Abstract
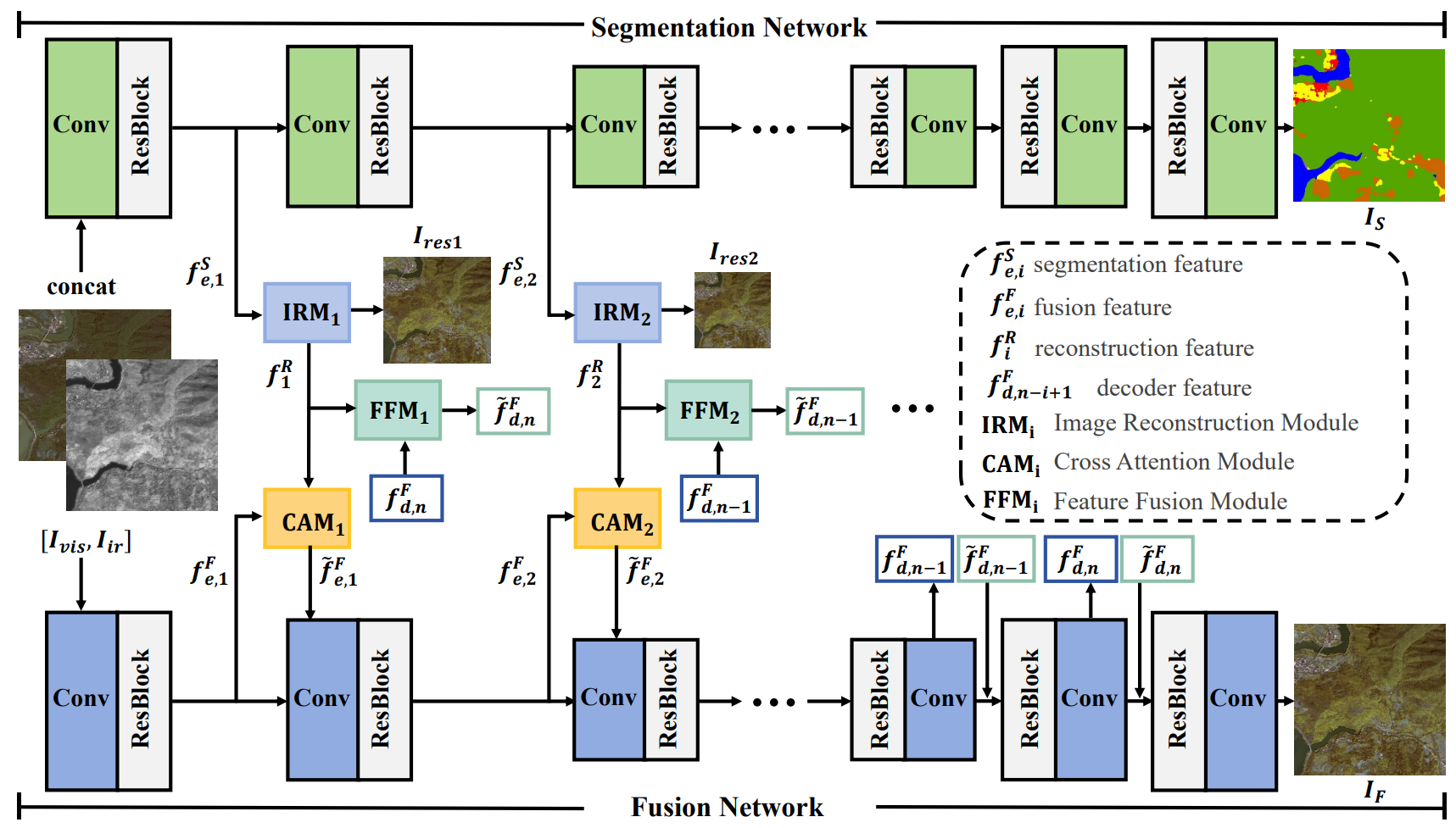
Existing deep learning-based methods for infrared and visible image fusion typically operate independently of other high-level vision tasks, overlooking the potential benefits these tasks could offer. For instance, semantic features from image segmentation could enrich the fusion results by providing detailed target information. However, segmentation focuses on target-level semantic feature information (e.g., object categories), while fusion focuses more on pixel-level detail feature information (e.g., local textures), creating a feature representation gap. To address this challenge, we propose a self-supervised segmentation feature alignment fusion network (SegFANet), which aligns target-level semantic features from segmentation tasks with pixel-level fusion features through self-supervised learning, thereby bridging the feature gap between the two tasks and improving the quality of image fusion. Extensive experiments on the WHU and Potsdam datasets show our method's effectiveness, outperforming the state-of-the-art methods.
Keywords
image fusion
self-supervised segmentation feature alignment
feature interaction
deep learning
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62522105.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Qiu, W., Zhao, W., & Wang, H. (2025). Self-supervised Segmentation Feature Alignment for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. Chinese Journal of Information Fusion, 2(3), 223–236. https://doi.org/10.62762/CJIF.2025.822280
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions

Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 