Abstract
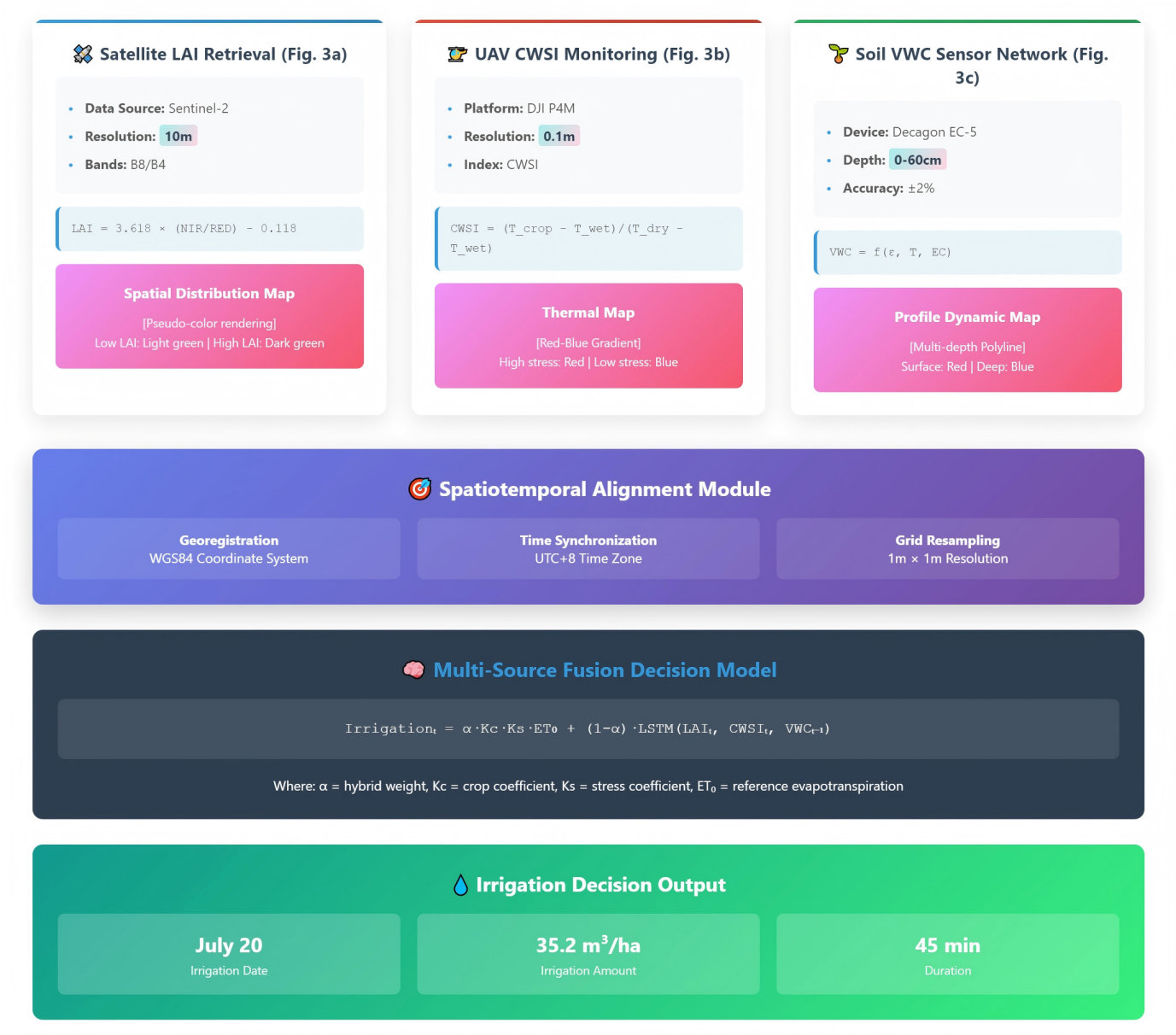
Rice cultivation accounts for 65% of agricultural water consumption in China but suffers from low irrigation water use efficiency (WUE ≈ 0.80kg/m^3) and severe nitrogen and phosphorus loss, contributing up to 30% of agricultural non-point source pollution. To address these core issues, this study developed a multi-source collaborative sensing-based Intelligent Precision Paddy Irrigation Control System (IPICS). The system integrates satellite and UAV remote sensing with IoT technologies to construct a ``sky-space-ground'' three-dimensional monitoring system, couples the FAO-56 Penman-Monteith model with LSTM deep learning algorithms to establish a dynamic irrigation decision model, and integrates a self-developed solar-powered intelligent sluice gate (AG-SOLAR-M7) for precise canal water control. A two-year field validation (2023-2024) was conducted at Youyi Farm (131.8121°E, 46.7825°N), comparing the Intelligent Precision Irrigation Control System (IPICS) with conventional flooding(each 40 ha, 3 replicates). Results demonstrated that: (1) IPICS reduced irrigation by 25.3% (625±32 mm vs. 837±41 mm, p<0.01); (2) maintained stable yield (7.0±0.4 t/ha vs. 7.1±0.5 t/ha); (3) increased WUE by 31.8% (1.12±0.08 kg/m^3 vs. 0.85±0.06 kg/m^3); (4) decreased nitrogen leaching by 57.4% (18.2±3.1 kg/ha vs. 42.7±5.9 kg/ha). The ``sensing-decision-execution'' closed-loop control of IPICS significantly enhanced water and fertilizer utilization efficiency, offering a replicable technical model and practical application for digital farmland development.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported by the Sub-project of the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences under Grant XDA28100401, and Cangnan County Modern Agricultural Industry Enhancement Project under Grant 2024CNYJY08.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Zhang, H., Xu, H., Zhu, M., Zeng, M., Zhao, X., & Wu, H. (2025). Research on Precision Paddy Field Irrigation Control Technology Based on Multi-Source Sensing Hybrid Model. Digital Intelligence in Agriculture, 1(1), 14–23. https://doi.org/10.62762/DIA.2025.680966
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions

Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 