Frontiers in Educational Innovation and Research
ISSN: 3068-5664 (Online)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
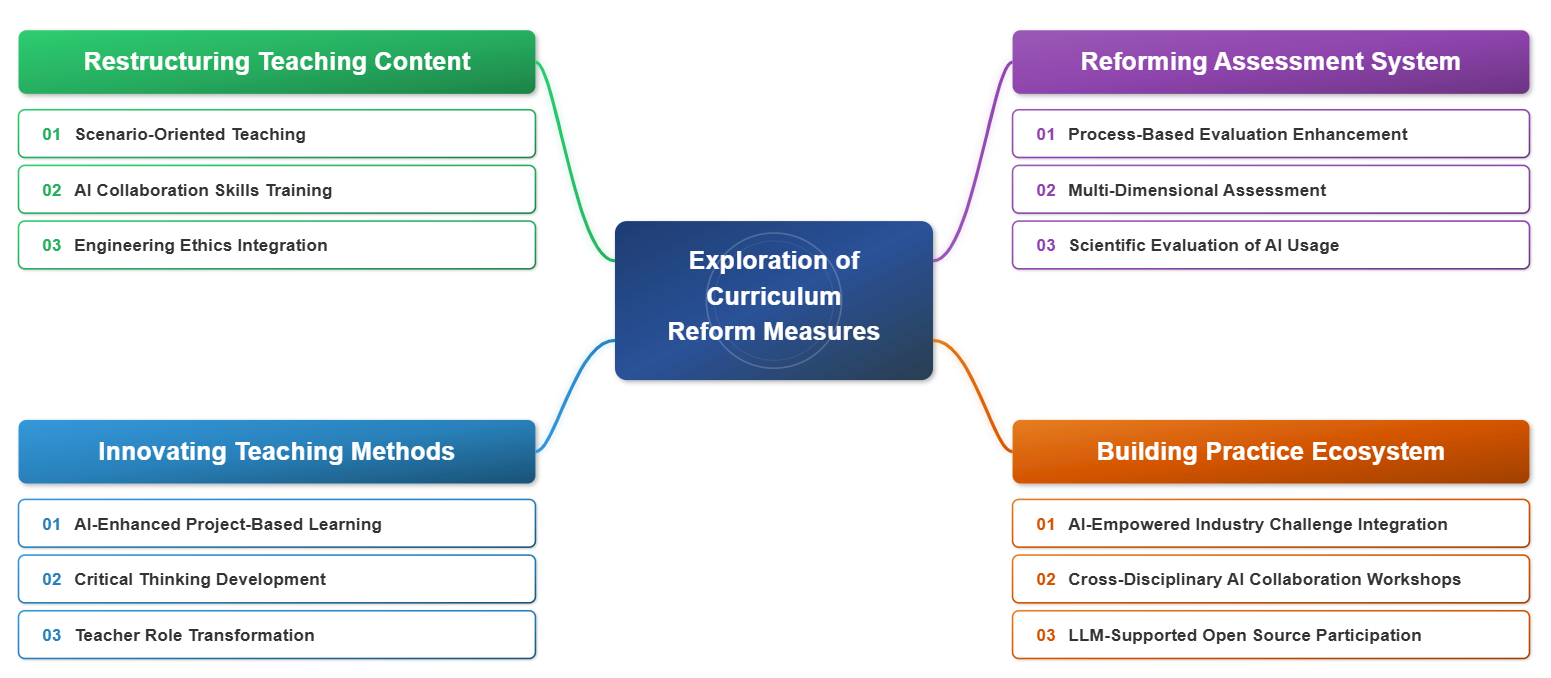
TY - JOUR AU - Guo, Nan AU - Han, Bing AU - Qiao, Junfei PY - 2025 DA - 2025/12/25 TI - Exploration of the Reform of Comprehensive Practice Course in Advanced Programming Driven by Large Models JO - Frontiers in Educational Innovation and Research T2 - Frontiers in Educational Innovation and Research JF - Frontiers in Educational Innovation and Research VL - 1 IS - 3 SP - 81 EP - 91 DO - 10.62762/FEIR.2025.722615 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/FEIR.2025.722615 KW - artificial intelligence KW - large language models KW - curriculum reform KW - competency-oriented AB - The rapid advancement of AI and large language models has placed newer and higher demands on comprehensive programming practice courses in higher education. Significant shifts in students' learning styles, knowledge acquisition channels, and innovative capabilities have rendered traditional curriculum content and teaching methods inadequate for meeting the talent development requirements of the new era. This paper thoroughly examines the profound impact of the widespread adoption of AI technologies on the curriculum system and proposes a systematic reform framework centered on "AI empowerment, competency orientation, and student-centered approaches." By integrating AI tools into the course, it aims to enhance the efficiency and innovation of students' programming practice, strengthen their ability to use intelligent tools rationally and critically, emphasize interdisciplinary integration and engineering ethics, and ultimately foster students' capacity to solve complex engineering problems systematically. SN - 3068-5664 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Guo2025Exploratio,
author = {Nan Guo and Bing Han and Junfei Qiao},
title = {Exploration of the Reform of Comprehensive Practice Course in Advanced Programming Driven by Large Models},
journal = {Frontiers in Educational Innovation and Research},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {3},
pages = {81-91},
doi = {10.62762/FEIR.2025.722615},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/FEIR.2025.722615},
abstract = {The rapid advancement of AI and large language models has placed newer and higher demands on comprehensive programming practice courses in higher education. Significant shifts in students' learning styles, knowledge acquisition channels, and innovative capabilities have rendered traditional curriculum content and teaching methods inadequate for meeting the talent development requirements of the new era. This paper thoroughly examines the profound impact of the widespread adoption of AI technologies on the curriculum system and proposes a systematic reform framework centered on "AI empowerment, competency orientation, and student-centered approaches." By integrating AI tools into the course, it aims to enhance the efficiency and innovation of students' programming practice, strengthen their ability to use intelligent tools rationally and critically, emphasize interdisciplinary integration and engineering ethics, and ultimately foster students' capacity to solve complex engineering problems systematically.},
keywords = {artificial intelligence, large language models, curriculum reform, competency-oriented},
issn = {3068-5664},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/