ICCK Transactions on Machine Intelligence
ISSN: 3068-7403 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
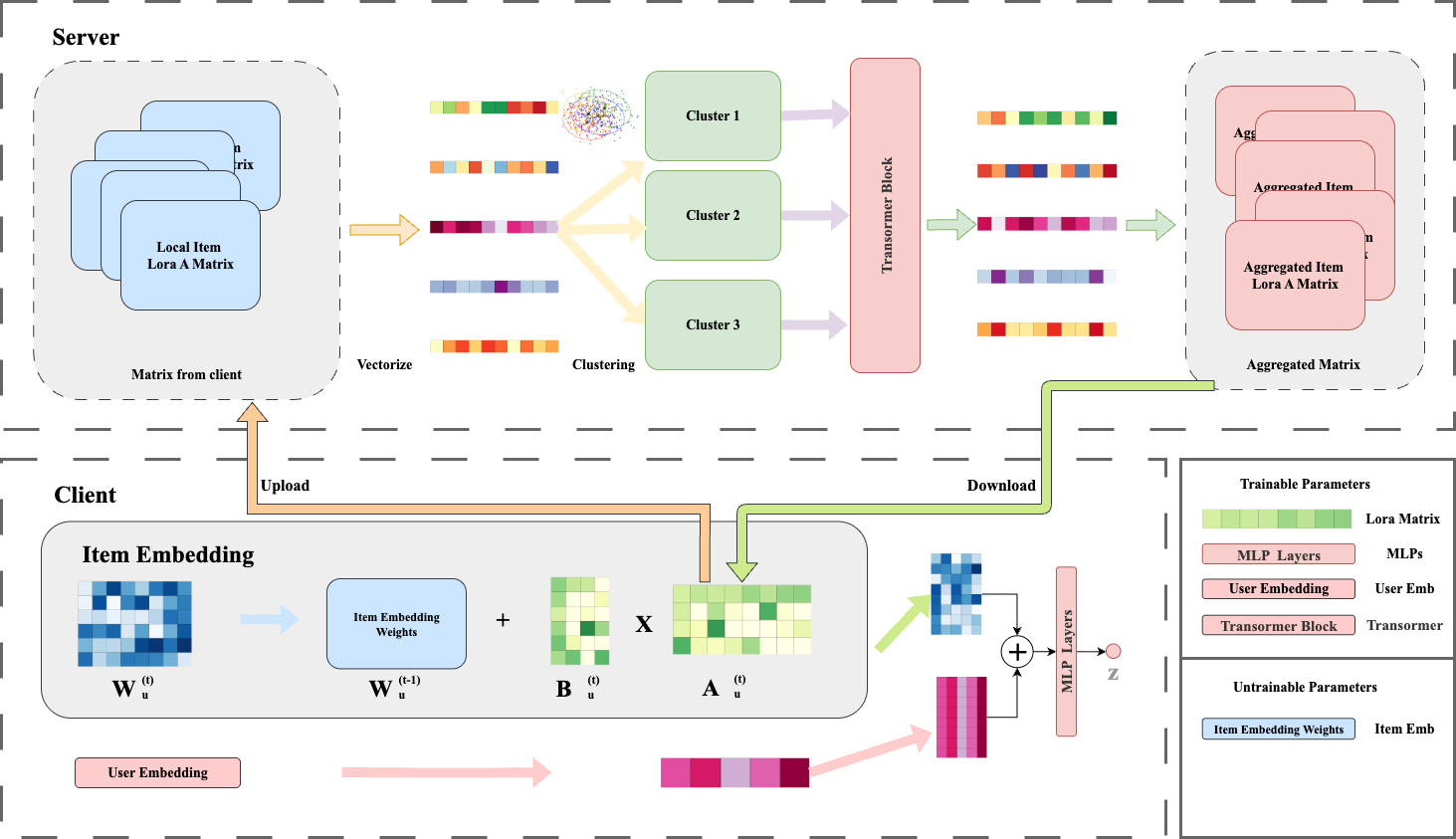
TY - JOUR AU - Wang, Xudong AU - Zhao, Ruixin PY - 2026 DA - 2026/02/08 TI - FedTLRec: Federated Recommendation with Transformer-based Parameter Aggregation and LoRA Compression JO - ICCK Transactions on Machine Intelligence T2 - ICCK Transactions on Machine Intelligence JF - ICCK Transactions on Machine Intelligence VL - 2 IS - 2 SP - 65 EP - 76 DO - 10.62762/TMI.2025.882476 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TMI.2025.882476 KW - federated recommendation KW - low-rank adaptation KW - transformer AB - Federated learning has emerged as a key paradigm in privacy-preserving computing due to its "data usable but not visible" property, enabling users to collaboratively train models without sharing raw data. Motivated by this, federated recommendation systems offer a promising architecture that balances user privacy with recommendation accuracy through distributed collaborative learning. However, existing federated recommendation systems face significant challenges in balancing model performance, communication efficiency, and user privacy. In this paper, we propose FedTLRec (Federated Recommendation with Transformer-based Parameter Aggregation and Collaborative LoRA), which introduces a federated recommendation framework that integrates Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) for parameter compression and Transformer-based aggregation. It addresses key challenges in communication efficiency and model performance by compressing client updates via LoRA and employing a Transformer model with attention mechanisms to effectively aggregate parameters from multiple clients. A K-means clustering strategy further enhances efficiency by grouping similar clients. Experiments on real-world datasets show that FedTLRec achieves superior recommendation accuracy with significantly reduced communication costs, while maintaining robust performance in client dropout scenarios. Code is available at: https://github.com/trueWangSyutung/FedTLRec. SN - 3068-7403 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Wang2026FedTLRec,
author = {Xudong Wang and Ruixin Zhao},
title = {FedTLRec: Federated Recommendation with Transformer-based Parameter Aggregation and LoRA Compression},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Machine Intelligence},
year = {2026},
volume = {2},
number = {2},
pages = {65-76},
doi = {10.62762/TMI.2025.882476},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TMI.2025.882476},
abstract = {Federated learning has emerged as a key paradigm in privacy-preserving computing due to its "data usable but not visible" property, enabling users to collaboratively train models without sharing raw data. Motivated by this, federated recommendation systems offer a promising architecture that balances user privacy with recommendation accuracy through distributed collaborative learning. However, existing federated recommendation systems face significant challenges in balancing model performance, communication efficiency, and user privacy. In this paper, we propose FedTLRec (Federated Recommendation with Transformer-based Parameter Aggregation and Collaborative LoRA), which introduces a federated recommendation framework that integrates Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) for parameter compression and Transformer-based aggregation. It addresses key challenges in communication efficiency and model performance by compressing client updates via LoRA and employing a Transformer model with attention mechanisms to effectively aggregate parameters from multiple clients. A K-means clustering strategy further enhances efficiency by grouping similar clients. Experiments on real-world datasets show that FedTLRec achieves superior recommendation accuracy with significantly reduced communication costs, while maintaining robust performance in client dropout scenarios. Code is available at: https://github.com/trueWangSyutung/FedTLRec.},
keywords = {federated recommendation, low-rank adaptation, transformer},
issn = {3068-7403},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/