ICCK Transactions on Emerging Topics in Artificial Intelligence | Volume 2, Issue 4: 220-228, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/TETAI.2025.851867
Abstract
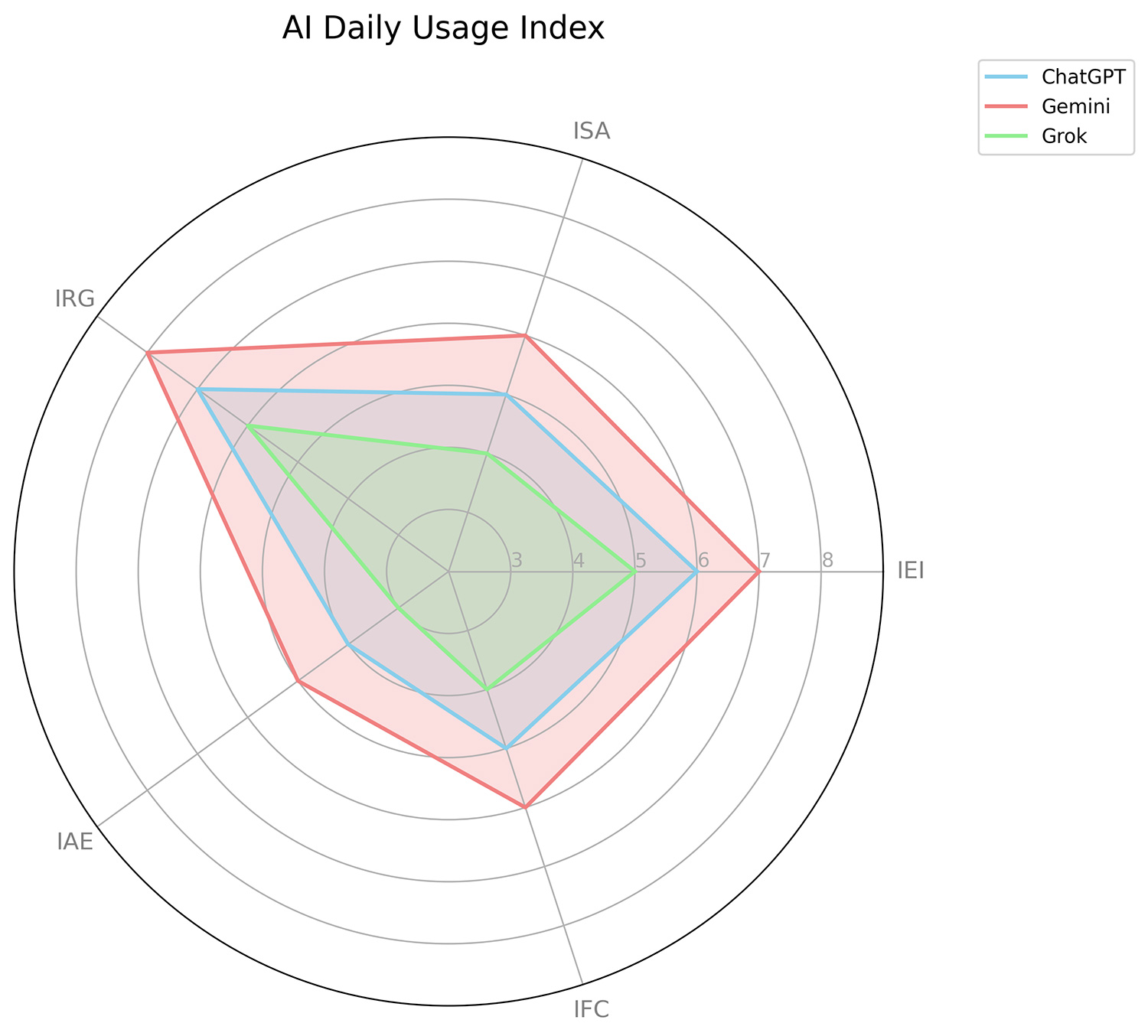
This innovative study analyzes the emotional reaction of 27 individuals from Generation X to flirtatious behaviors exhibited by conversational artificial intelligence. Using a quantitative methodology based on Sentiment Analysis, testimonies and experiences with three models—ChatGPT, Grok, and Gemini—were collected, focusing on phrases or linguistic gestures that could be considered seductive, empathetic, or emotionally warm. The results show that, although there is a clear awareness that no person is behind the AI, several responses generated feelings of companionship, affective validation, and even mild attachment, especially in moments of emotional vulnerability—very difficult to ex... More >
Graphical Abstract