Frontiers in Educational Innovation and Research
ISSN: 3068-5664 (Online)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
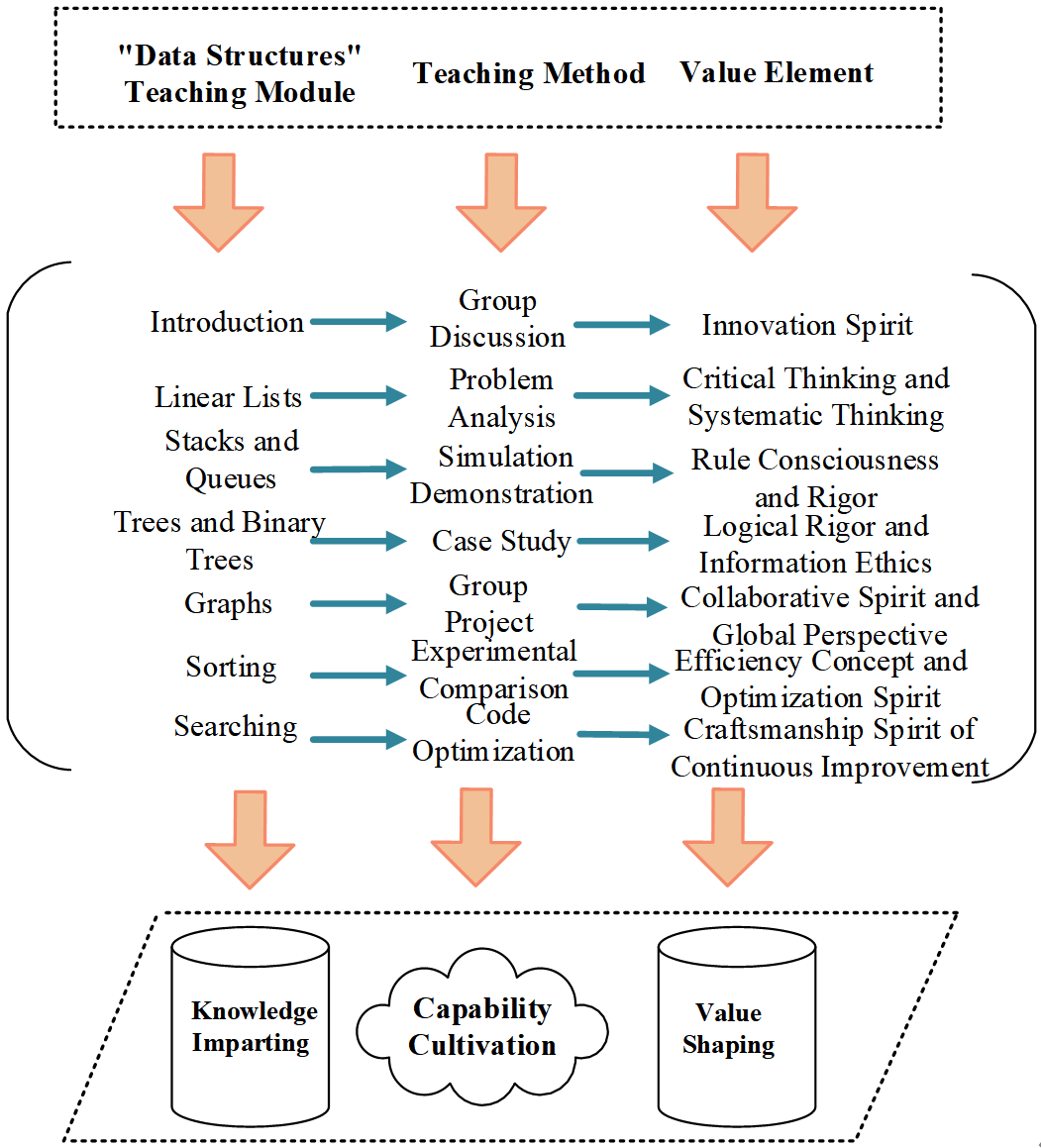
TY - JOUR AU - Yi, Wenlong AU - Chen, Jie AU - Weng, Liming PY - 2025 DA - 2025/12/29 TI - Reconstruction of Data Structures Course Teaching Model for Smart Agriculture Talent Cultivation: Integrated Practice of Value Shaping and Capability Development JO - Frontiers in Educational Innovation and Research T2 - Frontiers in Educational Innovation and Research JF - Frontiers in Educational Innovation and Research VL - 1 IS - 3 SP - 100 EP - 109 DO - 10.62762/FEIR.2025.323427 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/FEIR.2025.323427 KW - smart agriculture KW - soft systems methodology KW - three-dimensional teaching objectives KW - value-integrated teaching AB - In response to the current imbalance phenomenon of "emphasizing skills while neglecting values" in programming practice teaching oriented toward smart agriculture, this study employs the Data Structures course as a vehicle. It applies Checkland's Soft Systems Methodology (SSM) to construct a three-dimensional integrated teaching objective system of "knowledge transfer–capability cultivation–value shaping." Through systematic reconstruction of seven teaching modules centered on linear lists, trees, graphs, sorting, and searching, the teaching objectives are transformed from mere knowledge acquisition to an organic integration of knowledge, capability, and value objectives. In the value dimension, the teaching scheme emphasizes integrating core value elements oriented toward smart agriculture, including systematic engineering decision-making, data security and privacy protection, resource conservation and efficiency optimization, and rigorous professional ethics and compliance spirit. Statistical analysis of controlled experiments conducted over two rounds with 350 students demonstrates that the experimental group achieved improved average scores (p < 0.05) with more concentrated grade distribution and notably reduced standard deviation. This study provides an operational reform pathway for the deep integration of professional and value education in smart agriculture-related courses. SN - 3068-5664 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Yi2025Reconstruc,
author = {Wenlong Yi and Jie Chen and Liming Weng},
title = {Reconstruction of Data Structures Course Teaching Model for Smart Agriculture Talent Cultivation: Integrated Practice of Value Shaping and Capability Development},
journal = {Frontiers in Educational Innovation and Research},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {3},
pages = {100-109},
doi = {10.62762/FEIR.2025.323427},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/FEIR.2025.323427},
abstract = {In response to the current imbalance phenomenon of "emphasizing skills while neglecting values" in programming practice teaching oriented toward smart agriculture, this study employs the Data Structures course as a vehicle. It applies Checkland's Soft Systems Methodology (SSM) to construct a three-dimensional integrated teaching objective system of "knowledge transfer–capability cultivation–value shaping." Through systematic reconstruction of seven teaching modules centered on linear lists, trees, graphs, sorting, and searching, the teaching objectives are transformed from mere knowledge acquisition to an organic integration of knowledge, capability, and value objectives. In the value dimension, the teaching scheme emphasizes integrating core value elements oriented toward smart agriculture, including systematic engineering decision-making, data security and privacy protection, resource conservation and efficiency optimization, and rigorous professional ethics and compliance spirit. Statistical analysis of controlled experiments conducted over two rounds with 350 students demonstrates that the experimental group achieved improved average scores (p < 0.05) with more concentrated grade distribution and notably reduced standard deviation. This study provides an operational reform pathway for the deep integration of professional and value education in smart agriculture-related courses.},
keywords = {smart agriculture, soft systems methodology, three-dimensional teaching objectives, value-integrated teaching},
issn = {3068-5664},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/