Journal of Advanced Biomaterials
ISSN: pending (Online) | ISSN: pending (Print)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
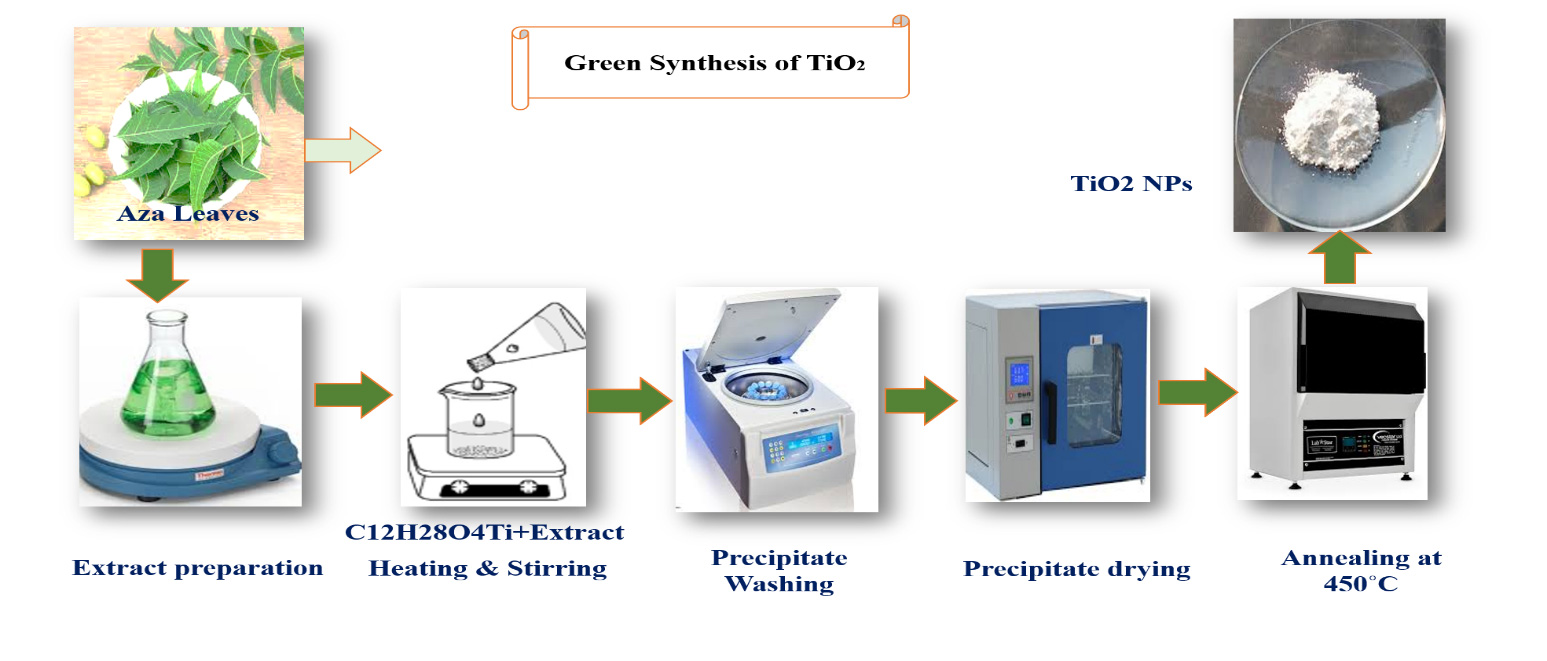
TY - JOUR AU - Mamoor, Sidra AU - Ullah, Atta AU - Khan, Sulaiman AU - Akber, Waleed Ahsan AU - Ali, Shakir AU - Sher, Adil AU - Rehman, Gauhar AU - Hayat, Khizar AU - Shah, Said Karim PY - 2026 DA - 2026/02/18 TI - Green Synthesis of TiO$_2$ Nanoparticles Using Azadirachta Indica with Multifunctional Bioactivity JO - Journal of Advanced Biomaterials T2 - Journal of Advanced Biomaterials JF - Journal of Advanced Biomaterials VL - 1 IS - 1 SP - 10 EP - 25 DO - 10.62762/JAB.2025.294658 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JAB.2025.294658 KW - green TiO$_2$-NPs KW - azadirachta indica leaf extract KW - anti-inflammatory KW - anti-diabetic KW - anti-bacterial efficacy AB - In this study, titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO$_2$-NPs) were synthesized via a green, cost-effective method using Azadirachta indica leaf extract as a natural capping and reducing agent. Characterization techniques including UV-vis, FTIR, XRD, SEM, EDX, and PL spectroscopy confirmed successful synthesis. UV-vis and FTIR confirmed surface functionalization by organic residues, while XRD revealed a well-crystalline anatase phase with average crystallite sizes of 42.2--54 nm. SEM analysis showed predominantly spherical particles (70--90 nm), and EDX confirmed high purity with only Ti and oxygen present. PL spectra exhibited emission peaks at 420, 468, 493, and 539 nm. The green TiO$_2$-NPs demonstrated multifunctional biomedical activities. In vitro anti-inflammatory assays showed significant human red blood cell membrane stabilization, with maximum inhibition of 74.7% and 71.3% in heat-induced hemolysis tests. Compared to diclofenac sodium standard, TiO$_2$-NPs achieved 87.3% and 76.3% inhibition at high concentrations. Anti-diabetic assays revealed up to 71.4% inhibition of glucose uptake by yeast cells (vs. 86.6% for standard drugs), while glucose adsorption ranged from 0.45 to 7.3 mg/g. Antibacterial activity against Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus) and Gram-negative (Escherichia coli) strains showed inhibition zones of 22.2 mm and 21.2 mm, respectively, comparable to standard drugs (23.3 mm and 21.7 mm). These results highlight green TiO$_2$-NPs as promising candidates for biomedical applications. SN - pending PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Mamoor2026Green,
author = {Sidra Mamoor and Atta Ullah and Sulaiman Khan and Waleed Ahsan Akber and Shakir Ali and Adil Sher and Gauhar Rehman and Khizar Hayat and Said Karim Shah},
title = {Green Synthesis of TiO\$\_2\$ Nanoparticles Using Azadirachta Indica with Multifunctional Bioactivity},
journal = {Journal of Advanced Biomaterials},
year = {2026},
volume = {1},
number = {1},
pages = {10-25},
doi = {10.62762/JAB.2025.294658},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JAB.2025.294658},
abstract = {In this study, titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO\$\_2\$-NPs) were synthesized via a green, cost-effective method using Azadirachta indica leaf extract as a natural capping and reducing agent. Characterization techniques including UV-vis, FTIR, XRD, SEM, EDX, and PL spectroscopy confirmed successful synthesis. UV-vis and FTIR confirmed surface functionalization by organic residues, while XRD revealed a well-crystalline anatase phase with average crystallite sizes of 42.2--54 nm. SEM analysis showed predominantly spherical particles (70--90 nm), and EDX confirmed high purity with only Ti and oxygen present. PL spectra exhibited emission peaks at 420, 468, 493, and 539 nm. The green TiO\$\_2\$-NPs demonstrated multifunctional biomedical activities. In vitro anti-inflammatory assays showed significant human red blood cell membrane stabilization, with maximum inhibition of 74.7\% and 71.3\% in heat-induced hemolysis tests. Compared to diclofenac sodium standard, TiO\$\_2\$-NPs achieved 87.3\% and 76.3\% inhibition at high concentrations. Anti-diabetic assays revealed up to 71.4\% inhibition of glucose uptake by yeast cells (vs. 86.6\% for standard drugs), while glucose adsorption ranged from 0.45 to 7.3 mg/g. Antibacterial activity against Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus) and Gram-negative (Escherichia coli) strains showed inhibition zones of 22.2 mm and 21.2 mm, respectively, comparable to standard drugs (23.3 mm and 21.7 mm). These results highlight green TiO\$\_2\$-NPs as promising candidates for biomedical applications.},
keywords = {green TiO\$\_2\$-NPs, azadirachta indica leaf extract, anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, anti-bacterial efficacy},
issn = {pending},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. Journal of Advanced Biomaterials
ISSN: pending (Online) | ISSN: pending (Print)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/