ICCK Transactions on Emerging Topics in Artificial Intelligence
ISSN: 3068-6652 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
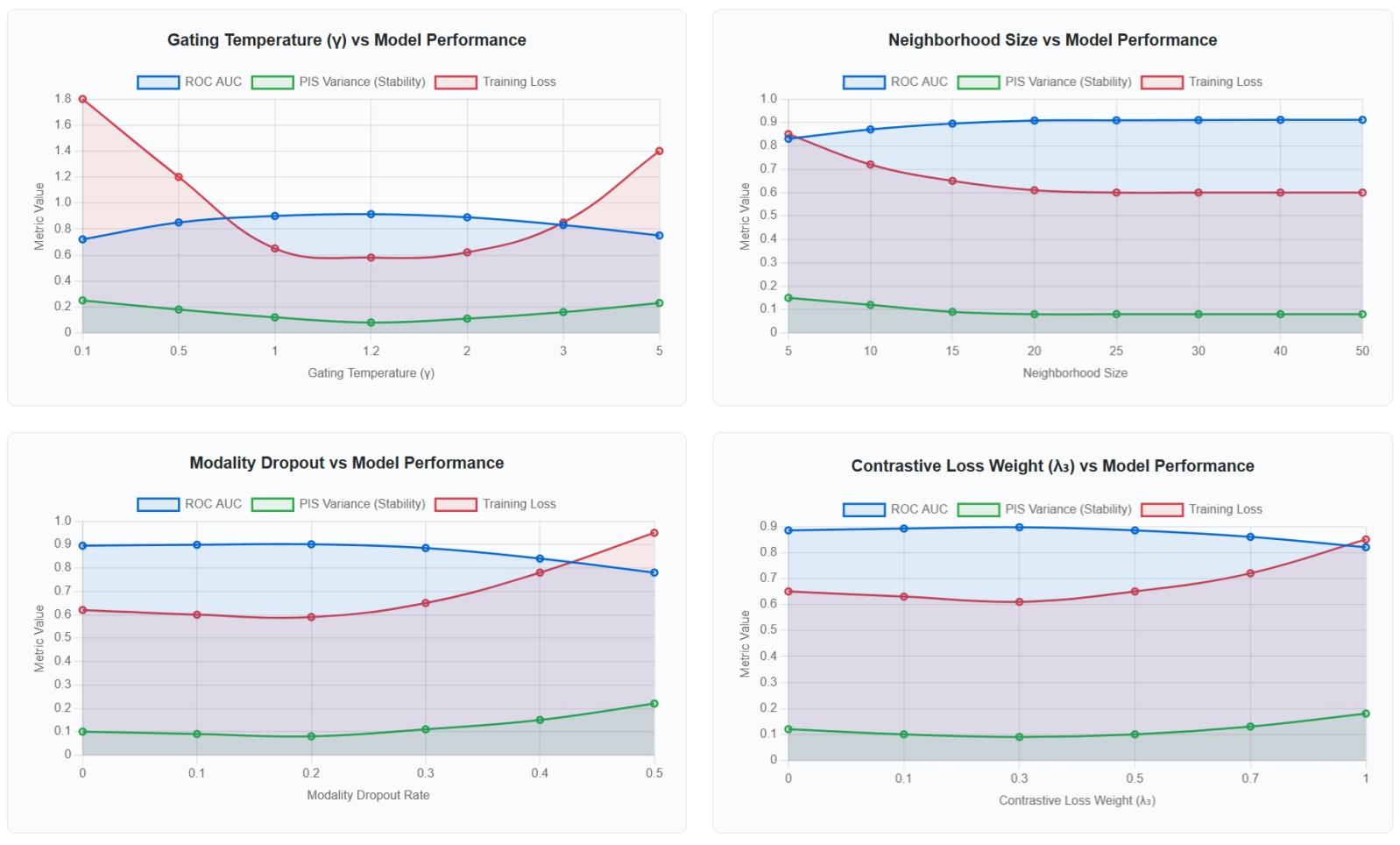
TY - JOUR AU - Yin, Min AU - Frank, Ledee-FI PY - 2026 DA - 2026/01/09 TI - Multi-Modal Fusion for Yield Optimization: Integrating Wafer Maps, Metrology, and Process Logs with Graph Models JO - ICCK Transactions on Emerging Topics in Artificial Intelligence T2 - ICCK Transactions on Emerging Topics in Artificial Intelligence JF - ICCK Transactions on Emerging Topics in Artificial Intelligence VL - 3 IS - 1 SP - 45 EP - 60 DO - 10.62762/TETAI.2025.259226 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TETAI.2025.259226 KW - heterogeneous graph learning KW - multi-modal data fusion KW - wafer maps KW - metrology time-series KW - process log mining KW - yield optimization KW - cross-Modal attention KW - bottleneck identification KW - explainable AI KW - semiconductor manufacturing AB - Yield optimization in advanced manufacturing rarely proceeds as a tidy pipeline; it arises from the gradual convergence of evidence across spatial wafer patterns, multivariate metrology, and asynchronous process and equipment events that interact in ways that are only partially observable. Prior studies often separate these modalities, assigning convolutional encoders to wafer maps, sequence models to metrology, and template based encoders to logs, an arrangement that can perform well locally yet struggles to sustain cross-modal alignment or to reason over the hierarchy that links defects to steps and equipment. Building on these observations, we introduce a manufacturing semantics oriented framework that embeds lots, wafers, dies, steps, equipment, and recipes in a heterogeneous graph, and uses cross modal attention gating to reconcile image, time series, and event representations while performing relation aware message passing. The research was not frictionless; time synchronization required iterative windowing, spatial normalization exposed orientation drift, and naive imputation inflated variance in rare steps, which motivated temperature controlled gating and a lightweight contrastive warm-up. On two production lines the approach improves, to some extent, standard classification metrics and stabilizes top k attribution under feasible latency. Alternative explanations remain possible, including benefits from stricter leakage control or product specific distributions. The work makes explicit the structural link among defects, process, and equipment, and points toward auditable, engineer actionable analytics; further research is needed on long term stability, cross site generalization, and the joint optimization of accuracy, cost, and energy. SN - 3068-6652 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Yin2026MultiModal,
author = {Min Yin and Ledee-FI Frank},
title = {Multi-Modal Fusion for Yield Optimization: Integrating Wafer Maps, Metrology, and Process Logs with Graph Models},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Emerging Topics in Artificial Intelligence},
year = {2026},
volume = {3},
number = {1},
pages = {45-60},
doi = {10.62762/TETAI.2025.259226},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TETAI.2025.259226},
abstract = {Yield optimization in advanced manufacturing rarely proceeds as a tidy pipeline; it arises from the gradual convergence of evidence across spatial wafer patterns, multivariate metrology, and asynchronous process and equipment events that interact in ways that are only partially observable. Prior studies often separate these modalities, assigning convolutional encoders to wafer maps, sequence models to metrology, and template based encoders to logs, an arrangement that can perform well locally yet struggles to sustain cross-modal alignment or to reason over the hierarchy that links defects to steps and equipment. Building on these observations, we introduce a manufacturing semantics oriented framework that embeds lots, wafers, dies, steps, equipment, and recipes in a heterogeneous graph, and uses cross modal attention gating to reconcile image, time series, and event representations while performing relation aware message passing. The research was not frictionless; time synchronization required iterative windowing, spatial normalization exposed orientation drift, and naive imputation inflated variance in rare steps, which motivated temperature controlled gating and a lightweight contrastive warm-up. On two production lines the approach improves, to some extent, standard classification metrics and stabilizes top k attribution under feasible latency. Alternative explanations remain possible, including benefits from stricter leakage control or product specific distributions. The work makes explicit the structural link among defects, process, and equipment, and points toward auditable, engineer actionable analytics; further research is needed on long term stability, cross site generalization, and the joint optimization of accuracy, cost, and energy.},
keywords = {heterogeneous graph learning, multi-modal data fusion, wafer maps, metrology time-series, process log mining, yield optimization, cross-Modal attention, bottleneck identification, explainable AI, semiconductor manufacturing},
issn = {3068-6652},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. ICCK Transactions on Emerging Topics in Artificial Intelligence
ISSN: 3068-6652 (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/