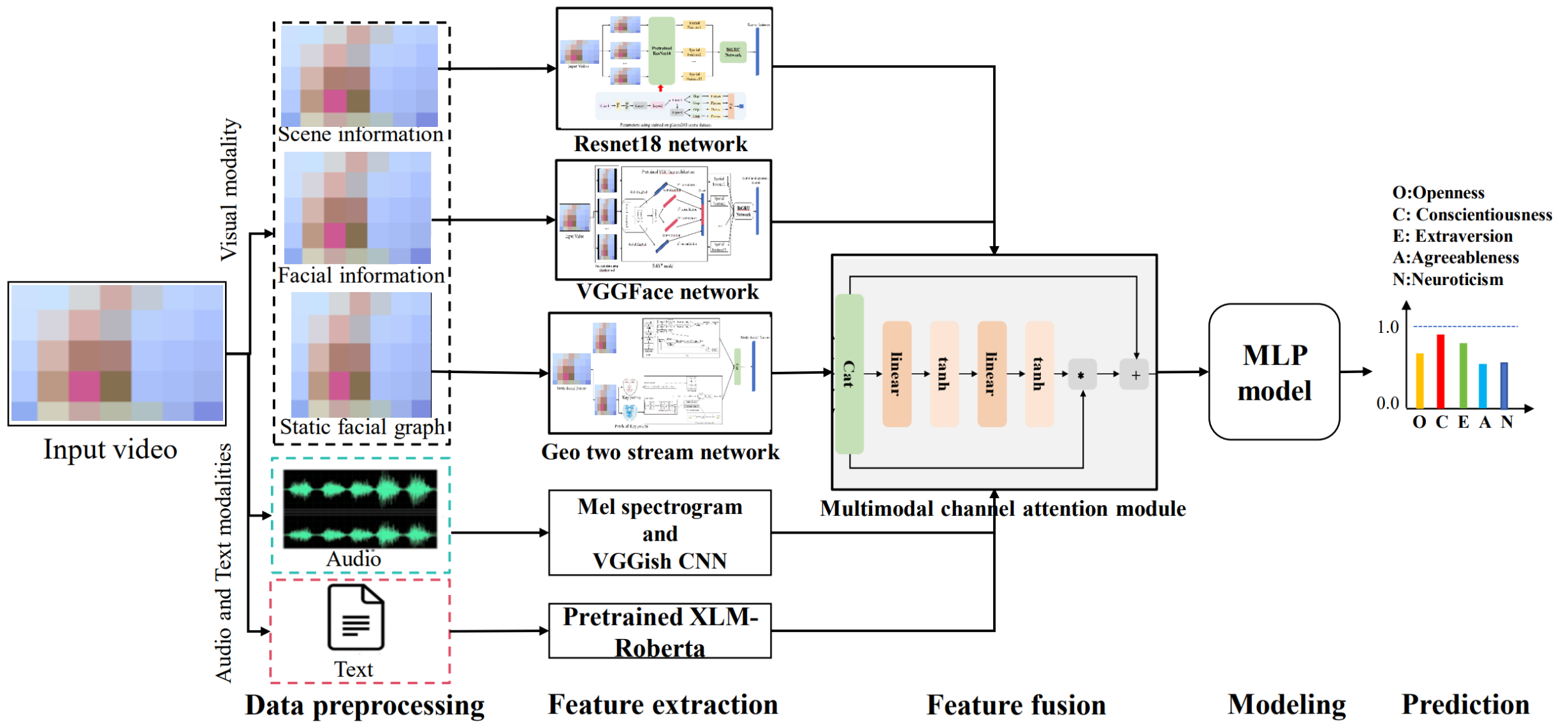
ICCK Transactions on Emerging Topics in Artificial Intelligence | Volume 3, Issue 2: 61-75, 2026 | DOI: 10.62762/TETAI.2025.197745
Abstract
This paper advances a decision-aligned post-processing layer for government bond yield forecasts, turning competent sequence predictions into curve-consistent and economically calibrated outputs with minimal engineering burden. Starting from capacity-fair baselines in the LSTM, GRU and compact transformer families, used only to generate initial point forecasts for five, ten and thirty year maturities at short horizons, we add two model-agnostic stages. A curve consistency projection enforces monotone ordering across maturities and, when warranted, mild convexity while preserving local signal. An asymmetric economic calibration then learns a monotone mapping that down-weights the costlier sid... More >
Graphical Abstract