challenged by both spatiotemporal data sparsity and error lag. Traditional offline sampling methods struggle to capture the dynamic fluctuations in production, while single-dimensional feedback controls fall short in addressing the nonlinear coupling between multi-dimensional process parameters and final product quality. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a production quality management system based on multi-dimensional data learning and an active error elimination method. First, to tackle the issue of sparse sampling, an Adaptive Gaussian Process Regression (AGPR) algorithm with mixed kernel functions is introduced to reconstruct continuous production quality time-series states, effectively resolving the "blind spot" problem caused by discrete monitoring. Second, a Dynamic Gated LSTM network with a "Correction Gate" is designed to explicitly model the dynamic intervention mechanism of process control variables on quality evolution, advancing from passive prediction to active deduction. Most importantly, this paper develops an active error elimination strategy using gradient inversion. By minimizing the quality deviation objective function, the optimal combination of process parameters is inversely determined. In practical terms, this approach enables the "dynamic re-matching of machine tool state and process requirements"—intelligently adjusting process parameters (such as injection pressure and holding time) according to the equipment's real-time state (e.g., thermal drift, wear). This method compensates for physical equipment performance degradation through dynamic scheduling. Experimental results show that the system significantly reduces the rejection rate in precision injection molding scenarios, marking a paradigm shift in production from "post-event rejection" to "pre-event self-healing". SN - pending PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Ding2026A,
author = {Yuxing Ding and Leilei Yin},
title = {A Multi-Dimensional Data Learning-Based Production Quality Management Method for Intelligent Manufacturing},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Cyber-Physical Systems},
year = {2026},
volume = {1},
number = {1},
pages = {38-50},
doi = {10.62762/TICPS.2026.380630},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TICPS.2026.380630},
abstract = {In the field of high-end precision manufacturing, quality control in production processes has long been challenged by both spatiotemporal data sparsity and error lag. Traditional offline sampling methods struggle to capture the dynamic fluctuations in production, while single-dimensional feedback controls fall short in addressing the nonlinear coupling between multi-dimensional process parameters and final product quality. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a production quality management system based on multi-dimensional data learning and an active error elimination method. First, to tackle the issue of sparse sampling, an Adaptive Gaussian Process Regression (AGPR) algorithm with mixed kernel functions is introduced to reconstruct continuous production quality time-series states, effectively resolving the "blind spot" problem caused by discrete monitoring. Second, a Dynamic Gated LSTM network with a "Correction Gate" is designed to explicitly model the dynamic intervention mechanism of process control variables on quality evolution, advancing from passive prediction to active deduction. Most importantly, this paper develops an active error elimination strategy using gradient inversion. By minimizing the quality deviation objective function, the optimal combination of process parameters is inversely determined. In practical terms, this approach enables the "dynamic re-matching of machine tool state and process requirements"—intelligently adjusting process parameters (such as injection pressure and holding time) according to the equipment's real-time state (e.g., thermal drift, wear). This method compensates for physical equipment performance degradation through dynamic scheduling. Experimental results show that the system significantly reduces the rejection rate in precision injection molding scenarios, marking a paradigm shift in production from "post-event rejection" to "pre-event self-healing".},
keywords = {production quality management, multi-dimensional data learning, adaptive gaussian process regression, dynamic gated LSTM, error elimination, smart manufacturing},
issn = {pending},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Cyber-Physical Systems
ISSN: pending (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/