Abstract
This paper addresses the problem of achieving prescribed-time synchronization of coupled switched neural networks (CSNNs) using state-dependent intermittent control. Unlike
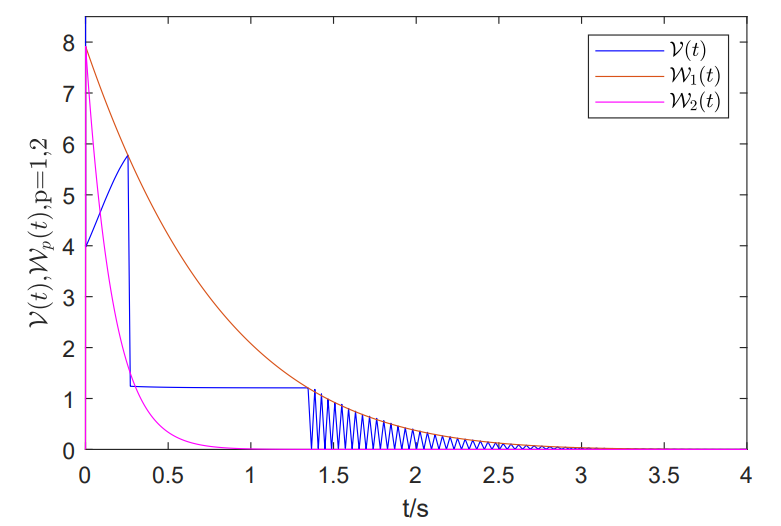
traditional intermittent control, the intervals for work and rest in this approach are not pre-designed but determined by the relationship between the designed Lyapunov function and the boundary auxiliary functions. The proposed control strategy can effectively mitigate chattering behavior arising from rapid switching in traditional intermittent control. Subsequently, leveraging Lyapunov theory and various inequality techniques, we develop a new set of sufficient conditions, formulated as linear matrix inequalities (LMIs), to ensure
prescribed-time synchronization of CSNNs under the designed intermittent control strategy. In the end, a numerical example is given to verify the obtained theoretical results.
Keywords
coupled switched neural networks
intermittent control
prescribed-time synchronization
Lyapunov function
linear matrix inequalities
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Yao, Y., & Long, C. (2025). State-Dependent Intermittent Synchronization Control for Coupled Switched Neural Networks: A Prescribed-Time Approach. Journal of Nonlinear Dynamics and Applications, 1(1), 3–9. https://doi.org/10.62762/JNDA.2025.493957
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions
Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge (ICCK) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue