ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography
ISSN: 3070-2429 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
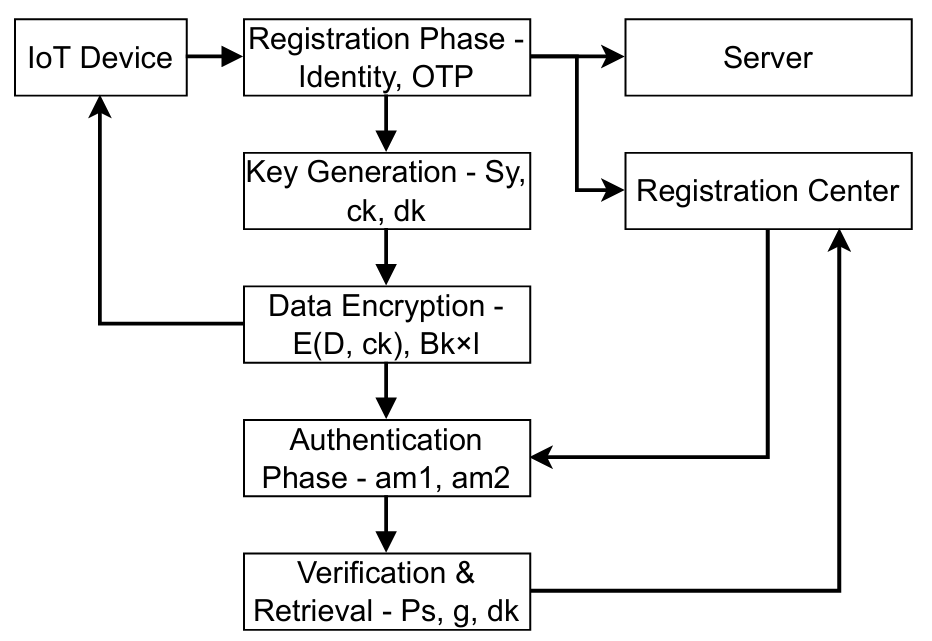
TY - JOUR AU - Khurana, Arjun AU - Gopikrishnan, Sundaram AU - Konda, Srinivasa Reddy AU - Kokila, M. PY - 2026 DA - 2026/02/08 TI - Secure and Efficient Authentication Architecture for IoT Devices in Resource-Limited Networks JO - ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography T2 - ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography JF - ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography VL - 2 IS - 1 SP - 16 EP - 28 DO - 10.62762/TISC.2025.221813 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TISC.2025.221813 KW - internet of things (IoTs) KW - privacy protection KW - key generation KW - data encryption KW - authentication KW - data retrieval AB - The widespread adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized various sectors, including healthcare and transportation, by facilitating extensive data gathering and the provision of advanced, intelligent services. However, this growth also amplifies the risks of privacy breaches, unauthorized access, and resource exhaustion, particularly in constrained devices that cannot afford heavy cryptographic operations. Existing solutions often compromise between efficiency and security, leaving systems exposed to replay, Man-in-the-Middle, and even quantum-era threats. This paper proposes a novel authentication and privacy-preserving framework tailored for resource-constrained IoT environments. The design integrates multi-phase processes, including registration, key generation, encryption, mutual authentication, verification, and secure data retrieval. The framework leverages physical-layer features such as RSSI and LQI for enhanced authentication accuracy, supported by cryptographic primitives like hashing and elliptic curve operations. Experimental evaluation using a large-scale IoT dataset demonstrates consistent encryption times between 0.01 and 0.10 seconds, stable latency performance, minimal memory consumption of 0.497 MB, and a detection rate of 0.85. Comparative analysis shows superior efficiency over baseline models in terms of computational overhead and resilience. The results confirm that the proposed scheme provides a robust yet lightweight security architecture, paving the way for secure IoT deployments in latency-sensitive and resource-limited applications. SN - 3070-2429 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Khurana2026Secure,
author = {Arjun Khurana and Sundaram Gopikrishnan and Srinivasa Reddy Konda and M. Kokila},
title = {Secure and Efficient Authentication Architecture for IoT Devices in Resource-Limited Networks},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography},
year = {2026},
volume = {2},
number = {1},
pages = {16-28},
doi = {10.62762/TISC.2025.221813},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TISC.2025.221813},
abstract = {The widespread adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized various sectors, including healthcare and transportation, by facilitating extensive data gathering and the provision of advanced, intelligent services. However, this growth also amplifies the risks of privacy breaches, unauthorized access, and resource exhaustion, particularly in constrained devices that cannot afford heavy cryptographic operations. Existing solutions often compromise between efficiency and security, leaving systems exposed to replay, Man-in-the-Middle, and even quantum-era threats. This paper proposes a novel authentication and privacy-preserving framework tailored for resource-constrained IoT environments. The design integrates multi-phase processes, including registration, key generation, encryption, mutual authentication, verification, and secure data retrieval. The framework leverages physical-layer features such as RSSI and LQI for enhanced authentication accuracy, supported by cryptographic primitives like hashing and elliptic curve operations. Experimental evaluation using a large-scale IoT dataset demonstrates consistent encryption times between 0.01 and 0.10 seconds, stable latency performance, minimal memory consumption of 0.497 MB, and a detection rate of 0.85. Comparative analysis shows superior efficiency over baseline models in terms of computational overhead and resilience. The results confirm that the proposed scheme provides a robust yet lightweight security architecture, paving the way for secure IoT deployments in latency-sensitive and resource-limited applications.},
keywords = {internet of things (IoTs), privacy protection, key generation, data encryption, authentication, data retrieval},
issn = {3070-2429},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography
ISSN: 3070-2429 (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/