ICCK Transactions on Emerging Topics in Artificial Intelligence
ISSN: 3068-6652 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
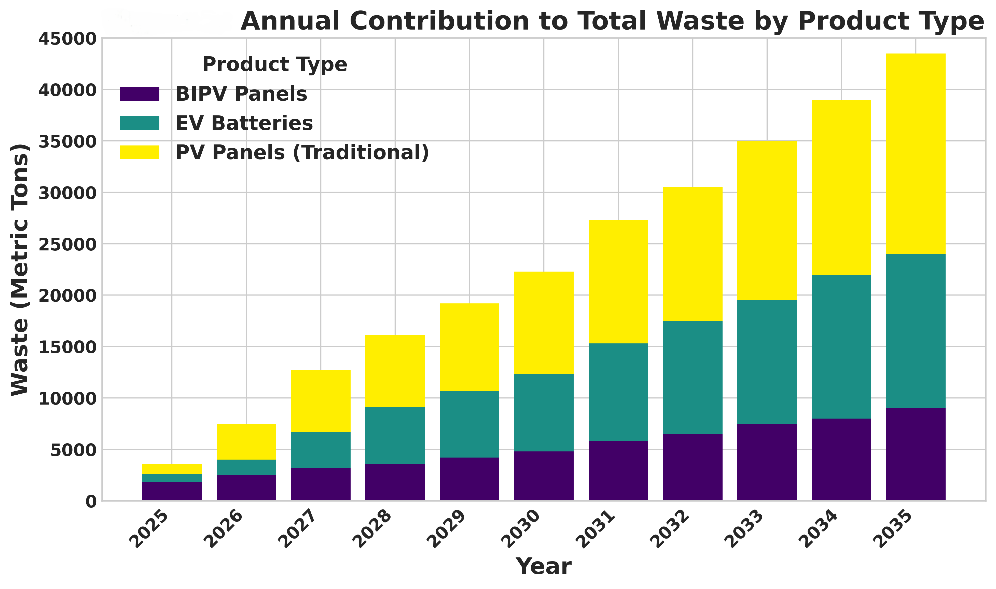
TY - JOUR AU - Hussain, Syed Amer AU - Hussain, Sayed Akif AU - Hussain, Syed Atif AU - Raza, Kumail AU - Imran, Muhammad AU - Komal, Asma PY - 2026 DA - 2026/01/07 TI - A Decision Support System for Reverse Logistics Network Design: Integrating Multi-Factorial Forecasting of Solar Panel End-of-Life Assets JO - ICCK Transactions on Emerging Topics in Artificial Intelligence T2 - ICCK Transactions on Emerging Topics in Artificial Intelligence JF - ICCK Transactions on Emerging Topics in Artificial Intelligence VL - 3 IS - 1 SP - 33 EP - 44 DO - 10.62762/TETAI.2025.782328 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TETAI.2025.782328 KW - reverse logistics KW - decision support system KW - solar panel waste KW - multi-objective optimization KW - multifactorial forecasting KW - sustainable supply chain AB - The rapid global deployment of solar photovoltaic (PV) technology presents a significant and often overlooked challenge: the effective management of end-of-life (EoL) solar panels. This issue is particularly acute in developing and emerging economies, where established reverse logistics infrastructure is often lacking. A critical limitation in current academic literature is the oversimplified forecasting of EoL waste streams, which fails to account for the dynamic interplay of socio-economic, policy, and environmental variables. To bridge this gap, we propose a novel decision support system (DSS) for the design of a sustainable reverse logistics network. Our system uniquely integrates a hybrid, multi-factorial forecasting model combining a SARIMAX time series approach with a Gradient Boosting Regressor to provide a robust prediction of waste volume. The output of this predictive engine dynamically informs a multi objective, mixed integer linear programming (MILP) model, which optimizes the network design to simultaneously minimize economic costs and environmental impacts. Our findings demonstrate that this integrated framework provides a more realistic and adaptable tool for strategic planning than existing models. The research identifies a hybrid network structure as the most viable solution, offering superior performance in cost efficiency and material recovery. Our study provides an actionable blueprint for policymakers and industry leaders to proactively build a resilient and circular economy for a sustainable energy future. SN - 3068-6652 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Hussain2026A,
author = {Syed Amer Hussain and Sayed Akif Hussain and Syed Atif Hussain and Kumail Raza and Muhammad Imran and Asma Komal},
title = {A Decision Support System for Reverse Logistics Network Design: Integrating Multi-Factorial Forecasting of Solar Panel End-of-Life Assets},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Emerging Topics in Artificial Intelligence},
year = {2026},
volume = {3},
number = {1},
pages = {33-44},
doi = {10.62762/TETAI.2025.782328},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TETAI.2025.782328},
abstract = {The rapid global deployment of solar photovoltaic (PV) technology presents a significant and often overlooked challenge: the effective management of end-of-life (EoL) solar panels. This issue is particularly acute in developing and emerging economies, where established reverse logistics infrastructure is often lacking. A critical limitation in current academic literature is the oversimplified forecasting of EoL waste streams, which fails to account for the dynamic interplay of socio-economic, policy, and environmental variables. To bridge this gap, we propose a novel decision support system (DSS) for the design of a sustainable reverse logistics network. Our system uniquely integrates a hybrid, multi-factorial forecasting model combining a SARIMAX time series approach with a Gradient Boosting Regressor to provide a robust prediction of waste volume. The output of this predictive engine dynamically informs a multi objective, mixed integer linear programming (MILP) model, which optimizes the network design to simultaneously minimize economic costs and environmental impacts. Our findings demonstrate that this integrated framework provides a more realistic and adaptable tool for strategic planning than existing models. The research identifies a hybrid network structure as the most viable solution, offering superior performance in cost efficiency and material recovery. Our study provides an actionable blueprint for policymakers and industry leaders to proactively build a resilient and circular economy for a sustainable energy future.},
keywords = {reverse logistics, decision support system, solar panel waste, multi-objective optimization, multifactorial forecasting, sustainable supply chain},
issn = {3068-6652},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. ICCK Transactions on Emerging Topics in Artificial Intelligence
ISSN: 3068-6652 (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/