Chinese Journal of Information Fusion
ISSN: 2998-3371 (Online) | ISSN: 2998-3363 (Print)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
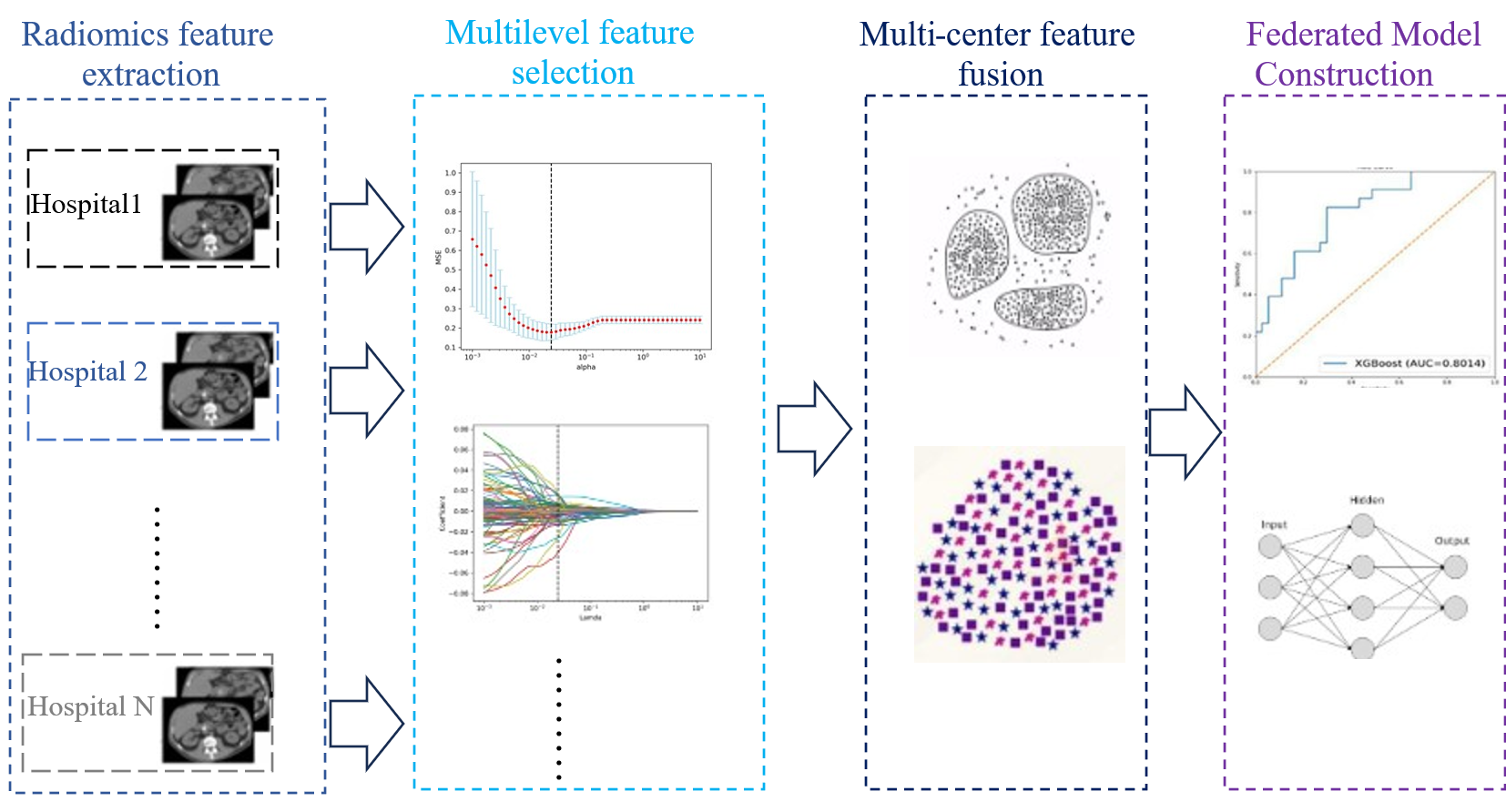
TY - JOUR AU - Long, Yuehong AU - Zeng, Yuliang AU - Zhang, Tao AU - Zhou, Jiancun AU - He, Qian AU - Liu, Xingqi AU - Wang, Ke PY - 2026 DA - 2026/01/04 TI - Radiomic Evaluation Model on the Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer A Multicenter Collaborative Research Based on Privacy Protection JO - Chinese Journal of Information Fusion T2 - Chinese Journal of Information Fusion JF - Chinese Journal of Information Fusion VL - 3 IS - 1 SP - 17 EP - 30 DO - 10.62762/CJIF.2025.125241 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/CJIF.2025.125241 KW - radiomics KW - federated learning KW - deep learning KW - distributed learning AB - Background: Practical implementation of radiomics research faces significant data accessibility challenges due to privacy and ethical restrictions on multicenter data aggregation. Federated Learning (FL) provides a secure distributed framework that preserves data privacy through cryptographic techniques. Its adoption in radiomics is an emerging trend, enabling collaborative training without sharing sensitive imaging data. However, the inherently Non-IID data distribution across clients in FL often leads to class imbalance, which can substantially degrade global model performance. Purpose: To develop a privacy-preserving, multicenter collaborative CT-radiomics model for evaluating neoadjuvant chemotherapy efficacy in non‑small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Methods: To mitigate FL performance degradation caused by data imbalance, we propose a parameter‑sharing federated aggregation algorithm (FedPS), where model parameters are sequentially shared via the server. Results: On an imbalanced NSCLC NAC efficacy dataset, centralized learning achieved an AUC of 0.92. FedPS attained competitive performance (AUC = 0.88), approaching the centralized benchmark while preserving privacy. Common FL algorithms performed lower: FedAvg (AUC = 0.84), FedSGD (0.85), and FedProx (0.85). On extremely imbalanced data, FedPS maintained good performance (AUC = 0.86), compared to FedAvg (0.80), FedSGD (0.83), and FedProx (0.85). Conclusions: The proposed FedPS algorithm demonstrates promising classification and generalization performance in imbalanced federated learning scenarios. SN - 2998-3371 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Long2026Radiomic,
author = {Yuehong Long and Yuliang Zeng and Tao Zhang and Jiancun Zhou and Qian He and Xingqi Liu and Ke Wang},
title = {Radiomic Evaluation Model on the Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer A Multicenter Collaborative Research Based on Privacy Protection},
journal = {Chinese Journal of Information Fusion},
year = {2026},
volume = {3},
number = {1},
pages = {17-30},
doi = {10.62762/CJIF.2025.125241},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/CJIF.2025.125241},
abstract = {Background: Practical implementation of radiomics research faces significant data accessibility challenges due to privacy and ethical restrictions on multicenter data aggregation. Federated Learning (FL) provides a secure distributed framework that preserves data privacy through cryptographic techniques. Its adoption in radiomics is an emerging trend, enabling collaborative training without sharing sensitive imaging data. However, the inherently Non-IID data distribution across clients in FL often leads to class imbalance, which can substantially degrade global model performance. Purpose: To develop a privacy-preserving, multicenter collaborative CT-radiomics model for evaluating neoadjuvant chemotherapy efficacy in non‑small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Methods: To mitigate FL performance degradation caused by data imbalance, we propose a parameter‑sharing federated aggregation algorithm (FedPS), where model parameters are sequentially shared via the server. Results: On an imbalanced NSCLC NAC efficacy dataset, centralized learning achieved an AUC of 0.92. FedPS attained competitive performance (AUC = 0.88), approaching the centralized benchmark while preserving privacy. Common FL algorithms performed lower: FedAvg (AUC = 0.84), FedSGD (0.85), and FedProx (0.85). On extremely imbalanced data, FedPS maintained good performance (AUC = 0.86), compared to FedAvg (0.80), FedSGD (0.83), and FedProx (0.85). Conclusions: The proposed FedPS algorithm demonstrates promising classification and generalization performance in imbalanced federated learning scenarios.},
keywords = {radiomics, federated learning, deep learning, distributed learning},
issn = {2998-3371},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. Chinese Journal of Information Fusion
ISSN: 2998-3371 (Online) | ISSN: 2998-3363 (Print)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/